Abstract
With super-resolution microscopy, we attempt to visualize (biological) structures and processes at the sub-cellular level (i.e., nanoscale). To obtain this information, the samples are labeled with fluorophores that have a stochastic on/off switching of their emissions, which help to overcome the optical diffraction limit of around 250 nm, related to the use of optical microscopes. However, nowadays, research focuses on the imaging of live cells and thicker samples. These investigations require a high amount of simultaneously active fluorophores (i.e., high-density imaging) and are challenging due to the collapse of the single-molecule localization techniques and the increased background in the image. Therefore, recent efforts have shifted towards the development of new ways to process the data. This publication gives an introduction to wide-field super-resolution fluorescence microscopy, explaining the concepts of the technique, and then gives an overview of the recently developed methods to provide super-resolution images for high-density data of live cells and ways to overcome the issues related to the imaging of these samples.



(adapted from [23])



The figure was adapted from [33]




The figure is adapted from [36]




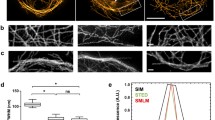
The figure is adapted from [53]

The figure was adapted from [60]

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Betzig E. Proposed method for molecular optical imaging. Opt Lett. 1995;20:237–9.
Betzig E, et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science. 2006;313:1642–5.
Hell S, Wichmann J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt Lett. 1994;19:780–2.
Klar T, Jakobs S, Dyba M, Egner A, Hell S. Fluorescence microscopy with diffraction resolution barrier broken by stimulated emission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:8206–10.
Moerner W, Kador L. Optical detection and spectroscopy of single molecules in a solid. Phys Rev Lett. 1989;62:2535–8.
Dickson R, Cubitt A, Tsien R, Moerner W. On/off blinking and switching behaviour of single molecules of green fluorescent protein. Nature. 1997;388:355–8.
Novotny L, Hecht B. Principles of nano-optics. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012.
Abbe E. Beiträge zur Theorie des Mikroskops und der mikroskopischen Wahrnehmung. Arch Für Mikrosk Anat. 1873;9:413–8.
Strutt J. On the theory of optical images, with special reference to the microscope. Philos Mag. 1896;42:167–95.
Huang B, Bates M, Zhuang X. Super resolution fluorescence microscopy. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:993–1016.
Shroff H, Galbraith C, Galbraith J, Betzig E. Live-cell photoactivated localization microscopy of nanoscale adhesion dynamics. Nat Methods. 2008;5:417–23.
Hell S. Toward fluorescence nanoscopy. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:1347–55.
Hell S. Far-field optical nanoscopy. Science. 2007;316:1153–8.
Ovesný M, Křížek P, Borkovec J, Svindrych Z, Hagen G. ThunderSTORM: a comprehensive ImageJ plug-in for PALM and STORM data analysis and super-resolution imaging. Bioinf Oxf Engl. 2014;30:2389–90.
Dertinger T, Colyer R, Iyer G, Weiss S, Enderlein J. Fast, background-free, 3D super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:22287–92.
Holden S, Uphoff S, Kapanidis A. DAOSTORM: an algorithm for high- density super-resolution microscopy. Nat Methods. 2011;8:279–80.
Ito S, et al. Restricted diffusion of guest molecules in polymer thin films on solid substrates as revealed by three-dimensional single-molecule tracking. Chem Commun Camb Engl. 2015;51:13756–9.
Enderlein J. Positional and temporal accuracy of single molecule tracking. Single Mol. 2000;1:225–30.
Kusumi A, Tsunoyama T, Hirosawa K, Kasai R, Fujiwara T. Tracking single molecules at work in living cells. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:524–32.
Tsujita K, et al. Coordination between the actin cytoskeleton and membrane deformation by a novel membrane tubulation domain of PCH proteins is involved in endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:269–79.
Li D, et al. Extended-resolution structured illumination imaging of endocytic and cytoskeletal dynamics. Science. 2015;349:aab3500.
Habuchi S, et al. Reversible single-molecule photoswitching in the GFP-like fluorescent protein Dronpa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:9511–6.
Dedecker P, Mo G, Dertinger T, Zhang J. Widely accessible method for superresolution fluorescence imaging of living systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:10909–14.
Rust M, Bates M, Zhuang X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat Methods. 2006;3:793–6.
Betzig E, et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science. 2006;313:1642–5.
Hess S, Girirajan T, Mason M. Ultra-high resolution imaging by fluorescence photoactivation localization microscopy. Biophys J. 2006;91:4258–72.
Huang B, Bates M, Zhuang X. Super resolution fluorescence microscopy. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:993–1016.
Lin E, Alessio A. What are the basic concepts of temporal, contrast, and spatial resolution in cardiac CT? J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2009;3:403–8.
Mondal P. Temporal resolution in fluorescence imaging. Front Mol Biosci. 2014;1:1–10.
Zhu L, Zhang W, Elnatan D, Huang B. Faster STORM using compressed sensing. Nat Methods. 2012;9:721–3.
Yamanaka M, Smith N, Fujita K. Introduction to super-resolution microscopy. Microsc Oxf Engl. 2014;63:177–92.
