Abstract
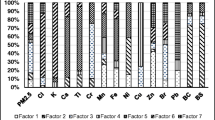
With growing urbanization and industrialization, problems such as poor disposal practices of solid waste and ensuing uncontrolled air pollution adjacent to landfill pose threats to human and environmental wellbeing. Ahmedabad is highly polluted urban city in India and unregulated burning of solid waste further aggravates already appalling situation caused by a large number of industries and vehicle fleets. The present work was carried out to understand sources of metals in ambient air surrounding a municipal landfill known as Pirana. For the study, surrounding area of the landfill was divided into 100 rectangular cells covering almost 5 km distance from its outer boundary. A location representing major land-use feature of each cell was classified. Sampling was carried out at these locations. A total of 100 PM5.0 samples were collected. Sampling was conducted for 3 h at each sampling location with samples collected on quartz filter paper. Measurements were performed over approximately 6 months from August to February, 2018. The filters were analyzed for metals using an Atomic Absorption Spectrometer. These measurements were used to identify pollution sources using positive matrix factorization technique and locate the hotspots of emission sources of heavy metals pollution. Five major sources namely, ferrous industry, nonferrous industry, vehicular emissions, re-suspended dust and solid waste burning/industrial coal combustion were identified and quantified. The average contributions of these sources to heavy metals were 20.7 ± 16.2, 18.4 ± 14.3, 19.9 ± 13.6, 21.4 ± 17.6, and 19.6 ± 10.6%, respectively. The average contribution from solid waste and industrial coal combustion is only 19.6% against the total from the combined remaining sources (~ 80.4), which means contribution from former will be lesser. Thus, solid waste burning is minor contributor for degradation of air quality; presence of many other sources around the site is actually the dominant cause of pollution.
Graphical abstract


source: Google Map)








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The relevant data used to support the study are included in the article and its supporting information.
References
Ahmed M, Guo X, Zhao X-M (2016) Determination and analysis of trace metals and surfactant in air particulate matter during biomass burning haze episode in Malaysia. Atmos Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.06.066
Ancona C, Badaloni C, Mataloni F, Bolignano A, Bucci S, Cesaroni G, Sozzi R, Davoli M, Forastiere F (2015) Mortality and morbidity in a population exposed to multiple sources of air pollution: A retrospective cohort study using air dispersion models. Environ Res 137:467–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.10.036
APM 801 User Manual (2012) http://envirotechindia.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/APM-801-min.pdf. Accessed 20 July 2018
ArcMap Documentation v10.8.1 (2020) https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/. Accessed 9 Aug 2020
Ashrafi K, Fallah R, Hadei M, Yarahmadi M, Shahsavani A (2018) Source apportionment of total suspended particles (TSP) by positive matrix factorization (PMF) and chemical mass balance (CMB) modeling in Ahvaz, Iran. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 75:278–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0500-z
Banerjee T, Murari V, Kumar M, Raju MP (2015) Source apportionment of airborne particulates through receptor modeling: Indian scenario. Atmos Res 164–165:167–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.04.017
Barwick VJ, Ellison SLR (2000) VAM Project 3.2.1 development and harmonisation of measurement uncertainty principles. Part (d): protocol for uncertainty evaluation from validation data, Version 5.1. Valid Anal Meas. https://blpd.dss.go.th/knowledge_el/VAM_uncertainty-0452.pdf. Accessed 21 July 2020
Bradshaw A, Simms N, Nicholls J (2008) Passage of trace metal contaminants through hot gas paths of gas turbines burning biomass and waste-fuels. Fuel 87:3529–3536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2008.06.012
Census of India (2011). https://censusindia.gov.in/2011-common/censusdata2011.html. Accessed 15 Aug 2020
Cesari D, Donateo A, Conte M, Contini D (2016) Inter-comparison of source apportionment of PM10 using PMF and CMB in three sites nearby an industrial area in central Italy. Atmos Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.08.003
Chadchan J, Shankar R (2012) An analysis of urban growth trends in the post-economic reforms period in India. Int J Sustain Built Environ 1:36–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsbe.2012.05.001
