Abstract
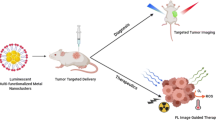
Gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) with near-infrared II (NIR-II) photoluminescence (PL) have emerged as novel bioimaging probes for in vivo disease diagnosis. So far, it still lacks a systematic review focusing on the synthesis, PL tuning, and in vivo imaging of NIR-II luminescent AuNCs. In this review, we briefly introduce the synthesis of NIR-II luminescent AuNCs using various surface ligands. We discuss the origins and properties of NIR-II PL in AuNCs, and summarize the strategies for improving and/or tuning NIR-II PL emissions. We also provide an overview of the recent progress in the application of AuNCs in tumor-targeted imaging, molecular imaging, and other areas (such as the sensitive imaging of bones, vessels, lymph nodes, etc.). Finally, we present the prospects and challenges in the field of NIR-II luminescent AuNCs and related imaging applications, expecting to offer comprehensive understanding of this field, and thereby deepening and broadening the biological application of AuNCs.

Reproduced with permission from Ref. [52]. Copyright 2023, Wiley–VCH; b Scheme illustration of the structure and NIR-II PL of AuNCs protected by mercaptohexanoic acid (MHA)/tetra (ethylene glycol) dithiol (TDT), MHA, GSH, and etc. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [36]. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society; c Scheme illustration of the incorporation of Au25NCs into BSA and corresponding PL spectra (λex = 700 nm). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [55]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier; d Schematic illustration of ligand exchange process of TPPTS-AuNCs by GSH, and the PL spectra and intensity changes at different GSH concentrations. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [53]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society

Reproduced with permission from Ref. [42]. Copyright 2020, Wiley–VCH. b Schematic diagram of tumor-targeted NIR-II PL imaging based on CDS-AuNCs that enabled the labeling of antibody (Ab) via host–guest interaction. NIR-II PL imaging of mice was shown at various time points post intravenous injection of non-target and target probes, respectively. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [35]. Copyright 2021, Wiley–VCH

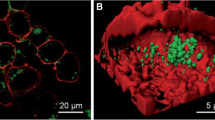
Reproduced with permission from Ref. [41]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. b Lymph node imaging studies based on PC-modified AuNCs. The structure of AuNCs and PC modification were shown. NIR-II PL images of mice were presented after the intratumor injection of AuNCs and PC-AuNCs, respectively. The excretion rates were also determined, revealing the higher renal clearance efficiency of PC-AuNCs than AuNCs. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [68]. Copyright 2022, Springer Nature

Reproduced with permission from Ref. [34]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society; b Schematic illustration of the assemblies of AuNCs and lanthanide NPs and their in vivo NIR-II PL imaging of mice tumors. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [77]. Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society; c Schematic illustration of in vivo GSH imaging of AuNCs based on the ligand exchange strategy, which enabled early imaging of metabolic acidosis-induced kidney injury. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [53]. Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society; d Schematic diagram of the synthesis of poly-dopamine-coated AuNCs (with loading of MB) for in vivo NIR-II PL imaging of gastric acid secretion. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [78]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier

Reproduced with permission from Ref. [24]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; b Dynamic brain imaging of stroke mouse and PCA overlaid images with arterial (red) and venous (blue) vessels. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [23]. Copyright 2019, Wiley–VCH; c Scheme of the MHA/TDT-Au NCs and NIR-II PL images of a Bmp9-KO mouse after MCR processing. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [36]. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society; d White-light images and NIR-II PL images of the precipitates of HA and different concentrations of AuNCs. NIR-II PL images of mice revealed the sensitive bone imaging capability of AuNCs. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [87]. Copyright 2020, Wiley–VCH
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Tao Y, Li MQ, Ren JS, Qu XG. Metal nanoclusters: novel probes for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(23):8636–63.
Lin ZK, Goswami N, Xue TT, Chai OJH, Xu HJ, Liu YX, Su Y, Xie JP. Engineering metal nanoclusters for targeted therapeutics: from targeting strategies to therapeutic applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(51):19.
