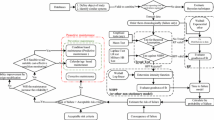
Abstract
This article presents an operational safety assessment model and analysis in cases where failure rate and repair rate vary over time, using the maximum likelihood analytical method as a method for estimating reliability parameters and uses Gumbel’s graphic paper for the estimation of maintainability parameters. The proposed approach takes into account both reliability and maintainability analyses, unlike current approaches in the literature which perform either reliability or maintainability analyses. A Weibull law for a reliability study has the advantage of being generalized and can also model, under certain conditions, one of the most frequent cases of distribution of technical repair times, namely the logarithmic normal distribution, which lends itself well to comparison with the laws of extreme values. The hypothesis acceptance test used is the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The application on the equipment of the Cameroonian Company of Petroleum Depots (CCPD) of Garoua is based on a FMEA analysis and provides parameters and curves after operation of the time between failures and technical times to repair (TTR).














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors do not have permission to share data.
Abbreviations
- FMECA:
-
Failure Modes Effets and Criticality Analysis
- PRA:
-
Preliminary Risk Analysis
- FTA:
-
Fault Tree Analysis
- TBF:
-
Time Between Failures
- TTR:
-
Technical Times to Repair
- CCPD:
-
Cameroonian Company of Petroleum Depots
References
Abdul KL, Singh VV (2019) Cost assessment of complex repairable system consisting two subsystems in series configuration using gumbel hougaard family copula. Int J Qual Reliab Manage 36(10):1683–1698
Avizienis A, Laprie JC, Randell B (2000) Fundamental concepts of dependability. Proceedings of ISW 2000. 34th Information Survivability Workshop. Los Alamitos, USA., 7–12
Bellaouar A (2014) Fiabilité, Maintenabilité, Disponibilité. Université de Constantine 1.
Ciame (2009) Réseaux de terrain – critères de sûreté de fonctionnement, traités IC2 (Information – Commande – Communication), série systèmes automatisés. Hermes-Lavoisier, Paris, France
Dhillon B (2006) Maintainability, maintenance, and reliability for engineers. Présenté à CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420006780
DIN EN 13306 (2010) Maintenance—Maintenance terminology (Norme). Deutsches Institut für Normung. European Committee for Standardization, Berlin, Allemagne
Gahlot M, Singh VV, Ayagi HI, Abdullahi I (2020) Stochastic analysis of a two units’ complex repairable system with switch and human failure using copula approach. Life Cycle Reliab Saf Eng 9(1):1–11
Guillerm R (2011) Intégration de la sûreté de fonctionnement dans les processus d’Ingénierie système. Université de Toulouse, Systèmes embarqués
Kadyan MS, Kumar R (2015) Availability and proft analysis of a feeding system in the sugar industry. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 7(2):1–16
Kuldeep N, Ram M, Dua AK (2017) A tree topology network environment analysis under reliability approach. Nonlinear Stud 24(1):193–202
Kumar A, Malik SC (2014) Reliability modeling of a computer system with priority to H/W repair over the replacement of H/W and up-gradation of S/W subject to MOT and MRT. Jordan J Mech Ind Eng 8(4):233–241
Kumar A, Ram M (2013) Reliability measures improvement and sensitivity analysis of a coal handling unit for thermal power plant. Int J Eng Trans C: Aspects 26(9):1059–1066
Lado AK, Singh VV, Ismail KH, Ibrahim Y (2018) Performance and cost assessment of repairable complex system with two sub-systems connected in series confguration. Int J Reliabil Appl 19(1):27–42
Lannoy A (1994) Procaccia. Méthodes avancées d’analyse des bases de données du retour d’expérience industriel. Editions Eyrolles.
Laprie JC (1995) Guide de la sûreté de fonctionnement. Cépaduès-Editions, Toulouse, France (ISBN 2-85428-382-1)
Lloyd K, Lipow M (1962) Reliability, management, methods and mathematics. In Prentice Hall.
Lyonnet P (2006) Ingénierie de la fiabilité. Tec & Doc Lavoisier, Paris, France (ISBN 9782743008239)
Morice E (1968) Quelques problèmes d’estimation relatifs à la loi de Weibull. In Revue de statistique appliquée. Tome 16, no. 3.
NF X 60–500. Fiabilité maintenabilité disponibilité, recueil des normes françaises
Niwas R, Garg H (2018) An approach for analyzing the reliability and proft of an industrial system based on the cost-free warranty policy. J Brazil Soc Mech Eng 40:1–9
Ntricker N, Lanza G (2014) The concept of robustness in production systems and its correlation to disturbances. Robust Manufacturing Conference (RoMaC). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.04.078
Nzié W (2006) Intégration de la maintenance en conception : application à un équipement agro-industrielle. UTBM, France
Nzié W, Morfow I, Tiogang A, Garro O (2017) Modelling and Improving Safety in Production System Design: Overall Approach and by Features, a Case Study. Int J Ind Manuf Syst Eng 2(3):24–33. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijimse.20170203.12
Perreault L, Bobee B (1992) Loi de Weibull à deux paramètres. Propriétés mathématiques et statistiques. Estimation des paramètres et des quantiles XT de période de retour T. Université du Québec, Rapport Scientifique 351.
Raghav D, Rawal DK, Yusuf I, Kankarofi RH, VV Singh (March 2021) Reliability prediction of distributed system with homogeneity in software and server… RT&A, No 1 (61) Volume 16.
Sari A, Akkaya M (2015) Fault tolerance mechanisms in distributed systems. Int J Commun Netw Syst Sci 8(12):471–482
Singh VV, Singh SB, Ram M, Goel CK (2013) Availability, MTTF and cost analysis of a system having two units in series confguration with controller. Int J Syst Assur Manag 4(4):34
Vijayalakshmi G (2015) Dependability analysis of homogeneous distributed software hardware systems. Int J Reliab Qual Saf Eng 22(2):1–19
Villemeur A (1991) Reliability, Availability, Maintainability and Safety Assessment. John Wiley & Sons ltd, New York, USA (ISBN 9780471930488)
Yusuf I, Yusuf B, Babagana M, Sani B, Lawan MA (2018) Some reliability characteristics of a linear consecutive 2-out-of-4system connected to 2-out-of-4 supporting device for operation. Int J Eng Technol 7(1):135–139
Zwingelstein G (1995) Diagnostic des défaillances : théorie et pratique pour les systèmes industriels. Traité des nouvelles technologies. Série Diagnostic et maintenance. Hermès, Paris, France (ISBN 9782866014636)
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The authors are grateful to the Cameroonian Company of Petroleum Depots of Garoua for having made available to them the data relating to their equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cedric Tatsinkou Fogang: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Software, Methodology, Formal analysis, Conceptualisation. Wolfgang Nzié: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Supervision. Aslain Brisco Ngnassi djami: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tatsinkou Fogang, C., Nzié, W. & Ngnassi Djami, A.B. A probabilistic model for evaluating the operational safety and operational safety analysis by the maximum likelihood method: application on the cameroonian company of petroleum depot of garoua. Life Cycle Reliab Saf Eng 13, 189–206 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41872-024-00255-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41872-024-00255-9