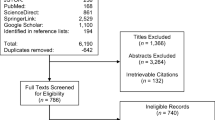
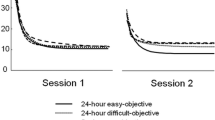
Abstract
Video game training was found to enhance executive functioning in different age groups. In terms of cognitive enhancement, rare studies have investigated the potential of casual games, an easily accessible and widely used class of video games. In this study, we investigated the efficacy of casual game playing as an executive functions training in younger adults. During a 12-session program, training group participants (n = 37) played the “MultiTask” game featuring simultaneous playing of two and more games assumed to tap executive functions. Active controls (n = 36) played a simple casual game (“Smooth Snake”). Each session lasted approximately 15–20 min. Training sessions were individual and conducted at participants’ homes. Posttest and follow-up (6 months) gains were assessed through various executive function measures (shifting, updating, inhibition, complex executive functions task, and working memory span). Using linear mixed-effects analysis no significant group × time interactions were found. Both groups decreased in the number of perseverative errors in complex executive function task immediately after the intervention and 6 months after the intervention. The study does not confirm beneficiary effects of casual video games on cognition of young adults. Also, it calls for caution when inferring on training gains in young adulthoods based on student samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Au, J., Sheehan, E., Tsai, N., Duncan, G. J., Buschkuehl, M., & Jaeggi, S. M. (2015). Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory: A meta-analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22, 366–377. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0699-x.
Baniqued, P. L., Lee, H., Voss, M. W., Basak, C., Cosman, J. D., Desouza, S., et al. (2013). Selling points: what cognitive abilities are tapped by casual video games? Acta Psychologica, 142, 74–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2012.11.009.
Baniqued, P. L., Kranz, M. B., Voss, M. V., Lee, H., Cosman, J. D., Severson, J., & Kramer, A. F. (2014). Cognitive training with casual video games: points to consider. Frontiers in Psychology, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.01010.
Basak, C., Boot, W. R., Voss, M. W., & Kramer, A. F. (2008). Can training in a real-time strategy video game attenuate cognitive decline in older adults? Psychology and Aging, 23, 765–777. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013494.
Bediou, B., Adamas, D. M., Mayer, R. E., Tipton, E., Green, S. C., & Bavelier, D. (2018). Meta-analysis of action video game impact on perceptual, attentional, and cognitive skills. Psychological Bulletin, 2018, 77–110. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000130.
Berkman, E. T., Kahn, L. E., & Merchant, J. S. (2014). Training-induced changes in inhibitory control network activity. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 34, 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3564-13.2014.
Blacker, K. J., Curby, K. M., Klobusicky, E., & Chein, J. M. (2014). Effects of action video game training on visual working memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 40, 1992–2004. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0037556.
Bull, R., & Scerif, G. (2001). Executive functioning as a predictorof Children’s mathematics ability: inhibition, switching, and working memory. Developmental Neuropsychology, 19, 273–293. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15326942DN1903_3.
Cattell, R. B., & Cattell, A. K. S. (2000). Cattell’s Culture Fair Intelligence Test (CTI) [Measurement instrument]. Jastrebarsko: Naklada Slap.
Chiu, H. L., Chu, H., Tsai, J. C., Liu, D., Chen, Y. R., Yang, H. L., & Chou, K. R. (2017). The effect of cognitive-based training for the healthy older people: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One, 12, e0176742. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176742.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Corsi, P. M. (1973). Human memory and the medial temporal region of the brain. Dissertation Abstracts International, 34(2-B), 891.
Dahlin, E., Nyberg, L., Bäckman, L., & Neely, A. S. (2008). Plasticity of executive functioning in young and older adults: Immediate training gains, transfer, and long-term maintenance. Psychology and Aging, 23, 720–730. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014296.
de Assis Faria, C., Dias Alves, H. V., & Charchat-Finchman, H. (2015). The most frequently used tests for assessing executive functions in aging. Demantia & Neuropsychologia, 9, 149–155. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-57642015DN92000009.
Dorbath, L., Hasselhorn, M., & Titz, C. (2011). Aging and executive functioning: a training study on focus-switching. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00257.
