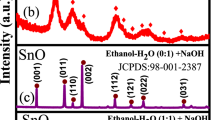
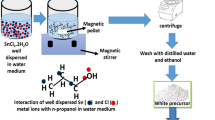
Abstract
The development of stable electrodes with significant capacitance is necessary for the commercial viability of supercapacitors, which have generated a lot of interest. Metal oxides are a promising material because they have multiple valence shells for charge transfer, a high theoretical specific capacitance, and variable redox properties. Because of this, we explore, for the first time to the best of our knowledge, the effects of Copper (Cu) doping on the super capacitive performance of tin oxide (SnO2). The pure, 2%, 7%, and 15% Cu-doped SnO2 are synthesised by facile coprecipitation. We demonstrate a maximum electrochemical performance for 2% Cu-doped sample with a specific capacitance of 27.099 F/g at a sweep rate of 10 mV s−1, while further increase in doping levels had a negative impact on the capacitive performance of SnO2. The specific capacitance vale was found to be decreased with an increase in Cu concentration, which could be explained by the increasing trend found in the charge transfer resistance upon doping as observed from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, the resistance increased from 5.85 to 7.19 Ω. The perfect reversible behaviour of a pseudocapacitor is estimated from the highly symmetric nature of chronopotentiometry (GCD) curves and the pseudo behaviour is further confirmed from the cyclic voltammetry curve with an excellent potential window of 1.3 V.
Highlights
-
For the first time, the role of copper doping in SnO2 in enhancing the electrochemical performance is studied
-
A negative impact upon copper doping on the performance of supercapacitors was observed
-
A maximum electrochemical performance was observed for 2% copper doping with a sweep rate of 10 mV/s.
-
The reason for anomalous behaviour shown upon copper doping is critically scrutinised.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah DH, Al-Taay HF, Khalaf MK, Oleiwi HF, Rahma AJ (2021) Structure, morphology and optical properties of SnO2 nanoparticle synthesized via ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique: effect of CuO doping concentration. J Phys Conf Ser. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2114/1/012074
AbdulWahab Y, Naseer MN, Zaidi AA, Umair T, Khan H, Siddiqi MM, Javed MS (2022) Super capacitors in various dimensionalities: applications and recent advancements. Encycl Energy Storage. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-819723-3.00020-2
Aoki KJ, Chen J, Liu Y, Jia B (2020) Peak potential shift of fast cyclic voltammograms owing to capacitance of redox reactions. J Electroanal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113609
Asaithambi S, Sakthivel P, Karuppaiah M, Sankar GU, Balamurugan K, Yuvakkumar R, Thambidurai M, Ravi G (2020) Investigation of electrochemical properties of various transition metals doped SnO2 spherical nanostructures for supercapacitor applications. J Energy Storage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101530
Asaithambi S, Sakthivel P, Karuppaiah M, Balamurugan K, Yuvakkumar R, Thambidurai M, Ravi G (2021) Synthesis and characterization of various transition metals doped SnO2@MoS2 composites for supercapacitor and photocatalytic applications. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157060
Augustyn V, Simon P, Dunn B (2014) Pseudocapacitive oxide materials for high-rate electrochemical energy storage. Energy Environ Sci 7(5):1597–1614. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee44164d
Bratovcic A (2019) Different applications of nanomaterials and their impact on the environment. Int J Mater Sci Eng 5(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.14445/23948884/ijmse-v5i1p101
Channu VS, Holze R, Wicker Sr SA, Walker EH Jr, Williams QL, Kalluru RR (2011) Synthesis and characterization of (Ru–Sn) O2 nanoparticles for supercapacitors. Mater Sci Appl. https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2011.29158
Chodankar NR, Pham HD, Nanjundan AK, Fernando JFS, Jayaramulu K, Golberg D, Han YK, Dubal DP (2020) True meaning of pseudocapacitors and their performance metrics: asymmetric versus hybrid supercapacitors. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202002806
Deva Priya P, Philip A, Ruban Kumar A (2024) An investigation on the compositional effects of 3D graphite on the electrochemical performance of NiO-Co3O4 composite. Diam Relat Mater 141:110597
