Abstract
Naznozymes have become an important alternative to natural enzymes for many sensing applications, due to their relatively high stability, easy synthesis, and cost-effectiveness. Nanozyme-based assays, especially paper-based assays are portable, and therefore, are convenient for use in field operations, especially in remote parts of the world. Decreasing water levels, depletion of water resources, and large scale mining create the need for rapid detection of heavy metal ions in various water samples. In comparison with traditional methods of heavy metal ion detection, nanozyme-based systems enable rapid and cheap screening on the spot with a very simple instrument such as a UV–Vis absorption spectrophotometer. The sensing mechanism of a nanozyme-based sensor is highly dependent on its surface properties. They often encounter selectivity issues, unlike natural enzyme-based assays. Therefore, different types of target recognition and inhibition/enhancement mechanisms have been reported to achieve high selectivity. In this short review, we mainly focus our discussion on various interaction of the heavy metal ions with the nanozyme, and their responses towards the catalytic activity in the sensing of target metal ions.


Reproduced from Ref. [16] with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry

Reproduced from Ref. [66] with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry

Reproduced from Ref. [75]

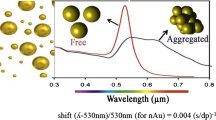
Reproduced with permission from [63]

Reproduced from Ref. [79] with permission from American Chemical Society
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 March 2020
The publisher has retracted this article [1] due to an operational error during the publication process.
References
Winkler M, Geier M, Hanlon SP, Nidetzky B, Glieder A. Human enzymes for organic synthesis. Angew Chem Int. 2018;57:13406–23.
Küchler A, Yoshimoto M, Luginbühl S, Mavelli F, Walde P. Enzymatic reactions in confined environments. Nat Nanotechnol. 2016;11:409–20.
Nguyen HH, Lee SH, Lee UJ, Fermin CD, Kim M. Immobilized enzymes in biosensor. Appl Mater. 2019;12(1):121.
Reetz MT. What are the limitations of enzymes in synthetic organic chemistry? Chem Rec. 2016;16:2449–59.
Wu J, Wang X, Wang Q, Lou Z, Li S, Zhu Y, et al. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48:1004–76.
Zhong Y, Tang X, Li J, Lan Q, Min L, Ren C, et al. A nanozyme tag enabled chemiluminescence imaging immunoassay for multiplexed cytokine monitoring. Chem Commun. 2018;54:13813–6.
Ganganboina AB, Doong R-A. The biomimic oxidase activity of layered V2O5 nanozyme for rapid and sensitive nanomolar detection of glutathione. Sens Actuators B. 2018;273:1179–86.
Mu J, Zhao X, Li J, Yang E-C, Zhao X-J. Novel hierarchical NiO nanoflowers exhibiting intrinsic superoxide dismutase-like activity. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4:5217–21.
Sloan-Dennison S, Laing S, Shand NC, Graham D, Faulds K. A novel nanozyme assay utilising the catalytic activity of silver nanoparticles and SERRS. Analyst. 2017;142:2484–90.
He Y, Li X, Xu X, Pan J, Niu X. A cobalt-based polyoxometalate nanozyme with high peroxidase-mimicking activity at neutral pH for one-pot colorimetric analysis of glucose. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6:5750–5.
Comotti M, Della Pina C, Matarrese R, Rossi M. The catalytic activity of “naked” gold particles. Angew Chem Int. 2004;43:5812–5.
Xi J, Wang W, Da L, Zhang J, Fan L, Gao L. Au-PLGA hybrid nanoparticles with catalase-mimicking and near-infrared photothermal activities for photoacoustic imaging-guided cancer therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4:1083–91.
Li W, Wang J, Zhu J, Zheng Y-Q. Co3O4 nanocrystals as an efficient catalase mimic for the colorimetric detection of glutathione. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6:6858–64.
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:577–83.
Han KN, Choi J-S, Kwon J. Gold nanozyme-based paper chip for colorimetric detection of mercury ions. Sci Rep. 2017;7:2806.