Edwards, J. D., Fausto, B. A., Tetlow, A., Corona, R. T., & Valdes, E. G. (2018). Systematic review and meta-analyses of useful field of view cognitive training. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 84,72–91
Enge, S., Behnke, A., Fleischhauer, M., Küttler, L., Kliegel, M., & Strobel, A. (2014). No evidence for true training and transfer effects after inhibitory control training in young healthy adults. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 40, 987–1001. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036165.
Fisk, J. E., & Sharp, C. A. (2004). Age-related impairment in executive functioning: updating inhibition, shifting, and access. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 26, 874–890. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803390490510680.
Gauffroy, C., & Barrouillet, P. (2014). Conditional reasoning in context: a developmental dual processes account. Thinking & Reasoning, 20, 372–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/13546783.2013.853695.
Glisky, E. L. (2007). Changes in cognitive function in human aging. In D. R. Riddle (Ed.), Frontiers in neuroscience. Brain aging: models, methods, and mechanisms (pp. 3–20). Boca Raton: CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420005523.sec1.
Green, C. S., & Seitz, A. R. (2015). The impacts of video games on cognition (and how the government can guide the industry). Policy Insights From the Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 2, 101–110. https://doi.org/10.1177/2372732215601121.
Grönholm-Nyman, P., Soveri, A., Rinne, J. O., Ek, E., Nyholm, A., Stigsdotter Neely, A., & Laine, M. (2017). Limited effects of set shifting training in healthy older adults. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00069.
Heaton, R., Chelune, G., Talley, J. L., Kay, G., & Curtiss, G. (1993). Wisconsin card sort test manual: revised and expanded. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Henrich, J., Heine, S. J., & Norenzayan, A. (2010). The weirdest people in the world? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 33, 61–83. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X0999152X.
Holmes Finch, W., Bolin, J. E., & Kelley, K. (2014). Multilevel modeling using R. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
IBM Corp Released. (2018). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows,Version 26.0. IBM Corp: Armonk, NY.
IcyLime. (2009). MultiTask [computer video game]. Retrieved from http://multitaskgames.com/multitask-game.html
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Jonides, J., & Perrig, W. J. (2008). Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105, 6829–6833. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0801268105.
Karbach, J., & Kray, J. (2009). How useful is executive control training? Age differences in near and far transfer of task-switching training. Developmental Science, 12, 978–990. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2009.00846.x.
Karbach, J., & Verhaeghen, P. (2014). Making working memory work: a meta-analysis of executive-control and working memory training in older adults. Psychological Science, 25, 2027–2037. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797614548725.
Lampit, A., Hallock, H., & Valenzuela, M. (2014). Computerized cognitive training in cognitively healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of effect modifiers. PLoS Medicine, 11, e1001756. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001756.
Lövdén, M., Brehmer, Y., Li, S. C., & Lindenberger, U. (2012). Training-induced compensation versus magnification of individual differences in memory performance. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 141. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00141.
Lustig, C., Shah, P., Seidler, R., & Reuter-Lorenz, P. A. (2009). Aging, training, and the brain: a review and future directions. Neuropsychology Review, 19, 504–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-009-9119-9.
Maillot, P., Perrot, A., & Hartley, A. (2012). Effects of interactive physical-activity video-game training on physical and cognitive function in older adults. Psychology and Aging, 27, 589–600. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026268.
McDowd, J. M., & Craik, F. I. M. (1988). Effects of aging and task difficulty on divided attention performance. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 14, 267–280. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.14.2.267.
Miyake, A., & Friedman, N. P. (2012). The nature and organization of individual differences in executive functions: four general conclusions. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21, 8–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721411429458.
Miyake, A., & Shah, P. (Eds.). (1999). Models of working memory: mechanisms of active maintenance and executive control. Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139174909.
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Emerson, M. J., Witzki, A. H., Howerter, A., & Wager, T. D. (2000). The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: a latent variable analysis. Cognitive Psychology, 41, 49–100. https://doi.org/10.1006/cogp.1999.073.
Mueller, S. T. (2011a). PEBL’s Berg Card Sorting Test (PBCST). Computer software retrieved from http://pebl.sf.net/battery.html.
Mueller, S. T. (2011b). PEBL’s Corsi block-tapping task. Computer software retrieved from http://pebl.sf.net/battery.html.