Divya J, Pramothkumar A, Joshua Gnanamuthu S, Bernice Victoria DC, Jobe Prabakar PC (2020) Structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Cu and Ni doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared via co-precipitation approach. Phys B Condens Matter 588:66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.412169
Feynman RP (1992) There’s plenty of room at the bottom. J Microelectromech Syst 1(1):60–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/84.128057
Gogotsi Y (2014) What nano can do for energy storage. ACS Nano 8(6):5369–5371. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn503164x
Hellsing B, Persson M (1984) Electronic damping of atomic and molecular vibrations at metal surfaces. Phys Scr 29(4):360–371. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/29/4/014
Jahnavi VS, Tripathy SK, Rao AVNR (2020) Study of the structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of copper-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J Electron Mater 49(6):3540–3554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08028-7
Kamat PV, Dimitrijevic NM, Nozik AJ (1989) Dynamic Burstein–Moss shift in semiconductor colloids. J Phys Chem 93(8):2873–2875. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100345a003
Ke Q, Wang J (2016) Graphene-based materials for supercapacitor electrodes—a review. J Mater 2(1):37–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2016.01.001
Khoudro A, Najeeb SH (2020) Studying the infrared spectroscopy of the SnO2:Sb (X= 0.00, 0.01) powders. Chem Mater Res. https://doi.org/10.7176/cmr/10-5-02.10.7176/cmr/10-5-02
Kounaves SP, Division P, Patterson W, Voltammetry C, Techniques LS, Jamil Z, Ruiz-Trejo E, Brandon NP, Vafaeian S, Fattah-Alhosseini A, Keshavarz MK, Mazaheri Y, Elgrishi N, Rountree KJ, McCarthy BD, Rountree ES, Eisenhart TT, Dempsey JL (2018) A practical beginner’s guide to cyclic voltammetry. J Chem Educ 677(2):42–51
Liu KK, Jiang Q, Kacica C, Derami HG, Biswas P, Singamaneni S (2018) Flexible solid-state supercapacitor based on tin oxide/reduced graphene oxide/bacterial nanocellulose. RSC Adv 8(55):31296–31302. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05270k
Lu W, Yuan Z, Xu C, Ning J, Zhong Y, Zhang Z, Hu Y (2019) Construction of mesoporous Cu-doped Co9S8 rectangular nanotube arrays for high energy density all-solid-state asymmetric supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 7(10):5333–5343. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta10998b
Majumdar D, Maiyalagan T, Jiang Z (2019) Recent progress in ruthenium oxide-based composites for supercapacitor applications. ChemElectroChem 6(17):4343–4372. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201900668
Majumder M, Choudhary RB, Thakur AK, Khodayari A, Amiri M, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S (2020) Aluminum based metal-organic framework integrated with reduced graphene oxide for improved supercapacitive performance. Electrochim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136609
Manikandan K, Dhanuskodi S, Maheswari N, Muralidharan G (2016) SnO2 nanoparticles for supercapacitor application. AIP Conf Proc. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4947702
Misra D, Yadav SK (2019) Prediction of site preference of implanted transition metal dopants in rock-salt oxides. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49011-5
Musilek P, Prauzek M, Krömer P, Rodway J, Bartoň T (2017) Intelligent energy management for environmental monitoring systems. Smart Sens Netw Commun Technol Intell Appl 66:67–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809859-2.00005-X
Nakrela A, Benramdane N, Bouzidi A, Kebbab Z, Medles M, Mathieu C (2016) Site location of Al-dopant in ZnO lattice by exploiting the structural and optical characterisation of ZnO:Al thin films. Results Phys 6:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.01.010
Naz S, Javid I, Konwar S, Surana K, Singh PK, Sahni M, Bhattacharya B (2020) A simple low cost method for synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles and its characterization. SN Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2812-2
Nilavazhagan S, Muthukumaran S, Ashokkumar M (2014) Structural, optical and morphological properties of La, Cu Co-doped SnO2 nanocrystals by co-precipitation method. Opt Mater 37(C):425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2014.07.003