Tseng C-W, Chang H-Y, Chang J-Y, Huang C-C. Detection of mercury ions based on mercury-induced switching of enzyme-like activity of platinum/gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2012;4:6823–30.
Lin S, Zhang Y, Cao W, Wang X, Qin L, Zhou M, et al. Nucleobase-mediated synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanozymes as efficient peroxidase mimics. Dalton Trans. 2019;48:1993–9.
Guo QJ, Pan ZY, Men C, Lv WY, Zou HY, Huang CZ. Visual detection of cancer cells by using in situ grown functional Cu2−xSe/reduced graphene oxide hybrids acting as an efficient nanozyme. Analyst. 2019;144:716–21.
Ko E, Tran V-K, Son SE, Hur W, Choi H, Seong GH. Characterization of Au@PtNP/GO nanozyme and its application to electrochemical microfluidic devices for quantification of hydrogen peroxide. Sens Actuators B. 2019;294:166–76.
Yu J, Ma D, Mei L, Gao Q, Yin W, Zhang X, et al. Peroxidase-like activity of MoS2 nanoflakes with different modifications and their application for H2O2 and glucose detection. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6:487–98.
Li D, Liu B, Huang P-JJ, Zhang Z, Liu J. Highly active fluorogenic oxidase-mimicking NiO nanozymes. Chem Commun. 2018;54:12519–22.
Zhang H, Liang X, Han L, Li F. “Non-naked” gold with glucose oxidase-like activity: a nanozyme for tandem catalysis. Small. 2018;14:1803256.
Weerathunge P, Ramanathan R, Torok VA, Hodgson K, Xu Y, Goodacre R, et al. Ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of murine norovirus using nanozyme aptasensor. Anal Chem. 2019;91:3270–6.
Chen J, Shu Y, Li H, Xu Q, Hu X. Nickel metal-organic framework 2D nanosheets with enhanced peroxidase nanozyme activity for colorimetric detection of H2O2. Talanta. 2018;189:254–61.
Miao L, Jiao L, Tang Q, Li H, Zhang L, Wei Q. A nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay for dual-modal colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent detection of cardiac troponin I. Sens Actuators B. 2019;288:60–4.
Kuo P-C, Lien C-W, Mao J-Y, Unnikrishnan B, Chang H-T, Lin H-J, et al. Detection of urinary spermine by using silver-gold/silver chloride nanozymes. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1009:89–97.
Liu R, Zuo L, Huang X, Liu S, Yang G, Li S, et al. Colorimetric determination of lead(II) or mercury(II) based on target induced switching of the enzyme-like activity of metallothionein-stabilized copper nanoclusters. Microchim Acta. 2019;186:250.
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Ding D, Guo R. Switching peroxidase-mimic activity of protein stabilized platinum nanozymes by sulfide ions: substrate dependence, mechanism, and detection. Langmuir. 2017;33:13811–20.
Karim MN, Singh M, Weerathunge P, Bian P, Zheng R, Dekiwadia C, et al. Visible-light-triggered reactive-oxygen-species-mediated antibacterial activity of peroxidase-mimic CuO nanorods. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2018;1:1694–704.
Dehghani Z, Hosseini M, Mohammadnejad J, Bakhshi B, Rezayan AH. Colorimetric aptasensor for Campylobacter jejuni cells by exploiting the peroxidase like activity of Au@Pd nanoparticles. Microchim Acta. 2018;185:448.
Wang X, Qin L, Zhou M, Lou Z, Wei H. Nanozyme sensor arrays for detecting versatile analytes from small molecules to proteins and cells. Anal Chem. 2018;90:11696–702.
Dai D, Liu H, Ma H, Huang Z, Gu C, Zhang M. In-situ synthesis of Cu2OAu nanocomposites as nanozyme for colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide. J Alloys Compd. 2018;747:676–83.
Han L, Shi J, Liu A. Novel biotemplated MnO2 1D nanozyme with controllable peroxidase-like activity and unique catalytic mechanism and its application for glucose sensing. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2017;252:919–26.