Mueller, S. T. (2011c). PEBL’s Plus-minus task. Computer software retrieved from http://pebl.sf.net/battery.html.
Mueller, S. T., & Esposito, A. G. (2014). Computerized testing software for assessing interference suppression in children and adults: the bivalent shape task (BST). Journal of Open Research Software, 2, e3. https://doi.org/10.5334/jors.ak.
Nouchi, R., Taki, Y., Takeuchi, H., Hashizume, H., Akitsuki, Y., Shigemune, Y., et al. (2012). Brain training game improves executive functions and processing speed in the elderly: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One, 7, e29676. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029676.
Oei, A. C., & Patterson, M. D. (2014). Playing a puzzle video game with changing requirements improves executive functions. Computers in Human Behavior, 37, 216–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.04.046.
Powers, K. L., & Brooks, P. J. (2014). Evaluating the specificity of effects of video game training. In F. Blumberg (Ed.), Learning by playing: frontiers of video gaming in education (pp. 302–330). Oxford: Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:osobl/9780199896646.003.0021.
Powers, K. L., Brooks, P. J., Aldrich, N. J., Palladino, M. A., & Alfieri, L. (2013). Effects of video-game play on information processing: a metaanalytic investigation. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 20, 1055–1079. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-013-0418-z.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2017). Does far transfer exist? Negative evidence from chess, music, and working memory training. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 26, 515–520. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721417712760.
Schmiedek, F., Lövdén, M., & Lindenberger, U. (2010). Hundred days of cognitive training enhance broad cognitive abilities in adulthood: findings from the COGITO study. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2, 27. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2010.00027.
Simons, D. J., Boot, W. R., Charness, N., Gathercole, S. E., Chabris, C. F., Hambrick, D. Z., & Stine-Morrow, E. A. L. (2016). Do “brain-training” programs work? Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 17, 103–186. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100616661983.
Smith, E. E., & Jonides, J. (1997). Working memory: a view from neuroimaging. Cognitive Psychology, 33, 5–42. https://doi.org/10.1006/cogp.1997.0658.
Soveri, A., Antfolk, J., Karlsson, L., Salo, B., & Laine, M. (2017). Working memory training revisited: a multi-level meta-analysis of n-back training studies. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 24, 1077–1096. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-016-1217-0.
Stafford, T., & Dewar, M. (2014). Tracing the trajectory of skill learning with a very large sample of online game players. Psychological Science, 25, 511–518. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613511466.
Strobach, T., Salminen, T., Karbach, J., & Schubert, T. (2014). Practice-related optimization and transfer of executive functions: a general review and a specific realization of their mechanisms in dual tasks. Psychological Research, 78, 836–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-014-0563-7.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2013). Using multivariate statistics. Boston: Pearson.
Tap2Play.io. (2014). Smooth snake [computer video game]. Retrieved from http://snake.tap2play.io/.
Thorell, L. B., Lindqvist, S., Bergman Nutley, S., Bohlin, G., & Klingberg, T. (2009). Training and transfer effects of executive functions in preschool children. Developmental Science, 12, 106–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2008.00745.x.
Thorndike, E. L., & Woodworth, R. S. (1901). The influence of improvement in one mental function upon the efficiency of other functions (I). Psychological Review, 8, 247–261. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0074898.
Verhaeghen, P. (2011). Aging and executive control: reports of a demise greatly exaggerated. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 20, 174–180. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721411408772.
Wang, P., Liu, H.-H., Zhu, X.-T., Meng, T., Li, H.-J., & Zuo, X.-N. (2016). Action video game training for healthy adults: a meta-analytic study. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 907. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00907.
Zelinski, E. M., & Reyes, R. (2009). Cognitive benefits of computer games for older adults. Gerontechnology: International Journal on the Fundamental Aspects of Technology to Serve the Ageing Society, 8, 220–235. https://doi.org/10.4017/gt.2009.08.04.004.00.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Both authors have given the final approval to the submitted manuscript.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martincevic, M., Vranic, A. Casual Game or Cognitive Gain: Multitask Casual Game as a Training for Young Adults. J Cogn Enhanc 4, 434–445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-020-00173-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-020-00173-5