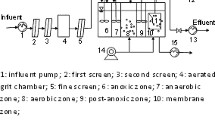
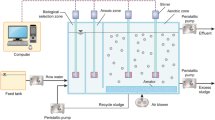
Abstract
In this paper, determination of parameter values for yield, growth rate, decay rate, and half-saturation coefficients of Activated Sludge Model No. 1 (ASM1) has been carried out. The activated sludge samples are collected from the sewage treatment plant used for the evaluation of ASM1 model parameters. The stoichiometric and kinetic parameters of autotrophic and heterotrophic biomass are determined using respiration rates in a respirometer operated at the temperature of 23 °C. These parameters are important when estimating oxygen demands, autotrophic, and heterotrophic biomass concentrations during the design and operation of activated sludge process. It should be noted that the parameters of ASM1 model are obtained from individual respirometric experiments. Results indicate that the parameter values determined in this study are in agreement within the range of values proposed in the literature at 20 °C and are useful for system analysis (modeling, optimization, and control) in activated sludge process. The estimated values of Y A, Y H, b A, b H, µ mA, µ mH, K S, and K NH are 0.22 mg cell COD formed (mg N oxidized)−1, 0.677 mg cell COD formed (mg COD oxidized)−1, 0.102 day−1, 0.196 day−1, 0.74 day−1, 3.836 day−1, 20.1893 mg COD/l and 1.016 mg NH3–N/l, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbrige M, Chesbro WR (1982) Very slow growth of Bacillus polymyxa: stringent responses and maintenance energy. Arch Microbiol 132(4):338–344
Brands E, Liebeskind M, Dohmann M (1994) Parameters for dynamic simulation of wastewater treatment plants with high rate and low-rate activated sludge tanks. Water Sci Technol 30(4):211–214
Brouwer H, Klapwijk A, Keesman KJ (1998) Identification of activated sludge characteristics using respirometric batch experiments. Water Res 32(4):1240–1254
Cech JS, Chudoba J, Grau P (1985) Determination of kinetic constants of activated sludge microorganisms. Water Sci Technol 17:259–272
Choubert JM, Marquot A, Stricker AE, Gillot S, Racault Y, Heduit A (2008) Maximum growth and decay rates of autotrophic biomass to simulate nitrogen removal at 10 °C with municipal activated sludge plants. Water SA 34:71–76
Chudoba J, Cech JS, Farkac J, Grau P (1985) Control of activated sludge filamentous bulking: experimental verification of a kinetic selection theory. Water Res 19:191–196
Copp JB (ed) (2001) The COST simulation benchmark-description and simulator manual. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Di Trapani D, Capodici M, Cosenza A, Di Bella G, Mannina G, Torregrossa M, Viviani G (2011) Evaluation of biomass activity and wastewater characterization in a UCT-MBR pilot lant by means of respirometric techniques. Desalination 269:190–197
Dold PL, Jones RM, Bye CM (2005) Importance and measurement of decay rate when assessing nitrification kinetics. Water Sci Technol 52:469–477
Drtil M, Nemeth P, Bodik I (1993) Kinetic constants of nitrification. Water Res 27(1):35–39
Esquivel-Rios I, Ramirez-Vargas R, Hernandez-Martinez GR, Vital-Jacome M, Ordaz A, Thalasso F (2014) A microrespirometric method for the determination of stoichiometric and kinetic parameters of heterotrophic and autotrophic cultures. Biochem Eng J 83:70–78
Gernaey AK, Petersen B, Ottoy JP, Vanrolleghem P (2001) Activated sludge monitoring with combined respirometric–titrimetric measurements. Water Res 35:1280–1294
Guisasola A, Sin G, Baeza JA, Carrera J, Vanrolleghem PA (2005) Limitations of ASM1 and ASM3:a comparison based on batch oxygen uptake rate profiles from different full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci Technol 52:69–77
Hao X, Wang Q, Zhang X, Cao Y, van Loosdrecht M (2009) Experimental evaluation of decrease in bacterial activity due to cell death and activity decay in activated sludge. Water Res 43:3604–3612
Henze M, Grady CPL, Gujer W, Marais GVR, Matsuo T (1987) A general model for single-sludge wastewater treatment systems. Water Res 21:505–515