Fan Y, Liu SG, Yi Y, Rong HP, Zhang JT. Catalytic nanomaterials toward atomic levels for biomedical applications: from metal clusters to single-atom catalysts. ACS Nano. 2021;15(2):2005–37.
Srinivasulu YG, Yao QF, Goswami N, Xie JP. Interfacial engineering of gold nanoclusters for biomedical applications. Mater Horizons. 2020;7(10):2596–618.
Yang G, Wang Z, Du F, Jiang F, Yuan X, Ying JY. Ultrasmall coinage metal nanoclusters as promising theranostic probes for biomedical applications. J Am Chem Soc. 2023;145(22):11879–98.
Yao Q, Wu Z, Liu Z, Lin Y, Yuan X, Xie J. Molecular reactivity of thiolate-protected noble metal nanoclusters: synthesis, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Sci. 2021;12(1):99–127.
Navarro M. Gold complexes as potential anti-parasitic agents. Coord Chem Rev. 2009;253(11–12):1619–26.
Tiekink ERT. Gold compounds in medicine: potential anti-tumour agents. Gold Bull. 2003;36(4):117–24.
Shaw CF. Gold-based therapeutic agents. Chem Rev. 1999;99(9):2589–600.
Hickey JL, Ruhayel RA, Barnard PJ, Baker MV, Berners-Price SJ, Filipovska A. Mitochondria-targeted chemotherapeutics: the rational design of gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes that are selectively toxic to cancer cells and target protein selenols in preference to Thiols. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(38):12570–1.
Rigobello MP, Messori L, Marcon G, AgostinaCinellu M, Bragadin M, Folda A, Scutari G, Bindoli A. Gold complexes inhibit mitochondrial thioredoxin reductase: consequences on mitochondrial functions. J Inorg Biochem. 2004;98(10):1634–41.
McKeage MJ, Berners-Price SJ, Galettis P, Bowen RJ, Brouwer W, Ding L, Zhuang L, Baguley BC. Role of lipophilicity in determining cellular uptake and antitumour activity of gold phosphine complexes. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2000;46(5):343–50.
Sanchez-Delgado RA, Anzellotti A. Metal complexes as chemotherapeutic agents against tropical diseases: trypanosomiasis, malaria and leishmaniasis. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004;4(1):23–30.
Takano S, Tsukuda T. Chemically modified gold/silver superatoms as artificial elements at nanoscale: design principles and synthesis challenges. J Am Chem Soc. 2021;143(4):1683–98.
Kang X, Zhu MZ. Tailoring the photoluminescence of atomically precise nanoclusters. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(8):2422–57.
Yao QF, Yuan X, Chen TK, Leong DT, Xie JP. Engineering functional metal materials at the atomic level. Adv Mater. 2018;30(47):23.
Qian HF, Zhu MZ, Wu ZK, Jin RC. Quantum sized gold nanoclusters with atomic precision. Acc Chem Res. 2012;45(9):1470–9.
Zheng K, Xie J. Engineering ultrasmall metal nanoclusters as promising theranostic agents. Trends Chem. 2020;2(7):665–79.
Zhang L, Wang E. Metal nanoclusters: new fluorescent probes for sensors and bioimaging. Nano Today. 2014;9(1):132–57.
Li S, Wei J, Yao Q, Song X, Xie J, Yang H. Emerging ultrasmall luminescent nanoprobes for in vivo bioimaging. Chem Soc Rev. 2023;52(5):1672–96.
Porret E, Le Guével X, Coll J-L. Gold nanoclusters for biomedical applications: toward in vivo studies. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(11):2216–32.
Qian S, Wang Z, Zuo Z, Wang X, Wang Q, Yuan X. Engineering luminescent metal nanoclusters for sensing applications. Coord Chem Rev. 2022;451:214268.
Liu HL, Hong GS, Luo ZT, Chen JC, Chang JL, Gong M, He H, Yang J, Yuan X, Li LL, Mu XY, Wang JY, Mi WB, Luo J, Xie JP, Zhang XD. Atomic-precision gold clusters for NIR-II imaging. Adv Mater. 2019;31(46):9.