Chakraborty A, Gupta T (2010) Chemical characterization and source apportionment of submicron (PM1) aerosol in Kanpur region. Aerosol Air Qual Res. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2009.11.0071
Chen LWA, Lowenthal DH, Watson JG, Koracin D, Kumar N, Knipping EM, Wheeler N, Craig K, Reid S (2010) Toward effective source apportionment using positive matrix factorization: experiments with simulated PM2.5 data. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 60:43–54. https://doi.org/10.3155/1047-3289.60.1.43
Dalal HD (2017) Energy generation opportunities from MSW of Ahmedabad City: a case study. Int J Eng Dev Res 5(4):87–91 (ISSN: 2321-9939)
Das R, Khezri B, Srivastava B, Datta S, Sikdar PK, Webster RD, Wang X (2015) Trace element composition of PM2.5 and PM10 from Kolkata – a heavily polluted Indian metropolis. Atmos Pollut Res 6:742–750. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2015.083
De S, Debnath B (2016) Prevalence of health hazards associated with solid waste disposal- a case study of Kolkata, India. Procedia Environ Sci 35:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.081
de Pereira TS, Fernandino G (2019) Evaluation of solid waste management sustainability of a coastal municipality from northeastern Brazil. Ocean Coast Manag 179:104839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2019.104839
Dutta S (2017) Nearly 35 years, Ahmedabad Pirana landfill is infamous for its garbage mountains and frequent fires. https://swachhindia.ndtv.com/nearing-35-years-ahmedabads-pirana-landfill-is-infamous-for-its-garbage-mountains-and-frequent-fires-11855/. Accessed 20 Jan 2019
Ellison SLR, Rosslein M, Williams A (2000) EURACHEM/CITAC guide quantifying uncertainty in analytical measurement. https://www.eurachem.org/index.php/publications/guides/quam. Accessed 19 Aug 2020
EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) v5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide (2014). https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/201502/documents/pmf_5.0_user_guide.pdf. Accessed 20 Sept 2019
Estrella C, Fuquay I (2010) Toxic emissions from open burning. Chemosphere 80:193–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.03.057
Gadi R, Shivani S, Sharma SK, Mandal T (2019) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of organic constituents in fine ambient aerosols (PM2.5): a complete year study over National Capital Region of India. Chemosphere 221:583–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.067
Gaga E, Ari A, Akyol N, ÖzdenÜzmez Ö, Kara M, Chow J, Watson J, Özel E, Dogeroglu T, Odabasi M (2018) Determination of real-world emission factors of trace metals, EC, OC, BTEX, and semivolatile organic compounds (PAHs, PCBs and PCNs) in a rural tunnel in Bilecik, Turkey. Sci Total Environ 643:1285–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.227
Gangwar C, Choudhari R, Chauhan A, Kumar A, Singh A, Tripathi A (2019) Assessment of air pollution caused by illegal e-waste burning to evaluate the human health risk. Environ Int 125:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.051
Goix S, Leveque T, Tiantian X, Schreck E, Baeza-Squiban A, Geret F, Uzu G, Austruy A, Dumat C (2014) Environmental and health impacts of fine and ultrafine metallic particles: assessment of threat scores. Environ Res 133:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.05.015
Gugamsetty B, Wei H, Liu C-N, Awasthi A, Tsai C-J, Roam YC, Yu D, Chen D (2012) Source characterization and apportionment of PM10, PM2.5 and PM0.1 by using positive matrix factorization. Aerosol Air Qual Res 12:491–496. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2012.04.0084
Gupta I, Salunkhe A, Kumar R (2012) Source apportionment of PM10 by positive matrix factorization in urban area of Mumbai, India. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/585791
Gurjar B, Khaiwal R, Nagpure A (2016) Air pollution trends over Indian megacities and their local-to-global implications. Atmos Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.06.030
Habil M, Massey DD, Taneja A (2016) Personal and ambient PM2.5 exposure assessment in the city of Agra. Data Brief 6:495–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2015.12.040
Hao Y, Gao C, Deng S, Yuan M, Song W, Lu Z, Qiu Z (2019) Chemical characterisation of PM2.5 emitted from motor vehicles powered by diesel, gasoline, natural gas and methanol fuel. Sci Total Environ 674:128–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.410
Hopke PK (2016) Review of receptor modeling methods for source apportionment. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 66:237–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2016.1140693
