Abstract
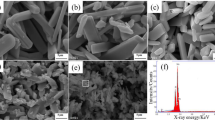
Molybdenum carbide (Mo2C) is one of most widely used transition metal carbides due to its remarkable physical and chemical properties, such as outstanding catalytic properties, good thermal stability, high hardness, excellent corrosion, and wear resistances. In the current work, a facile and feasible method was proposed to synthesize ultrafine molybdenum carbide powders with a high purity. Firstly, molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) powder was reduced with insufficient carbon black powder to remove oxygen from MoO3 and generate a mixture of Mo2C and Mo. Then, the mixture was further carbided at 1100 °C or 1200 °C by carbon black to obtain pure Mo2C with an average particle size of 230 nm or 250 nm, respectively. A complete deoxidation at the first step is of significant importance for the precisely determining the amount of carbon addition in the carbonization step. The currently proposed method is a low-cost and efficient method to produce high purity and ultrafine Mo2C in a large scale.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torabi, O., Golabgir, M.H., Tajizadegan, H., Torabi, H.: A study on mechanochemical behavior of MoO3–Mg–C to synthesize molybdenum carbide. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater. 47, 18–24 (2014)
Wang, X.-H., Hao, H.-L., Zhang, M.-H., Li, W., Tao, K.-Y.: Synthesis and characterization of molybdenum carbides using propane as carbon source. J Solid State Chem. 179(2), 538–543 (2006)
Nelson, J.A., Wangner, M.J.: High surface area Mo2C and WC prepared by alkalide reduction. Chem Mater. 14(4), 1639–1642 (2002)
Wang, L., Zhang, G.-H., Chou, K.-C.: Preparation of Mo2C by reducing ultrafine spherical β-MoO3 powders with CO or CO-CO2 gases. J Aust Ceram Soc. 54(1), 97–107 (2017)
Zhou, Z.N., Wu, K.M.: Molybdenum carbide precipitation in an Fe–C–Mo alloy under a high magnetic field. Scr Mater. 61(7), 670–673 (2009)
Levy, R.B., Boudart, M.: Platinum-like behavior of tungsten carbide in surface catalysis. Science. 181(4099), 547–549 (1973)
Yang, Z., Cai, P., Shi, L., Gu, Y., Chen, L., Qian, Y.: A facile preparation of nanocrystalline Mo2C from graphite or carbon nanotubes. J Solid State Chem. 179(1), 29–32 (2006)
Liang, C., Ying, P., Li, C.: Nanostructured β-Mo2C prepared by carbothermal hydrogen reduction on ultrahigh surface area carbon material. Chem Mater. 14, 3148–3151 (2002)
Dhandapani, B., Clair, T.S., Oyama, S.T.: Simultaneous hydrodesulfurization, hydrodeoxygenation, and hydrogenation with molybdenum carbide. Appl. Catal. A. 168(2), 219–228 (1998)
Markel, E.J., Van Zee, J.W.: Catalytic hydrodesulfurization by molybdenum nitride. J Catal. 126(2), 643–657 (1990)
Park, K.Y., Seo, W.K., Lee, J.S.: Selective synthesis of light olefins from syngas over potassium-promoted molybdenum carbide catalysts. Catal Lett. 11(3–6), 349–356 (1991)
Claridge, J.B., York, A.P.E., Brungs, A.J., Marquez-Alvarez, C., Sloan, J., Tsang, S.C., Green, M.L.H.: New catalysts for the conversion of methane to synthesis gas: molybdenum and tungsten carbide. J. Catal. 180(1), 85–100 (1998)
Gu, Y., Li, Z., Chen, L., Ying, Y., Qian, Y.: Synthesis of nanocrystalline Mo2C via sodium co-reduction of MoCl5 and CBr4 in benzene. Mater Res Bull. 38(7), 1119–1122 (2003)
Guzmán, H.J., Xu, W., Stacchiola, D., Vitale, G., Scott, C.E., Rodríguez, J.A., Pereira-Almao, P.: In situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction study of the synthesis of Mo2C with different carburization agents. Can J Chem. 91(7), 573–582 (2013)