Chen Y, Montana DM, Wei H, Cordero JM, Schneider M, Le Guevel X, Chen O, Bruns OT, Bawendi MG. Shortwave infrared in vivo imaging with gold nanoclusters. Nano Lett. 2017;17(10):6330–4.
Luo ZT, Yuan X, Yu Y, Zhang QB, Leong DT, Lee JY, Xie JP. From aggregation-induced emission of Au(I)-thiolate complexes to ultrabright Au(0)@Au(I)-thiolate core-shell nanoclusters. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134(40):16662–70.
Zhou C, Long M, Qin Y, Sun X, Zheng J. Luminescent gold nanoparticles with efficient renal clearance. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2011;50(14):3168–72.
Xie J, Zheng Y, Ying JY. Protein-directed synthesis of highly fluorescent gold nanoclusters. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131(3):888–9.
Edwards PP, Thomas JM. Gold in a metallic divided state—from faraday to present-day nanoscience. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46(29):5480–6.
Negishi Y, Nobusada K, Tsukuda T. Glutathione-protected gold clusters revisited: bridging the gap between Gold(I)−thiolate complexes and thiolate-protected gold nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(14):5261–70.
Brust M, Walker M, Bethell D, Schiffrin DJ, Whyman R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two-phase Liquid-Liquid system. J Chem Soc Chem Commun. 1994;0(7):801–2.
Zhang K, Chen FR, Wang L, Hu J. Second Near-Infrared (NIR-II) Window for Imaging-Navigated Modulation of Brain Structure and Function. Small. 2023;19(14):2206044.
Xin Q, Ma H, Wang H, Zhang XD. Tracking tumor heterogeneity and progression with near-infrared II fluorophores. Exploration. 2023;3(2):20220011.
Ma H, Wang J, Zhang X. Near-infrared II emissive metal clusters: from atom physics to biomedicine. Coord Chem Rev. 2021;448: 214184.
Li SH, Ma QP, Wang CL, Yang KD, Hong ZZ, Chen QS, Song JB, Song XR, Yang HH. Near-infrared II gold nanocluster assemblies with improved luminescence and biofate for in vivo ratiometric imaging of H2S. Anal Chem. 2022;94(5):2641–7.
Song XR, Zhu W, Ge XG, Li RF, Li SH, Chen X, Song JB, Xie JP, Chen XY, Yang HH. A new class of NIR-II gold nanocluster-based protein biolabels for in vivo tumor-targeted imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(3):1306–12.
Yu ZX, Musnier B, Wegner KD, Henry M, Chovelon B, Desroches-Castan A, Fertin A, Resch-Genger U, Bailly S, Coll JL, Usson Y, Josserand V, Le Guevel X. High-resolution shortwave infrared imaging of vascular disorders using gold nanoclusters. ACS Nano. 2020;14(4):4973–81.
Yu M, Xu J, Zheng J. Renal clearable luminescent gold nanoparticles: from the bench to the clinic. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(13):4112–28.
Zhang X, Wu D, Shen X, Liu P, Fan F, Fan S. In vivo renal clearance, biodistribution, toxicity of gold nanoclusters. Biomaterials. 2012;33(18):4628–38.
Yu Y, Luo Z, Yu Y, Lee JY, Xie J. Observation of cluster size growth in CO-directed synthesis of Au25(SR)18 nanoclusters. ACS Nano. 2012;6(9):7920–7.
Yang G, Mu X, Pan X, Tang Y, Yao Q, Wang Y, Jiang F, Du F, Xie J, Zhou X, Yuan X. Ligand engineering of Au44 nanoclusters for NIR-II luminescent and photoacoustic imaging-guided cancer photothermal therapy. Chem Sci. 2023;14(16):4308–18.
Pang ZY, Yan WX, Yang J, Li QZ, Guo Y, Zhou DJ, Jiang XY. Multifunctional gold nanoclusters for effective targeting, near-infrared fluorescence imaging, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer lymphatic metastasis. ACS Nano. 2022;16(10):16019–37.