Hopke P, Dai Q, Li L (2020) Global review of recent source apportionments for airborne particulate matter. Sci Total Environ 740:140091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140091
Hsu CY, Chiang HC, Chen MJ, Chuang CY, Tsen CM, Fang GC, Tsai YI, Chen NT, Lin TY, Lin SL, Chen YC (2017) Ambient PM2.5 in the residential area near industrial complexes: patio-temporal variation, source apportionment, and health impact. Sci Total Environ 590–591:204–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.212
Hu S, Herner JD, Shafer M, Robertson W, Schauer JJ, Dwyer H, Collins J, Huai T, Ayala A (2009) Metals emitted from heavy-duty diesel vehicles equipped with advanced PM and NOX emission controls. Atmos Environ 43:2950–2959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.02.052
Jiang SY, Kaul DS, Yang F, Sun L, Ning Z (2015) Source apportionment and water solubility of metals in size segregated particles in urban environments. Sci Total Environ 533:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.146
Jorquera H, Barraza F (2013) Source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in a desert region in northern Chile. Sci Total Environ 444:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.007
Kanjiyangat V, Hareendran M (2018a) Coal dust exposure reduction using water mist system: a case study. J Chem Health Saf 25:28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchas.2017.10.003
Kanjiyangat V, Hareendran M (2018b) Engineering intervention to reduce API dust exposure during milling operation. J Chem Health Saf 25:36–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchas.2017.07.002
Kanjiyangat V, Hareendran M (2018c) Engineering intervention to reduce API dust exposure during milling operationJ. Chem Health Saf 25:36–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchas.2017.07.002
Karanasiou A (2014) Road dust emission sources and assessment of street washing effect. Aerosol Air Qual Res. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2013.03.0074
Kazi T, Lashari A, Ali J, Baig J, Afridi H (2018) Volatilization of toxic elements from coal samples of Thar coal field, after burning at different temperature and their mobility from ash: Risk assessment. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.209
Kim NK, Kim P, KangKang YCH (2011) Long-term trend of aerosol composition and direct radiative forcing due to aerosols over Gosan: TSP, PM10, and PM2.5 data between 1992 and 2008. Atmos Environ 45:6107–6115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.08.051
Kothai P (2011) Chemical characterization and source identification of particulate matter at an urban site of Navi Mumbai, India. Aerosol Air Qual Res. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2011.02.0017
Koukoulakis KG, Chrysohou E, Kanellopoulos PG, Karavoltsos S, Katsouras G, Dassenakis M, Nikolelis D, Bakeas E (2019) Trace elements bound to airborne PM10 in a heavily industrialized site nearby Athens: seasonal patterns, emission sources, health implications. Atmos Pollut Res 10:1347–1356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2019.03.007
Kovacs H, Szemmelveisz K, Koós T (2016) Theoretical and experimental metals flow calculations during biomass combustion. Fuel 185:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.08.007
Kulshrestha A, Satsang PG, Masih J, Taneja A (2009) Metal concentration of PM2.5 and PM10 particles and seasonal variations in urban and rural environment of Agra, India. Sci Total Environ 407:6196–6204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.050
Kumar S, Aggarwal SG, Gupta PK, Kawamura K (2015) Investigation of the tracers for plastic-enriched waste burning aerosols. Atmos Environ 108:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.066
Labus K (1995) Heavy-metal emissions from coal combustion in Southwestern Poland. Energy 20:1115–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-5442(95)00062-L
Landis MS, Pancras JP, Graney JR, White EM, Edgerton ES, Legge A, Percy KE (2017) Source apportionment of ambient fine and coarse particulate matter at the Fort McKay community site, in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region, Alberta, Canada. Sci Total Environ 584–585:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.110
Lemieux PM, Lutes CC, Santoianni DA (2004) Emissions of organic air toxics from open burning: a comprehensive review. Prog Energy Combust Sci 30:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2003.08.001
Lisk DJ (1991) Environmental effects of landfills. Sci Total Environ 100:415–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(91)90387-T
