Abstract
Introduction
X-ray metrology, including the metrological calibration of X-ray detectors, optical elements and sources, is important for many frontier science, such as X-ray astronomy, EUV-lithography, plasma physics. Among many types of X-ray sources, synchrotron-radiation is considered perfect for X-ray metrology, mainly due to that arbitrarily X-rays specifications can be tailored to meet the demands of metrological calibration of X-ray detectors and optical elements. As a consequence, many metrology beamlines around the world are built, upgrading or to be constructed, including the metrology sector to be constructed at High Energy Photon Source (HEPS).
Method
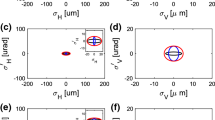
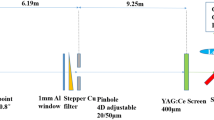
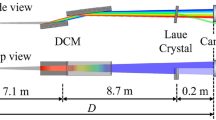
One reasonable way to access good metrological data is using a stable X-ray beam, which means that beam position as well as flux should be as constant as possible and the beamline configuration should be simple and robust to reduce the uncertainty from beamline itself. In addition, the spectral purity of monochromatic X-rays is another crucial factor for X-ray metrology, which means stray X-rays and harmonic X-rays must be as low as possible. Many measures are taken to satisfy these requirements.
Conclusion
An optical design of the metrology sector optimized for synchrotron-radiation-based- metrology is described here. The metrology sector, ranging from 50 eV to 20 keV, will be set up to meet the growing needs of X-ray metrology in China. All beamlines’ configurations are simple and easy to use, with an acceptable ratio of high-order harmonics and stray X-rays, which can be under 1% in the entire energy range.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Idir, P. Mercere, T. Moreno, A. Delmotte, Synchrotron. Radiat. News. 19, 18 (2006)
G. Brandt, J. Eden, R. Fliegauf, A. Gottwald, G. Wüstefeld, A. Hoehl, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 258, 445 (2007)
B. Wende, Metrologia 32, 419 (1996)
E. Ziegler, J. Hoszowska, T. Bigault, L. Peverini, J.Y. Massonnat, R. Hustache, AIP Conf. Proc. 705, 436 (2004)
Y. Kitajima, Y. Yonamoto, K. Amemiya, H. Tsukabayashi, T. Ohta, K. Ito, J. Electron. Spectrosc. 101–103, 927 (1999)
J.H. Underwood, E.M. Gullikson, M. Koike, P.J. Batson, Proc Spie 3113, 214 (1997)
K. Kaznatcheev, O. Chubar, J.W. Keister, M. Idir, J. Phys. Conf. 425, 162009 (2013)
K.J.S. Sawhney, I.P. Dolbnya, M.K. Tiwari, L. Alianelli, S.M. Scott, G.M. Preece et al., AIP Conf. Proc. 1234, 387 (2010)
V. S. K. Gluskin, O.A. Makarov, V.I. Ogurtsov, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 246, 397(1986)
R. Reininger, J.C. Woicik, S.L. Hulbert, D.A. Fischer, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 649, 49 (2011)
G. Ulm, G. Brandt, R. Fliegauf, A. Hoehl, R. Klein, R. Müller et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 582, 26 (2007)
B. Beckhoff, A. Gottwald, R. Klein, M. Krumrey, Physica Status Solidi 246, 1415 (2009)
G. Ulm, B. Beckhoff, R. Klein, M. Krumrey, H. Rabus, R. Thornagel, SPIE's International Symposium on Optical Science, Engineering, and Instrumentation, 3444, 20 (1998)
C. Mingqi, Z. Yidong, Z. Lei, Z. Jia, Y. Jiamin, Chin. J. Laser. 37, 2271 (2010)
Y. Jiao, G. Xu, X.-H. Cui, Z. Duan, Y.-Y. Guo, P. He et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 25, 1611 (2018)
S. Kexu, Acta. Opt. Sinica. 22, 379 (2002)
C. Xue, L. Xue, Y. Wu, Y. Wang, S. Yang, R. Tai, J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 1192 (2019)
K. Tang, L. Zheng, Y.D. Zhao, S.H. Liu, Y.H. Dong, J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 1835 (2019)
N. Canestrari, D. Karkoulis, M.S.D. Río, Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 8141, 371 (2011)
A. Sokolov, M.G. Sertsu, A. Gaupp, M. Lüttecke, F. Schäfers, J. Synchrotron Rad. 25, 100 (2018)
L. Zheng, Y. Zhao, M. Cui, J. Zhu, Y. Han, K. Zhou et al., Nucl. Tech. 30, 3 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by High Energy Photon Source (HEPS), a major national science and technology infrastructure in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Zhao, Y., Zheng, L. et al. Optical design and optimization study of metrology sector at high energy photon source. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 5, 174–180 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-021-00241-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-021-00241-0