Wang WL, Kong YF, Jiang J, Xie QQ, Huang Y, Li GN, Wu D, Zheng HZ, Gao M, Xu SJ, Pan YX, Li W, Ma RL, Wu MX, Li XH, Zuilhof H, Cai XM, Li RB. Engineering the protein corona structure on gold nanoclusters enables red-shifted emissions in the second near-infrared window for gastrointestinal imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59(50):22431–5.
Zhao H, Wang H, Li HR, Zhang TC, Zhang J, Guo WH, Fu K, Du GQ. Magnetic and near-infrared-II fluorescence Au-Gd nanoclusters for imaging-guided sensitization of tumor radiotherapy. Nanoscale Adv. 2022;4(7):1815–26.
Dan Q, Yuan Z, Zheng S, Ma HR, Luo WX, Zhang L, Su N, Hu DH, Sheng ZH, Li YJ. Gold nanoclusters-based NIR-II photosensitizers with catalase-like activity for boosted photodynamic therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(8):17.
Tang L, Zeng XD, Zhou H, Gui CH, Luo QL, Zhou WY, Wu J, Li QQ, Li Y, Xiao YL. Theranostic gold nanoclusters for NIR-II imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2021;37(4):934–42.
Wang J, Wang ZY, Li SJ, Zang SQ, Mak TCW. Carboranealkynyl-protected gold nanoclusters: size conversion and UV/Vis–NIR optical properties. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;133(11):6024–9.
Wang G, Huang T, Murray RW, Menard L, Nuzzo RG. Near-IR luminescence of monolayer-protected metal clusters. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(3):812–3.
Li Q, Zeman CJ, Ma ZR, Schatz GC, Gu XW. Bright NIR-II photoluminescence in rod-shaped icosahedral gold nanoclusters. Small. 2021;17(11):7.
Zhou M, Song YB. Origins of visible and near-infrared emissions in [Au25(SR)18]- nanoclusters. J Phys Chem Lett. 2021;12(5):1514–9.
Pyo K, Thanthirige VD, Kwak K, Pandurangan P, Ramakrishna G, Lee D. Ultrabright luminescence from gold nanoclusters: rigidifying the Au(I)-thiolate shell. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(25):8244–50.
Wang SX, Meng XM, Das A, Li T, Song YB, Cao TT, Zhu XY, Zhu MZ, Jin RC. A 200-fold quantum yield boost in the photoluminescence of silver-doped AgxAu25-x nanoclusters: the 13th silver atom matters. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53(9):2376–80.
Huang Y, Chen K, Liu L, Ma HZ, Zhang XN, Tan KX, Li Y, Liu Y, Liu CL, Wang H, Zhang XD. Single atom-engineered NIR-II gold clusters with ultrahigh brightness and stability for acute kidney injury. Small. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202300145.
Zhao ZP, Chen HR, He K, Lin JC, Cai W, Sun YD, Liu JB. Glutathione-activated emission of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in the second near-infrared window for imaging of early kidney injury. Anal Chem. 2023;95(11):5061–8.
Haye L, Diriwari PI, Alhalabi A, Gallavardin T, Combes A, Klymchenko AS, Hildebrandt N, Le Guével X, Reisch A. Enhancing near infrared II emission of gold nanoclusters via encapsulation in small polymer nanoparticles. Adv Opt Mater. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202201474.
Bertorelle F, Wegner KD, Bakulic MP, Fakhouri H, Comby-Zerbino C, Sagar A, Bernado P, Resch-Genger U, Bonacic-Koutecky V, Le Guevel X, Antoine R. Tailoring the NIR-II photoluminescence of single thiolated Au25 nanoclusters by selective binding to proteins. Chem-Eur J. 2022;28(39):8.
Wen Y, Long ZQ, Huo FJ, Yin CX. Novel strategy for accurate tumor labeling: endogenous metabolic imaging through metabolic probes. Sci China Chem. 2022;65(12):2517–27.
Crosby D, Bhatia S, Brindle KM, Coussens LM, Dive C, Emberton M, Esener S, Fitzgerald RC, Gambhir SS, Kuhn P, Rebbeck TR, Balasubramanian S. Early detection of cancer. Science. 2022;375(6586):eaay9040.