Manousakas MI, Florou K, Pandis SN (2020) Source apportionment of fine organic and inorganic atmospheric aerosol in an urban background area in Greece. Atmos 11(4):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11040330
Meij R, te Winkel H (2007) The emissions of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from modern coal-fired power stations. Atmos Environ 41:9262–9272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.04.042
Mohammed G, Karani G, Mitchell D (2017) Trace elemental composition in PM10 and PM2.5 collected in Cardiff, Wales. Energy Procedia 111:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.216
Mohiuddin K, Strezov V, Nelson PF, Stelcer E (2014) Characterisation of trace metals in atmospheric particles in the vicinity of iron and steelmaking industries in Australia. Atmos Environ 83:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.11.011
Morales R, Toro Araya R, Morales-Salinas L, Leyva-Guzmán M (2017) Landfill fire and airborne aerosols in a large city: lessons learned and future needs. Air Qual Atmos Health 11:111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-017-0522-8
Najem GR, Cappadona JL (1991) Health effects of hazardous chemical waste disposal sites in New Jersey and in the united states: a review. Am J Prev Med 7:352–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-3797(18)30872-9
Newman JR (1979) Effects of industrial air pollution on wildlife. Biol Conserv 15:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3207(79)90039-9
Norris G, Duval R, Brown S, Bai S (2014) EPA positive matrix factorization (PMF) 5.0 fundamentals and user guide. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, EPA/600/R-14/108. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-02/documents/pmf_5.0_user_guide.pdf. Accessed 21 Sept 2019
Paatero P, Hopke P (2003) Discarding or downweighting high-noise variables in factor analytic models. Anal Chim Acta 490:277–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(02)01643-4
Paatero P, Hopke PK, Song XH, Ramadan Z (2002) Understanding and controlling rotations in factor analytic models. Chem Intell Lab Syst 60:253–264
Pakbin P, Ning Z, Schauer J, Sioutas C (2011) Seasonal and spatial coarse particle elemental concentrations in the Los Angeles area. Aerosol Sci Technol 45:949–963. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2011.571309
Pant P, Harrison R (2012) Critical review of receptor modelling for particulate matter: a case study of India. Atmos Environ 49:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.11.060
Pervez S, Mathew J, Sharma R (2005) Investigation of personal-indoor-outdoor particulate relationships in welding workshops. J Sci Ind Res 64:454–458
Polissar A, Hopke P, Malm W, Sisler J (1998) Atmospheric aerosol over Alaska: 1. Spatial and seasonal variability. J Geol Phys Res 103:19035–19044. https://doi.org/10.1029/98JD01365
Prakash J, Lohia T, Mandariya A, Habib G, Gupta T, Gupta S (2018) Chemical characterization and quantitativ e assessment of source-specific health risk of trace metals in PM1.0 at a road site of Delhi, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:8747–8764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1174-9
Querol X, Viana M, Alastuey A, Amato F, Moreno T, Castillo S, Pey J, de la Rosa J, de la Campa AS, Artíñano B, Salvador P, Santos SGD, Fernández-Patier R, Moreno-Grau S, Negral L, Minguillón MC, Monfort E, Gil JI, Inza A, Ortega LA et al (2007) Source origin of trace elements in PM from regional background, urban and industrial sites of Spain. Atmos Environ 41:7219–7231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.05.022
Reff A, Eberly SI, Bhave PV (2007) Receptor modeling of ambient particulate matter data using positive matrix factorization: review of existing methods. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 57:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2007.10465319
Rengarajan R, Sudheer AK, Sarin MM (2011) Wintertime PM2.5 and PM10 carbonaceous and inorganic constituents from urban site in western India. Atmos Res 102:420–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.09.005
Sathe Y, Atul A, Srinikethan G (2011) Application of US EPA PMF model to the source apportionment of trace elements in atmospheric aerosols at Kolhapur, Maharashtra (India). J Environ Res Dev 5:597–607
Sheth J, Patel K, Shah D (2016) Solid waste management: a case study of Ahmedabad. IJSRD, 28–34, conference 5: habitat conclave. http://www.ijsrd.com/C_Article.php?manuscript=HABTP006. Accessed 26 Sept 2019
