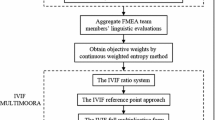
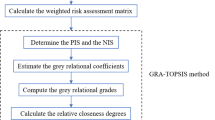
Abstract
This study develops a new hybrid multi-criticality approach to enhance the use of the traditional Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) method. The proposed model is based on replacing the computation of the mono criticality from the conventional method with a fuzzy model providing five criticalities that calculate the failure impact on the personnel, equipment, time, cost, and quality. Furthermore, an analytical hierarchy method (AHP) is adopted to construct a criticality matrix and compute the different weights for each criticality in order to assess the total criticality and effectively improve the prioritization of the failure modes. In addition, a real case study of an auto LPG Dispensing Station is provided to illustrate the factual application of the suggested model and show its pertinence in dealing with a risk evaluation and prioritization of failure mode with handling different forms of uncertainty and divergent judgments of experts.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chakhrit A, Bougofa M, Guetarni I, Nehal N, Bouafia A, Ghazli F et al (2022)New risk assessment and prioritization failure modes based approach in a gas turbine system. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, p 012009
Joubert F, Steyn E, Pretorius L (2021) Using the HAZOP method to conduct a risk assessment on the dismantling of large industrial machines and associated structures: case study. J Constr Eng Manag 147:05020021
Guetarni IH, Aissani N, Châlet E, Lounis Z (2019) Reliability analysis by mapping probabilistic importance factors into Bayesian belief networks for making decision in water deluge system. Process Saf Prog 38:e12011
Bougofa M, Taleb-Berrouane M, Bouafia A, Baziz A, Kharzi R, Bellaouar A (2021) Dynamic availability analysis using dynamic Bayesian and evidential networks. Process Saf Environ Prot 153:486–499
Bougofaa M, Bouafiab A, Bellaouara A (2020) Availability assessment of complex systems under parameter uncertainty using dynamic evidential networks. Int J Perform Eng 16:510–519
Geum Y, Cho Y, Park Y (2011) A systematic approach for diagnosing service failure: service-specific FMEA and grey relational analysis approach. Math Comput Model 54:3126–3142
Certa A, Enea M, Galante GM, La Fata CM (2017) ELECTRE TRI-based approach to the failure modes classification on the basis of risk parameters: an alternative to the risk priority number. Comput Ind Eng 108:100–110
Liu H-C, Hu Y-P, Wang J-J, Sun M (2018) Failure mode and effects analysis using two-dimensional uncertain linguistic variables and alternative queuing method. IEEE Trans Reliab 68:554–565
Liu H-C, Wang L-E, You X-Y, Wu S-M (2019) Failure mode and effect analysis with extended grey relational analysis method in cloud setting. Total Qual Manage Bus Excellence 30:745–767
Mohsen O, Fereshteh N (2017) An extended VIKOR method based on entropy measure for the failure modes risk assessment–A case study of the geothermal power plant (GPP). Saf Sci 92:160–172
Li X, Li H, Sun B, Wang F (2018) Assessing information security risk for an evolving smart city based on fuzzy and grey FMEA. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 34:2491–2501
Ghoushchi SJ, Yousefi S, Khazaeili M (2019) An extended FMEA approach based on the Z-MOORA and fuzzy BWM for prioritization of failures. Appl Soft Comput 81:105505
Fattahi R, Khalilzadeh M (2018) Risk evaluation using a novel hybrid method based on FMEA, extended MULTIMOORA, and AHP methods under fuzzy environment. Saf Sci 102:290–300
Zhou Q, Thai VV (2016) Fuzzy and grey theories in failure mode and effect analysis for tanker equipment failure prediction. Saf Sci 83:74–79
Udhaya Sankar S, Praveen R, Jagadish Kumar N, Jagatheswari S (2023) Fuzzy ELECTRE multi-criteria decision-making technique for achieving reliable data dissemination in MANETs. Int J Inform Technol 15:1985–1998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01251-5
Anes V, Henriques E, Freitas M, Reis L (2018) A new risk prioritization model for failure mode and effects analysis. Qual Reliab Eng Int 34:516–528
Seiti H, Fathi M, Hafezalkotob A, Herrera-Viedma E, Hameed IA (2021) Developing the modified R-numbers for risk-based fuzzy information fusion and its application to failure modes, effects, and system resilience analysis (FMESRA). ISA Trans 113:9–27
Yousefi S, Alizadeh A, Hayati J, Baghery M (2018) HSE risk prioritization using robust DEA-FMEA approach with undesirable outputs: a study of automotive parts industry in Iran. Saf Sci 102:144–158
Kumar M, "Maniram Kumar A, Rajakarunakaran S, Pitchipoo P, Vimalesan R (2018) Fuzzy based risk prioritisation in an auto LPG dispensing station. Saf Sci 101:231–247
Liu S-J, Wang D, Li S-J, Wang Q-H (2017) Speckle noise suppression method in holographic display using time multiplexing. Opt Eng 56:063107–063107
Wang Z, Gao J-M, Wang R-X, Chen K, Gao Z-Y, Zheng W (2017) Failure mode and effects analysis by using the house of reliability-based rough VIKOR approach. IEEE Trans Reliab 67:230–248
Yazdi M (2019) Improving failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) with consideration of uncertainty handling as an interactive approach. Int J Interact Des Manuf (IJIDeM) 13:441–458
Liu H-C, You J-X, Shan M-M, Su Q (2019) Systematic failure mode and effect analysis using a hybrid multiple criteria decision-making approach. Total Qual Manage Bus Excellence 30:537–564
Bian T, Zheng H, Yin L, Deng Y (2018) Failure mode and effects analysis based on D numbers and TOPSIS. Qual Reliab Eng Int 34:501–515
Wang X, Zhang Y, Shen G (2016) An improved FMECA for feed system of CNC machining center based on ICR and DEMATEL method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83:43–54
Chakhrit A, Chennoufi M (2021) Failure mode, effects and criticality analysis improvement by using new criticality assessment and prioritization based approach. J Eng Des Technol. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEDT-07-2021-0395 (Ahead-of-print)
Lekhraj A, Kumar, Kumar A (2022) Multi criteria decision making based energy efficient clustered solution for wireless sensor networks. Int J Inform Technol 14:3333–3342
Singh P, Agrawal R (2021) AHP based network selection scheme for heterogeneous network in different traffic scenarios. Int J Inform Technol 13:2505–2513
Chakhrit A, Chennoufi M (2021) Fuzzy multi-criteria approach for criticality assessment and optimization of decision making, J Intell Fuzzy Syst, pp. 1–16.
Acharjee S, Sinha Chaudhuri S (2023) Fuzzy inference based decision making model to control the operational parameters of motion estimation algorithms. Int J Inform Technol 15:2197–2207
Kharya S, Soni S, Swarnkar T (2023) Fuzzy weighted bayesian belief network: a medical knowledge-driven bayesian model using fuzzy weighted rules, Int J Inform Technol, pp. 1–9.
Kumar AM, Rajakarunakaran S, Prabu VA (2015) Human reliability analysis by cognitive approach for unloading process in an ALDS (auto LPG dispensing Station). Indian J Sci Technol 8:1–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chennoufi, M., Chakhrit, A. An extended FMECA approach using new risk assessment and prioritization based approach. Int. j. inf. tecnol. 16, 1595–1604 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01455-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01455-9