Hong B, Zu Y. Detecting circulating tumor cells: current challenges and new trends. Theranostics. 2013;3(6):377–94.
Zhu H, Fan JL, Du JJ, Peng XJ. Fluorescent probes for sensing and imaging within specific cellular organelles. Acc Chem Res. 2016;49(10):2115–26.
Weissleder R, Schwaiger MC, Gambhir SS, Hricak H. Imaging approaches to optimize molecular therapies. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(355):7.
Ueno T, Nagano T. Fluorescent probes for sensing and imaging. Nat Methods. 2011;8(8):642–5.
Li YL, Hung WC. Reprogramming of sentinel lymph node microenvironment during tumor metastasis. J Biomed Sci. 2022;29(1):1–15.
Heerdt AS. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(3):431.
Lee WC, Kopetz S, Wistuba II, Zhang J. Metastasis of cancer: when and how? Ann Oncol. 2017;28(9):2045–7.
Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331(6024):1559–64.
Tian R, Ma HL, Zhu SJ, Lau J, Ma R, Liu YJ, Lin LS, Chandra S, Wang S, Zhu XF, Deng HZ, Niu G, Zhang MX, Antaris AL, Hettie KS, Yang B, Liang YY, Chen XY. Multiplexed NIR-II probes for lymph node-invaded cancer detection and imaging-guided surgery. Adv Mater. 2020;32(11):10.
Li CY, Torres VC, Tichauer KM. Noninvasive detection of cancer spread to lymph nodes: A review of molecular imaging principles and protocols. J Surg Oncol. 2018;118(2):301–14.
Baghdasaryan A, Wang F, Ren F, Ma Z, Li J, Zhou X, Grigoryan L, Xu C, Dai H. Phosphorylcholine-conjugated gold-molecular clusters improve signal for Lymph Node NIR-II fluorescence imaging in preclinical cancer models. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5613.
Zhou ZX, Lu ZR. Molecular imaging of the tumor microenvironment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;113:24–48.
Chen LY, Wang CW, Yuan ZQ, Chang HT. Fluorescent gold nanoclusters: recent advances in sensing and imaging. Anal Chem. 2015;87(1):216–29.
Chen LL, Lyu Y, Zhang X, Zheng LT, Li QQ, Ding D, Chen FM, Liu YH, Li W, Zhang YT, Huang QL, Wang ZQ, Xie TT, Zhang Q, Sima Y, Li K, Xu S, Ren TB, Xiong MY, Wu Y, Song JB, Yuan L, Yang HH, Zhang XB, Tan WH. Molecular imaging: design mechanism and bioapplications. Sci China Chem. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-022-1461-3.
Fang H, Yu H, Lu Q, Fang X, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Zhu L, Ma Q. A new ratiometric fluorescent probe for specific monitoring of hROS under physiological conditions using boric acid-protected L-DOPA gold nanoclusters. Anal Chem. 2020;92(19):12825–32.
Ju E, Liu Z, Du Y, Tao Y, Ren J, Qu X. Heterogeneous assembled nanocomplexes for ratiometric detection of highly reactive oxygen species in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano. 2014;8(6):6014–23.
Bai XL, Xu SY, Wang LY. Full-range pH stable Au-clusters in nanogel for confinement-enhanced emission and improved sulfide sensing in living cells. Anal Chem. 2018;90(5):3270–5.
Xiang H, He SY, Zhao G, Zhang MT, Lin J, Yang LN, Liu HL. Gold nanocluster-based ratiometric probe with surface structure regulation-triggered sensing of hydrogen sulfide in living organisms. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(10):12643–52.
Chen TT, Hu YH, Cen Y, Chu X, Lu Y. A dual-emission fluorescent nanocomplex of gold-cluster-decorated silica particles for live cell imaging of highly reactive oxygen species. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(31):11595–602.
Hu SQ, Huang LX, Zhou LY, Wu TC, Zhao SL, Zhang LL. Single-excitation triple-emission down-/up-conversion nanoassemblies for tumor microenvironment-enhanced ratiometric NIR-II fluorescence imaging and chemo-/photodynamic combination therapy. Anal Chem. 2023;95(7):3830–9.