Shukla PC, Gupta T, Labhsetwar NK, Agarwal AK (2017) Trace metals and ions in particulates emitted by biodiesel fuelled engine. Fuel 188:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.059
Srivastava A, Gupta SK, Jain V (2008) Source apportionment of total suspended particulate matter in coarse and fine size ranges over Delhi. Aerosol Air Qual Res 8:188–200. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2007.09.0040
Suess MJ (1980) Ambient air pollution from industrial sources. In: Benarie MM (ed) Atmospheric pollution. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 361–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-1116(08)71679-0
Taghvaee S, Sowlat MH, Mousavi A, Hassanvand MS, Yunesian M, Naddafi K, Sioutas C (2018) Source apportionment of ambient PM2.5 in two locations in central Tehran using the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model. Sci Total Environ 628–629:672–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.096
Taiwo A, Beddows D, Calzolai G, Harrison R, Lucarelli F, Nava S, Shi Z, Valli G, Vecchi R (2014) Receptor modelling of airborne particulate matter in the vicinity of a major steelworks site. Sci Total Environ 490C:488–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.118
Tapia J, Audry S (2013) Control of early diagenesis processes on trace metal (Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and U) and metalloid (As, Sb) behaviours in mining- and smelting-impacted lacustrine environments of the Bolivian Altiplano. Appl Geochem 31:60–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.12.006
Taus N, Tarulescu S, Idomir M, Taus R (2008) Respiratory exposure to air pollutants. J Environ Prot Ecol 9:15–25
Tsuboi T, Yoshikawa N (2019) Traffic flow analysis in Ahmedabad (India). Case Stud Transp Policy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cstp.2019.06.001
UN Population Trend Report, World Population Prospects, the 2012 Revision (2013). https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/publications/world-population-prospects-the-2012-revision.html. Accessed 12 July 2018
Vassiliadis I, Papadopoulos A, Fotopoulos D, Vassiliadis S, Cristoforo S, Leontiasis L (2009) Dioxin contamination after an accidental fire in the municipal landfill of Tabards, Thessaloniki, Greece. Chemosphere 74:879–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.016
VIRS User’s Guide Version 1.4 (2018) NASA VIIRS land science investigator processing system (SIPS) visible infrared imaging radiometer suite (VIIRS) 375 m & 750 m active fire products. https://viirsland.gsfc.nasa.gov/PDF/VIIRS_activefire_User_Guide.pdf. Accessed 20 Nov 2020
Waked A, Favez O, Alleman LY, Piot C, Petit J-E, Delaunay T, Verlinden E, Golly B, Besombes J-L, Jaffrezo J-L, Leoz-Garziandia E (2014) Source apportionment of PM10 in a north-western Europe regional urban background site (Lens, France) using positive matrix factorization and including primary biogenic emissions. Atmos Chem Phys 14:3325–3346. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-3325-2014
Weichenthal S, Van Rijswijk D, Kulka R, You H, Van Ryswyk K, Willey J, Dugandzic R, Sutcliffe R, Moulton J, Baike M, White L, Charland J-P, Jessiman B (2015) The impact of a landfill fire on ambient air quality in the North: a case study in Iqaluit, Canada. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.06.018
World Health Statistics Report (2014). https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/112738/9789240692671_eng.pdf;jsessionid=354B63A7EAD6BFEF8BCA50A48CC7165F?sequence=1. Accessed 17 Dec 2020
Wu Z, Ye H, Shan Y, Chen B, Li J (2019) A city-level inventory for atmospheric mercury emissions from coal combustion in China. Atmos Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.117245
Yu R, He L, Cai R, Li B, Li Z, Yang K (2017) Heavy metal pollution and health risk in China. Glob Health J 1:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2414-6447(19)30059-4
Zhang H (2008) An assessment of heavy metals contributed by industry in urban atmosphere from Nanjing. China Environ Monit Assess 154:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0411-6
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the use of data and imagery from LANCE FIRMS operated by NASA’s Earth Science Data and Information System (ESDIS) with funding provided by NASA Headquarters.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehta, U.H., Kaul, D.S., Westerdahl, D. et al. Understanding the Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution in Ambient Air of Neighboring a Solid Waste Landfill Site. Aerosol Sci Eng 6, 161–175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41810-022-00131-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41810-022-00131-y