Henze M, Gujer W, Mino T, Matsuo T, Wentzel M, Marais GVR, van Loosdrecht MCM (1999) Activated sludge model No. 2d, ASM 2d. Water Sci Technol 39(1):165–182
Henze M, Gujer W, Mino T, van Loosdrecht MCM (2000) Activated sludge Models ASM1, ASM2, ASM2d, and ASM3. IWA Publishing in its Scientific and Technical Report, London
Kappeler J, Gujer W (1992) Estimation of kinetic parameters of heterotrophic biomass under aerobic conditions and characterization of wastewater for activated sludge modelling. Water Sci Technol 25(6):125–139
Liu G, Wang J (2012) Probing the stoichiometry of the nitrification process using the respirometric approach. Water Res 46:5954–5962
Manser R, Gujer W, Siegrist H (2006) Decay processes of nitrifying bacteria in biological wastewater treatment systems. Water Res 40:2416–2426
Marsili-Libelli S, Tabani F (2002) Accuracy analysis of a respirometer for activated sludge dynamic modelling. Water Res 36:1181–1192
Mason CA, Hamer G, Bryers JD (1986) The death and lysis of micro-organisms in environmental processes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39(4):373–401
Metcalf and Eddy (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. McGraw Hill, Newyork
Moussa MS, Lubberding HJ, Hooijmans CM, van Loosdrecht MCM, Gijzen HJ (2003) Improved method for determination of ammonia and nitrite oxidation activities in mixed bacterial cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(2):217–221
Munz G, Gori R, Cammilli L, Lubello C (2008) Characterization of tannery wastewater and biomass in a membrane bioreactor using respirometric analysis. Bioresour Technol 99:8612–8618
Orhon D, Babuna FG, Karahan O (2009) Industrial wastewater treatment by activated sludge. IWA Publishing, London
Riefler RG, Ahlfeld DP, Smets BF (1998) Respirometric assay for biofilm kinetics estimation: parameter identifiability and retrievability. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:35–45
Salem S, Berends DHJG, van der Roest HF, van der kuij RJ, van Loosdrecht MCM (2004) Full-scale application of the BABE technology. Water Sci Technol 50(7):87–96
Salem S, Moussa MS, van Loosdrecht MCM (2006) Determination of the decay rate of nitrifying bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 94(2):252–262
Sollfrank U, Gujer W (1991) Characterisation of domestic wastewater for mathematical modelling of the activated sludge process. Water Sci Technol 23:1057–1066
Spanjers H, Vanrolleghem PA (1995) Respirometry as a tool for rapid characterisation of wastewater and activated sludge. Water Sci Technol 31(2):105–114
Spanjers H, Vanrolleghem PA, Olsson G, Dold PL (1998) Respirometry in control of the activated sludge process: principles. IAWQ Scientific and Technical Report No. 7
Spanjers H, Takacs I, Brouwer H (1999) Direct parameter extraction from respirograms for wastewater and biomass characterization. Water Sci Technol 39:137–145
van Loosdrecht MCM, Henze M (1999) Maintenance, endogenous respiration, lysis, decay and predation. Water Sci Technol 39(1):107–117
Vanrolleghem PA, Spanjers H, Petersen B, Ginestet P, Takacs I (1999) Estimating (combinations of) activated sludge model no. 1 parameters and components by respirometry. Water Sci Technol 39(1):195–214
Williamson KJ, McCarty PL (1975) Rapid measurement of monod half-velocity coefficients for bacterial kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng 17:915–924
Acknowledgements
This work is funded by a Grant from Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, under Extra Mural Research Funding with Grant No. EMR/2016/002750.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vivekanandan, B., Rao, A.S. Estimation of Yield, Growth Rate, Decay Rate, and Half-Saturation Coefficients of ASM1 Model Parameters. Int J Environ Res 11, 415–423 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0037-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0037-z