Liang M, Hu Q, Yi SX, Chi YJ, Xiao Y. Development of an Au nanoclusters based activatable nanoprobe for NIR-II fluorescence imaging of gastric acid. Biosens Bioelectron. 2023;224:9.
Yang J, Wang T, Zhao LN, Rajasekhar VK, Joshi S, Andreou C, Pal S, Hsu HT, Zhang HW, Cohen IJ, Huang RM, Hendrickson RC, Miele MM, Pei WB, Brendel MB, Healey JH, Chiosis G, Kircher MF. Gold/alpha-lactalbumin nanoprobes for the imaging and treatment of breast cancer. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020;4(7):686–703.
Loynachan CN, Soleimany AP, Dudani JS, Lin YY, Najer A, Bekdemir A, Chen Q, Bhatia SN, Stevens MM. Renal clearable catalytic gold nanoclusters for in vivo disease monitoring. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14(9):883–90.
Jiang XY, Du BJ, Zheng J. Glutathione-mediated biotransformation in the liver modulates nanoparticle transport. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14(9):874–82.
de Palma M, Biziato D, Petrova TV. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(8):457–74.
Tu CY, Das S, Baker AB, Zoldan J, Suggs LJ. Nanoscale strategies: treatment for peripheral vascular disease and critical limb ischemia. ACS Nano. 2015;9(4):3436–52.
Yang Y, Rosenberg GA. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke. 2011;42(11):3323–8.
Rosell A, Cuadrado E, Ortega-Aznar A, Hernandez-Guillamon M, Lo EH, Montaner J. MMP-9-Positive neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2008;39(4):1121–6.
Viallard C, Larrivee B. Tumor angiogenesis and vascular normalization: alternative therapeutic targets. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(4):409–26.
Li DL, Liu Q, Qi QR, Shi H, Hsu EC, Chen WY, Yuan WL, Wu YF, Lin SE, Zeng YT, Xiao ZY, Xu LY, Zhang YR, Stoyanova T, Jia W, Cheng Z. Gold nanoclusters for NIR-II fluorescence imaging of bones. Small. 2020;16(43):9.
Zou D, Lin R, Han Y, Jia J, Zhou G, Zhang H, Ge K. Lanthanum promoting bone formation by regulating osteogenesis, osteoclastogenesis and angiogenesis. J Rare Earths. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2023.01.019.
Wu P, Siegwart DJ, Xiong H. Recent advances in the targeted fluorescent probes for the detection of metastatic bone cancer. Sci China Chem. 2021;64(8):1283–96.
Zaheer A, Lenkinski RE, Mahmood A, Jones AG, Cantley LC, Frangioni JV. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging of osteoblastic activity. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19(12):1148–54.
Sun WT, Ge K, Jin Y, Han Y, Zhang HS, Zhou GQ, Yang XJ, Liu DD, Liu HF, Liang XJ, Zhang JC. Bone-targeted nanoplatform combining zoledronate and photothermal therapy to treat breast cancer bone metastasis. ACS Nano. 2019;13(7):7556–67.
Xiong H, Zuo H, Yan YF, Occhialini G, Zhou KJ, Wan YH, Siegwart DJ. High-contrast fluorescence detection of metastatic breast cancer including bone and liver micrometastases via size-controlled pH-activatable water-soluble probes. Adv Mater. 2017;29(29):10.
Li CY, Zhang YJ, Chen GC, Hu F, Zhao K, Wang QB. Engineered multifunctional nanomedicine for simultaneous stereotactic chemotherapy and inhibited osteolysis in an orthotopic model of bone metastasis. Adv Mater. 2017;29(13):7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research & Development Program of China (2020YFA0709900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22027805, 22274024), the Major Project of Science and Technology of Fujian Province (2020HZ06006), the Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by CAST (YESS20200110), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M720737, 2021T140117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, S., Liu, Y., Tong, S. et al. Emerging NIR-II Luminescent Gold Nanoclusters for In Vivo Bioimaging. J. Anal. Test. 7, 260–271 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-023-00256-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-023-00256-0