Abstract
Background
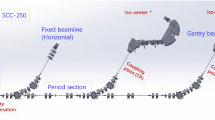
Heavy ion medical machine (HIMM) is built by the Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, with a high-energy beam transport line with a height of 18 m, and its complex space mounting structure increases the difficulty of installation and alignment.
Purpose
The aim of this paper is to provide methods to install all accelerator components efficiently and to ensure that the alignment accuracies of all installed components are within the designed values.
Methods
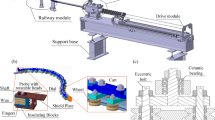
We accomplished the fiducialization and pre-alignment of complex modules by combining the laser tracker and the alignment telescope. By analyzing various elements that affect the accuracy of alignment, a method of alignment for high-energy beam transport line was proposed based on high-precision three-dimensional control network.
Results
All components have been installed and aligned in a short time, alignment position accuracy of magnets is less than 0.1 mm, and the treatment components alignment accuracy is no more than 0.4 mm.
Conclusions
On the basis of error analysis, all alignment results are better than the required precisions, and all of these guaranteed the successful operation of HIMM.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.J. Chen, L.Z. Ma, G.Z. Cai et al., Alignment and installation of high energy beam-line for Wuwei heavy ion medical machine. High Power Laser Part. Beams 28(8), 085101-058105 (2015). (in Chinese)
W.J. Chen, K.D. Man, S.M. Wang et al., Survey and alignment technology of Lanzhou heavy ion research facility. Nucl. Tech. 33(1), 65–68 (2010). (in Chinese)
C.H. Yu. Ph.D. thesis, Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics. CAS (2008)
G.Z. Cai, W.J. Chen, K.D. Man et al., Using the target accelerator magnet alignment installation positioning solution. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 25(1), 82–87 (2013). (in Chinese)
G.Z. Cai, W.J. Chen, K.D. Man et al., Application of laser tracker and SA software in large particle accelerators in collimating measurement. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 38(4), 162–164 (2013). (in Chinese)
Y.X. Kong, Control and measurement (Wuhan University Press, Wuhan, 1996), pp. 65–66
D.Y. Wang, X.L. Zhang, Q. Ma et al., Procrustes method in coordinate transformation on multi-station of large-scale measurement. Opt. Precis. Eng. 22(4), 949–955 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3788/OPE.20142204.0949. (in Chinese)
C.H. Yu, L.X. Yin, H.W. Du et al., Alignment and survey design of Shanghai light source. High Power Laser Part. Beams. 18(7), 1167–1172 (2008). (in Chinese)
W.J. Chen, L.Z. Ma, G.Z. Cai et al., Survey and Alignment of synchrotron ring for Wuwei Heavy Ion Medical machine. Nucl. Phys. Rev. 33(3), 297–301 (2015). (in Chinese)
Y.T. Fei, Error theory and data processing (Mechanical Industry Press, Wuhan, 2010), p. 102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Yang, Y., Cai, G. et al. Alignment technology of heavy ion medical machine. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 3, 15 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-018-0092-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-018-0092-9