Karim MN, Anderson SR, Singh S, Ramanathan R, Bansal V. Nanostructured silver fabric as a free-standing NanoZyme for colorimetric detection of glucose in urine. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;110:8–15.
Bhagat S, Srikanth Vallabani NV, Shutthanandan V, Bowden M, Karakoti AS, Singh S. Gold core/ceria shell-based redox active nanozyme mimicking the biological multienzyme complex phenomenon. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;513:831–42.
Kumar S, Bhushan P, Bhattacharya S. Facile synthesis of Au@Ag–hemin decorated reduced graphene oxide sheets: a novel peroxidase mimetic for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. RSC Adv. 2017;7:37568–77.
Guo Y, Yan L, Zhang R, Ren H, Liu A. CoO-supported ordered mesoporous carbon nanocomposite based nanozyme with peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection of glucose. Process Biochem. 2019;81:92–8.
Cho S, Lee SM, Shin HY, Kim MS, Seo YH, Cho YK, et al. Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of allergies based on an immunoassay using peroxidase-mimicking nanozymes. Analyst. 2018;143:1182–7.
Zhuge W, Tan X, Zhang R, Li H, Zheng G. Fluorescent and colorimetric immunoassay of nuclear matrix protein 22 enhanced by porous Pd nanoparticles. Chin Chem Lett. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.02.026.
Cheng N, Song Y, Zeinhom MMA, Chang Y-C, Sheng L, Li H, et al. Nanozyme-mediated dual immunoassay integrated with smartphone for use in simultaneous detection of pathogens. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:40671–80.
Oh S, Kim J, Tran VT, Lee DK, Ahmed SR, Hong JC, et al. Magnetic nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay for ultrasensitive influenza A virus detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:12534–43.
Farka Z, Čunderlová V, Horáčková V, Pastucha M, Mikušová Z, Hlaváček A, et al. Prussian blue nanoparticles as a catalytic label in a sandwich nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Chem. 2018;90:2348–54.
Chen W, Fang X, Li H, Cao H, Kong J. A simple paper-based colorimetric device for rapid mercury(II) assay. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31948.
Liu B, Liu J. Surface modification of nanozymes. Nano Res. 2017;10:1125–48.
Jan TA, Azam M, Siddiqui K, Ali A, Choi I, Haq MQ. Heavy metals and human health: mechanistic insight into toxicity and counter defense system of antioxidants. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:29592–630.
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2014;7:60–72.
Pohl P. Determination of metal content in honey by atomic absorption and emission spectrometries. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2009;28:117–28.
Hu P, Wang X, Yang L, Yang H, Tang Y, Luo H, et al. Speciation of mercury by hydride generation ultraviolet atomization-atomic fluorescence spectrometry without chromatographic separation. Microchem J. 2018;143:228–33.
Day PL, Eckdahl SJ, Maleszewski JJ, Wright TC, Murray DL. Establishing human heart chromium, cobalt and vanadium concentrations by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2017;41:60–5.
Yu X, He Q, Li Y, He H, Zhang J. Atomic fluorescence spectrometric detection of methylmercury in seawater at sub ng L−1 level by UV-induced atomization of gaseous methylethylmercury after NaBEt4 derivatization with purge and trap preconcentration and gas chromatography separation. Spectrochim Acta Part B. 2019;152:1–5.
Lu X, Zhao J, Liang X, Zhang L, Liu Y, Yin X, et al. The application and potential artifacts of zeeman cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry in mercury stable isotope analysis. Environ Sci Technol Lett. 2019;6:165–70.
Wang Z, Tang W, Yu J, Zhang F, He P. Phytic acid@Ag-based all-solid-state ion selective electrode for potentiometric detection of Cu2+. J Electroanal Chem. 2019;835:137–42.
Ahmed MA. Determination of Na, K and Fe in Lactuca sativa by using atomic absorption spectrophotometric and flame photometry techniques. AJPS. 2017;17:1–6.
Zinoubi K, Majdoub H, Barhoumi H, Boufi S, Jaffrezic-Renault N. Determination of trace heavy metal ions by anodic stripping voltammetry using nanofibrillated cellulose modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem. 2017;799:70–7.