Parthibavarman M, Hariharan V, Sekar C, Singh VN (2010) Effect of copper on structural, optical and electrochemical properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 12(9):1894–1898
Philip A, Ruban Kumar A (2023a) Solvent effects on the drop cast films of few layers of MoS2 primed by facile exfoliation to realize optical and structural properties. Inorg Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110967
Philip A, Ruban Kumar A (2023b) Recent advancements and developments employing 2D-materials in enhancing the performance of electrochemical supercapacitors: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.113423
Ren S, Yang Y, Xu M, Cai H, Hao C, Wang X (2014) Hollow SnO2 microspheres and their carbon-coated composites for supercapacitors. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 444:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.12.028
Revathy JS, Priya NSC, Sandhya K, Rajendran DN (2021) Structural and optical studies of cerium doped gadolinium oxide phosphor. Bull Mater Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02299-w
Sedky A, Afify N, Hakamy A, Abd-Elnaiem AM (2023) Structural, optical, and dielectric properties of hydrothermally synthesized SnO2 nanoparticles, Cu/SnO2, and Fe/SnO2 nanocomposites. Phys Scr. https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ad081a
Shameem A, Devendran P, Siva V, Packiaraj R, Nallamuthu N, Asath Bahadur S (2019) Electrochemical performance and optimization of α-NiMoO 4 by different facile synthetic approach for supercapacitor application. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30(4):3305–3315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00603-3
Somayajulu GR (1958) dependence of force constant on electronegativity, bond strength, and bond order. VII. J Chem Phys 28(5):814–821. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1744276
Sopiha KV, Malyi OI, Persson C, Wu P (2021) Chemistry of oxygen ionosorption on SnO2 surfaces. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(28):33664–33676. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c08236
Suthakaran S, Dhanapandian S, Krishnakumar N, Ponpandian N (2020a) Hydrothermal synthesis of surfactant assisted Zn doped SnO2 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic performance and energy storage performance. J Phys Chem Solids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109407
Suthakaran S, Dhanapandian S, Krishnakumar N, Ponpandian N, Dhamodharan P, Anandan M (2020b) Surfactant-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Zr doped SnO2 nanoparticles with photocatalytic and supercapacitor applications. Mater Sci Semicond Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.104982
Teles JJS, Faria ER, Santos JHM, De Sousa LG, Franco DV, Nunes WG, Zanin H, Da Silva LM (2019) Supercapacitive properties, anomalous diffusion, and porous behavior of nanostructured mixed metal oxides containing Sn, Ru, and Ir. Electrochim Acta 295:302–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.10.131
Ul-Hamid A (2018) A beginners’ guide to scanning electron microscopy. Begin Guid Scan Electron Microsc. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98482-7
Varshney B, Siddiqui MJ, Anwer AH, Khan MZ, Ahmed F, Aljaafari A, Hammud HH, Azam A (2020) Synthesis of Mesoporous SnO2/NiO nanocomposite using modified sol–gel method and its electrochemical performance as electrode material for supercapacitors. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67990-8
Yadav AA (2016) Spray deposition of tin oxide thin films for supercapacitor applications: effect of solution molarity. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27(7):6985–6991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4654-7
Yngman S, McKibbin SR, Knutsson JV, Troian A, Yang F, Magnusson MH, Samuelson L, Timm R, Mikkelsen A (2019) Surface smoothing and native oxide suppression on Zn doped aerotaxy GaAs nanowires. J Appl Phys 125(2):66. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5058727
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge VIT management for the facilities provided for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mathew, G., Chamoli, P., Philip, A. et al. Effects of Copper Doping on the Electrochemical Performance of Tin Oxide Synthesised by Facile Co-precipitation Root. Int J Environ Res 18, 48 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-024-00587-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-024-00587-5