Min J, et al. FALCON: fast and unbiased reconstruction of high-density super-resolution microscopy data. Sci Rep. 2014;4:srep04577.
Hugelier S, et al. Sparse deconvolution of high-density super-resolution images. Sci Rep. 2016;6:srep21413.
Hugelier S, Eilers P, Devos O, Ruckebusch C. Improved superresolution microscopy imaging by sparse deconvolution with an interframe penalty. J Chemom. 2017;31:e2847.
Dertinger T, Colyer R, Iyer G, Weiss S, Enderlein J. Fast, background-free, 3D super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:22287–92.
Ruckebusch C, et al. Mapping pixel dissimilarity in wide-field super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Anal Chem. 2015;87:4675–82.
Cox S, et al. Bayesian localization microscopy reveals nanoscale podosome dynamics. Nat Methods. 2012;9:195–200.
Rosten E, Jones G, Cox S. ImageJ plug-in for Bayesian analysis of blinking and bleaching. Nat Methods. 2013;10:97–8.
Mukamel E, Babcock H, Zhuang X. Statistical deconvolution for superresolution fluorescence microscopy. Biophys J. 2012;102:2391–400.
Ghiglia D, Romero L, Mastin G. Systematic approach to two-dimensional blind deconvolution by zero-sheet separation. J Opt Soc Am Part Opt Image Sci. 1993;10:1024–36.
de Rooi J, Eilers P. Deconvolution of pulse trains with the L0 penalty. Anal Chim Acta. 2011;705:218–26.
Candes E, Wakin M. An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2008;25:21–30.
Candes E, Fernandez-Granda C. Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution. Commun Pure Appl Math. 2014;67:906–56.
Babcock H, Moffitt J, Cao Y, Zhuang X. Fast compressed sensing analysis for super-resolution imaging using L1-homotopy. Opt Express. 2013;21:28583–96.
de Rooi J, Ruckebusch C, Eilers P. Sparse deconvolution in one and two dimensions: applications in endocrinology and single-molecule fluorescence imaging. Anal Chem. 2014;86:6291–8.
Tikhonov A. Solution of incorrectly formulated problems and the regularization method. Sov Math. 1963;4:1035–8.
Dertinger T, Colyer R, Vogel R, Enderlein J, Weiss S. Achieving increased resolution and more pixels with superresolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI). Opt Express. 2010;18:18875–85.
Dertinger T, Heilemann M, Vogel R, Sauer M, Weiss S. Superresolution optical fluctuation imaging with organic dyes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010;49:9441–3.
Girsault A, et al. SOFI simulation tool: a software package for simulating and testing super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0161602.
Dertinger T, Xu J, Naini O, Vogel R, Weiss S. SOFI-based 3D superresolution sectioning with a widefield microscope. Opt Nanoscopy. 2012;1:2.
Sanchez F, Toft J, van den Bogaert B, Massart D. Orthogonal projection approach applied to peak purity assessment. Anal Chem. 1996;68:79–85.
Sage D, et al. Quantitative evaluation of software packages for single-molecule localization microscopy. Nat Methods. 2015;12:717–24.
Hoogendoorn E, et al. The fidelity of stochastic single-molecule super-resolution reconstructions critically depends upon robust background estimation. Sci Rep. 2014;4:srep03854.
de Rooi J, Devos O, Sliwa M, Ruckebusch C, Eilers P. Mixture models for two-dimensional baseline correction, applied to artifact elimination in time-resolved spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;771:7–13.
Currie I, Durban M, Eilers P. Generalized linear array models with applications to multidimensional smoothing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. 2006;68:259–80.
Wolter S, et al. RapidSTORM: accurate, fast open-source software for localization microscopy. Nat Methods. 2012;9:1040–1.
Berglund A. Nonexponential statistics of fluorescence photobleaching. J Chem Phys. 2004;121:2899–903.
Hirschfeld T. Quantum efficiency independence of the time integrated emission from a fluorescent molecule. Appl Opt. 1976;15:3135–9.
Wells K, Sandison D, Strickler J, Webb W. Quantitative fluorescence imaging with laser scanning confocal microscopy. In: Pawley J, editor. The handbook for biological confocal microscopy. Wisconsin: IMR Press; 1989. p. 27–39.
Peeters Y, et al. Correcting for photodestruction in super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging. Sci Rep. 2017;7:srep10470.
Vicente N, Diaz Zamboni J, Adur J, Paravani E, Casco V. Photobleaching correction in fluorescence microscopy images. J Phys: Conf Ser. 2007;90:012068.
Geissbuehler S, et al. Live-cell multiplane three-dimensional super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging. Nat Comm. 2014;5:5830.
Deschout H, et al. Complementarity of PALM and SOFI for super-resolution live-cell imaging of focal adhesions. Nat Comm. 2016;7:13693.
Barsic A, Grover G, Piestun R. Three-dimensional super-resolution and localization of dense clusters of single molecules. Sci Reports. 2014;4:srep5388.
Nehme E, Weiss L, Michaeli T, Shechtman Y. Deep-STORM: super-resolution single-molecule microscopy by deep learning. Optica. 2018;5:458–64.
Niehörster T, et al. Multi-target spectrally resolved fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Nat Methods. 2015;13:257–65.
Acknowledgements
C.R. and M.S acknowledge the financial support of the Agence National de la Recherche (ANR-14-CE08-0015-01 Ultrafast Nanoscopy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hugelier, S., Sliwa, M. & Ruckebusch, C. A Perspective on Data Processing in Super-resolution Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging. J. Anal. Test. 2, 193–209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-018-0076-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-018-0076-2