Kumar V, Singh DK, Mohan S, Bano D, Gundampati RK, Hasan SH. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle for the selective and sensitive colorimetric detection of mercury (II) ion. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;168:67–77.
Li S, Wei T, Tang M, Chai F, Qu F, Wang C. Facile synthesis of bimetallic Ag-Cu nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of mercury ion and catalysis. Sens Actuators B. 2018;255:1471–81.
Li X, Wu Z, Zhou X, Hu J. Colorimetric response of peptide modified gold nanoparticles: an original assay for ultrasensitive silver detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:496–501.
Hong SP, Kang SH, Kim DK, Kang BS. Eu3+-doped gadolinium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by chemical coprecipitation predicted by thermodynamic modeling. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014;14:8296–304.
Niu X, Zhong Y, Chen R, Wang F, Liu Y, Luo D. A “turn-on” fluorescence sensor for Pb2+ detection based on graphene quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B. 2018;255:1577–81.
Bian S, Shen C, Qian Y, Liu J, Xi F, Dong X. Facile synthesis of sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots as fluorescent sensing probes for Ag+ ions detection. Sens Actuators B. 2017;242:231–7.
Niu X, He Y, Li X, Zhao H, Pan J, Qiu F, et al. A peroxidase-mimicking nanosensor with Hg2+-triggered enzymatic activity of cysteine-decorated ferromagnetic particles for ultrasensitive Hg2+ detection in environmental and biological fluids. Sens Actuators B. 2019;281:445–52.
Liao H, Liu G, Liu Y, Li R, Fu W, Hu L. Aggregation-induced accelerating peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoclusters and their applications for colorimetric Pb2+ detection. Chem Commun. 2017;53:10160–3.
Liu Y, Ding D, Zhen Y, Guo R. Amino acid-mediated ‘turn-off/turn-on’ nanozyme activity of gold nanoclusters for sensitive and selective detection of copper ions and histidine. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:140–6.
Kora AJ, Rastogi L. Peroxidase activity of biogenic platinum nanoparticles: a colorimetric probe towards selective detection of mercuric ions in water samples. Sens Actuators B. 2018;254:690–700.
Zhang W, Niu X, Meng S, Li X, He Y, Pan J, et al. Histidine-mediated tunable peroxidase-like activity of nanosized Pd for photometric sensing of Ag+. Sens Actuators B. 2018;273:400–7.
Hsu C-L, Lien C-W, Harroun SG, Ravindranath R, Chang H-T, Mao J-Y, et al. Metal-deposited bismuth oxyiodide nanonetworks with tunable enzyme-like activity: sensing of mercury and lead ions. Mater Chem Front. 2017;1:893–9.
Huang L, Zhu Q, Zhu J, Luo L, Pu S, Zhang W, et al. Portable colorimetric detection of mercury(II) based on a non-noble metal nanozyme with tunable activity. Inorg Chem. 2019;58:1638–46.
Sculfort S, Braunstein P. Intramolecular d10–d10 interactions in heterometallic clusters of the transition metals. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:2741–60.
Krishnadas KR, Udayabhaskararao T, Choudhury S, Goswami N, Pal SK, Pradeep T. Luminescent AgAu alloy clusters derived from Ag nanoparticles—manifestations of tunable AuI–CuI metallophilic interactions. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2014;2014:908–16.
Chen P-C, Ma J-Y, Chen L-Y, Lin G-L, Shih C-C, Lin T-Y, et al. Photoluminescent AuCu bimetallic nanoclusters as pH sensors and catalysts. Nanoscale. 2014;6:3503–7.
Deng H, He S, Lin X, Yang L, Lin Z, Chen R, Peng H, Chen W. Target-triggered inhibiting oxidase-mimicking activity of platinum nanoparticles for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of silver ion. Chin Chem Lett. 2019;30:1659–62.
Peng C-F, Zhang Y-Y, Wang L-Y, Jin Z-Y, Shao G. Colorimetric assay for the simultaneous detection of Hg2+ and Ag+ based on inhibiting the peroxidase-like activity of core–shell Au@Pt nanoparticles. Anal Methods. 2017;9:4363–70.
