Abstract
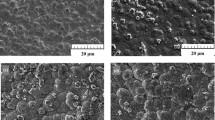
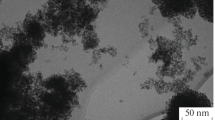
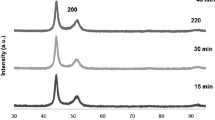
In this study, the nickel–iron–titanium carbide (Ni–Fe–TiC) nanocomposite was applied on the St14 low-carbon steel via pulse electrodeposition. Electroplating was applied on the substrate with different values of current density, frequency, duty cycle, electroplating time (t) and concentration of TiC nanoparticles, and the properties of the applied coatings were evaluated. To the study the microstructure and morphology of the applied coatings, field emission electron microscope (FESEM) was used. The amount of deposited elements in the coating was determined by energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). To evaluate the corrosion resistance of the coatings, potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance (EIS) tests were carried out in 3.5% NaCl solution as a corrosive environment. The optimum coating was obtained at the current density (J) of 30 mA/cm2, duty cycle (\(\gamma\)) of 60%, frequency (f) of 20 Hz and 2 g/L concentration of TiC nanoparticles. The optimum coating increased the corrosion potential from -0.675 V to -0.332 V and decreased the corrosion current density from 157.200μA/cm2 to 0.790μA/cm2. The presence of TiC nanoparticles in the coating reduced the corrosion current density from 2.130μA/cm2 (Ni–Fe coating) to 0.790μA/cm2 (Ni–Fe–TiC nanocomposite coating).














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goral, A., Nowak, M., Berent, K., Kania, B.: Influence of current density on microstructure and properties of electrodeposited nickel-alumina composite coatings. J. Alloys. Compd. 615, 406–410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.01.025
E. Ghahabi, Y. Shajari, M. Razavi, I. Mobasherpour, S. A. Tayebi far, Effect of iron content on the wear behavior and adhesion strength of TiC–Fe nanocomposite coatings on low carbon steel produced by air plasma spray, Ceram. Inter. 46 (2020) 2670–2676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.255
Alizadeh, M., Mirak, M., Salahinejad, E., Ghaffari, M., Amini, R., Roosta, A.: Structural characterization of electro-codeposited Ni–Al2O3–SiC nanocomposite coatings. J. Alloys. Compd. 611, 161–166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.04.181
Samiee, M., Hanachi, M., Seyedraoufi, Z.S., Eshraghi, M.J., Shajari, Y.: Biodegradable magnesium alloy coated with TiO2/MgO two-layer composite via magnetic sputtering for orthopedic applications: A study on the surface characterization, corrosion, and biocompatibility. Ceram. Int. 47(5), 6179–6186 (2021)
Tripathi, M.K., Singh, D.K., Singh, V.B.: Electrodeposition of Ni-Fe/BN nano-composite coatings from a nonaqueous bath and their characterization. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8, 3454–3471 (2013)
Yang, Y., Cheng, Y.F.: Mechanistic aspects of electrodeposition of Ni–Co–SiC composite nano-coating on carbon steel. Electrochim. Acta. 109, 638–644 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.106
M. Aliofkhazraei, Size Effect in Electrochemical Properties of Nanostructured Coatings, in: Nanocoatings, Springer, 2011, pp. 111–147.
Zoikis-Karathanasis, A., Pavlatou, E.A., Spyrellis, N.: Pulse electrodeposition of Ni–P matrix composite coatings reinforced by SiC particles. J. Alloys. Compd. 494, 396–403 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.01.057
Aliofkhazraei, M., Ahangarani, S., Rouhaghdam, A.S.: Effect of the duty cycle of pulsed current on nanocomposite layers formed by pulsed electrodeposition. Rare. Met. 29, 209–213 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-010-0036-0
Chandrasekar, M.S., Pushpavanam, M.: Pulse and pulse reverse plating—Conceptual, advantages and applications. Electrochim. Acta. 53, 3313–3322 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.11.054
Spanou, S., Pavlatou, E.A.: Pulse electrodeposition of Ni/nano-TiO2 composites: effect of pulse frequency on deposits properties. J. Appl. Electrochem. 40, 1325–1336 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-010-0080-3
Tripathi, M.K., Singh, V.B., Singh, H.K.: Structure and properties of electrodeposited functional Ni–Fe/TiN nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 278, 146–156 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.08.016
Podlaha, E.J.: Selective electrodeposition of nano particulates into metal matrices. Nano. Lett. 1, 413–416 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl015508u
Clark, D., Wood, D., Erb, U.: Industrial applications of electrodeposited nanocrystals. Nanostruct. Mater. 9, 755–758 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9773(97)00163-3
Robertson, A., Erb, U., Palumbo, G.: Practical applications for electrodeposited nanocrystalline materials. Nanostruct. Mater. 12, 1035–1040 (1999)
Zhang, H., Guo, Z.C., Song, Y.H., Li, A.I.: New study trend of composite electrodeposition. Electropl. Finish. 6, 29–33 (2011)
Kim, S.K., Woo, H.J.: Formation of bilayer Ni–SiC composite coatings by electrodeposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 108–109, 564–569 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(98)00589-1
Radhakrishnamurty, P.: Current effect of alloy plating and the electrochemical equivalent of an alloy. Bull. Electrochem. 15, 252–256 (1999)
G. Heidari, H. Tavakoli, S.M. Mousavi Khoie, Nano SiC-Nickel Composite Coatings from a Sulfanat Bath Using Direct Current and Pulsed Direct Current, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2010.
J.C. Puippe, Qualitative Approach to Pulse Plating, in J.C. Puippe and F. Leaman eds., Theory and Practice of Pulse Plating,American Electroplaters and Surface Finishers Society, 1986.
Chandrasekar, M.S., Pushpavanam, M.: Pulse and pulse reverse plating Conceptual, advantages and applications. Electrochim. Acta. 53, 3313–3322 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.11.054
Esfahani, H.A., Vaezi, M.R., Nikzade, L., Yazdani, B., Sadrnezhaada, S.K.: Influence of SiC nanoparticles and saccharin on the structure and properties of electrodeposited Ni–Fe/SiC nanocomposite coatings. J. Alloys. Compd. 484, 540–544 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.04.146
Torabinejad, V., Rouhaghdam, A.S., Aliofkhazraei, M., Allahyarzadeh, M.H.: Electrodeposition of Ni-Fe and Ni-Fe-(nano Al2O3) multilayer coatings. J. Alloys. Compd. 657, 526–536 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.154
V. Torabinejad, M. Aliofkhazraei, A. Sabour Rouhaghdam, M.H. Allahyarzadeh, Functionally graded coating of Ni- Fe fabricated by pulse electrodeposition, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25 (2016) 5494-5501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2376-x
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganji, M., Yousefnia, H., Seyedraoufi, Z.S. et al. The corrosion behavior of Ni–Fe and Ni–Fe–TiC nanoparticles deposited using pulse electrodeposition on low-carbon steel. J Aust Ceram Soc 58, 1283–1295 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-022-00747-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-022-00747-w