Khabbaz, S., Honarbakhsh-Raouf, A., Ataie, A., Saghafi, M.: Effect of processing parameters on the mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline molybdenum carbide. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Metal. 41, 402–407 (2013)
Hoseinpur, A., Jalaly, M., Bafghi, M.S., Khaki, J.V.: On the formation of Mo2C nanocrystals by a novel system through microwave assisted combustion synthesis. Mater Charact. 108, 79–84 (2015)
Xia, Z.P., Shen, Y.Q., Shen, J.J., Li, Z.Q.: Mechanosynthesis of molybdenum carbides by ball milling at room temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 453(1–2), 185–190 (2008)
Chaudhury, S., Mukerjee, S.K., Vaidya, V.N., Venugopal, V.: Kinetics and mechanism of carbothermic reduction of MoO3 to Mo2C. J Alloy Compd. 261(1–2), 105–113 (1997)
Yao, Z.W.: Exploration on synthesis of activated carbon supported molybdenum carbide, nitride and phosphide via carbothermal reduction route. J. Alloy. Compd. 475(1–2), L38–L41 (2009)
Bale, C., Chartrand, P., Degterov, S., Eriksson, G., Hack, K., Mahfoud, R.B., Melançon, J., Pelton, A., Petersen, S.: FactSage thermochemical software and databases. Calphad. 26, 189 (2002)
Wang, D.-H., Jiao, S., Zhang, G.-H., Wang, L., Chou, K.-C.: Preparation of submicron Mo powders by the reaction between MoO2 and activated carbon. J Aust Ceram Soc. 55(2), 297–303 (2019)
Wang, L., Zhang, G.-H., Wang, J.-S., Chou, K.-C.: Study on hydrogen reduction of ultrafine MoO2 to produce ultrafine Mo. J Phys Chem C. 120(7), 4097–4103 (2016)
Dang, J., Zhang, G.-H., Chou, K.-C.: Study on kinetics of hydrogen reduction of MoO2. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Metal. 41, 356–362 (2013)
Majumdar, S., Sharma, I.G., Samajdar, I., Bhargava, P.: Kinetic studies on hydrogen reduction of MoO3 and morphological analysis of reduced Mo powder. Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci. 39(3), 431–438 (2008)
Sun, G.D., Zhang, G.H., Chou, K.C.: Preparation of Mo nanoparticles through hydrogen reduction of commercial MoO2 with the assistance of molten salt. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Metal. 78, 68–75 (2019)
Wang, D.-H., Sun, G.-D., Zhang, G.-H.: Preparation of ultrafine Mo powders via carbothermic pre-reduction of molybdenum oxide and deep reduction by hydrogen. Int J Refract Met Hard Metal. 75, 70–77 (2018)
Tracy, C.E., Benson, D.K.: Preparation of amorphous electrochromic tungsten oxide and molybdenum oxide by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J Vac Sci Technol A. 4(2377–2383), (1986)
Dang, J., Zhang, G., Wang, L., Chou, K., Pistorius, P.C.: Study on reduction of MoO2 powders with CO to produce Mo2C. J Am Ceram Soc. 99(3), 819–824 (2016)
Deevi, S.C.: Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of molybdenum disilicide. J Mater Sci. 26(12), 3343–3353 (1991)
Utigard, T.: Oxidation mechanism of molybdenite concentrate. Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci. 40(4), 490–496 (2009)
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51725401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, CM., Cao, WC., Bu, CY. et al. Preparation of ultrafine molybdenum carbide (Mo2C) powder by carbothermic reduction of molybdenum trioxide (MoO3). J Aust Ceram Soc 56, 1333–1340 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-020-00485-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-020-00485-x