Hsu C-L, Lien C-W, Wang C-W, Harroun SG, Huang C-C, Chang H-T. Immobilization of aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles on BiOCl nanosheets: tunable peroxidase-like activity by protein recognition. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;75:181–7.
Lien C-W, Yu P-H, Chang H-T, Hsu P-H, Wu T, Lin Y-W, Huang C-C, Lai J-Y. DNA engineered copper oxide-based nanocomposites with multiple enzyme-like activities for specific detection of mercury species in environmental and biological samples. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.009.
Wang Y-W, Wang M, Wang L, Xu H, Tang S, Yang H-H, et al. A simple assay for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of Ag+ at picomolar levels using platinum nanoparticles. Sensors. 2017;17:2521.
Liu Y, Xiang Y, Ding D, Guo R. Structural effects of amphiphilic protein/gold nanoparticle hybrid based nanozyme on peroxidase-like activity and silver-mediated inhibition. RSC Adv. 2016;6:112435–44.
Borthakur P, Darabdhara G, Das MR, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S. Solvothermal synthesis of CoS/reduced porous graphene oxide nanocomposite for selective colorimetric detection of Hg(II) ion in aqueous medium. Sens Actuators B. 2017;244:684–92.
Deng H-H, Luo B-Y, He S-B, Chen R-T, Lin Z, Peng H-P, Xia X-H, Chen W. Redox recycling-triggered peroxidase-like activity enhancement of bare gold nanoparticles for ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of rare-earth Ce3+ ion. Anal Chem. 2019;91:4039–46.
Lien C-W, Tseng Y-T, Huang C-C, Chang H-T. Logic control of enzyme-like gold nanoparticles for selective detection of lead and mercury ions. Anal Chem. 2014;86:2065–72.
Li C-R, Hai J, Fan L, Li S-L, Wang B-D, Yang Z-Y. Amplified colorimetric detection of Ag+ based on Ag+-triggered peroxidase-like catalytic activity of ZIF-8/GO nanosheets. Sens Actuators B. 2019;284:213–9.
Wu L-L, Qian Z-J, Xie Z-J, Zhang Y-Y, Peng C-F. Colorimetric detection of copper ions based on surface modification of silver/platinum cluster nanozyme. Chin J Anal Chem. 2017;45:471–6.
Mu J, Li J, Zhao X, Yang E-C, Zhao X-J. Novel urchin-like Co9S8 nanomaterials with efficient intrinsic peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric sensing of copper (II) ion. Sens Actuators B. 2018;258:32–41.
He Y, Niu X, Li L, Li X, Zhang W, Zhao H, Lan M, Pan J, Zhang X. Microwave-assisted fabrication of bimetallic PdCu nanocorals with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and efficiency for thiocyanate sensing. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2018;1:2397–405.
Lien C-W, Unnikrishnan B, Harroun SG, Wang C-M, Chang J-Y, Chang H-T, Huang C-C. Visual detection of cyanide ions by membrane-based nanozyme assay. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;102:510–7.
Wen S-H, Zhong X-L, Wu Y-D, Liang R-P, Zhang L, Qiu J-D. Colorimetric assay conversion to highly sensitive electrochemical assay for bimodal detection of arsenate based on cobalt oxyhydroxide nanozyme via arsenate absorption. Anal Chem. 2019;91:6487–97.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under Contract No. 107-2622-B-182-001-CC2, 107-2113-M-019-004-MY3, 107-2622-M-019-001-CC2 and 107-2627-M-007-007-MY3, University System of Taipei Joint Research Program under contract USTP-NTUT-NTOU-108-02, and the Center of Excellence for the Oceans, National Taiwan Ocean University from The Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
The publisher has retracted this article due to an operational error during the publication process. The authors agree with this retraction.
About this article
Cite this article
Unnikrishnan, B., Lien, CW. & Huang, CC. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Nanozyme Based Detection of Heavy Metal Ions and its Challenges: A Minireview. J. Anal. Test. 3, 206–218 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-019-00110-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-019-00110-2