Abstract
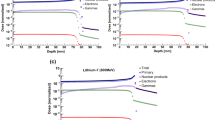
The applications of carbon ion beam in tumor therapy have attracted more attention in recent years. Monte Carlo simulation is an important approach to obtain accurate radiotherapy parameters. In this work, a 400 MeV/u carbon ion beam incident on water phantom was simulated with Gate/Geant4 tools. In methods, the authors set up a carbon ion beam source according to the experiment parameters of Haettner, defined the geometries and materials, set up the physics processes, and designed the means of information collection. In results, the authors obtained the longitudinal dose distribution, the lateral dose distribution, and the relative uncertainty of dose. The dose contributions of all kinds of fragments were calculated detailedly and compared with the Francis results. This work is helpful for people’s understanding of the dose distributions produced by carbon ion beam and fragments in water. The simulation method is also significative for radiotherapy treatment planning of carbon ion beam, and it is easy to extend. For obtaining a special result, we may change the particle energy, particle type, target material, target geometry, physics process, detector, etc.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.T. Bache, T. Juang, M.D. Belley, Investigating the accuracy of microstereotactic-body-radiotherapy utilizing anatomically accurate 3D printed rodent-morphic dosimeters. Med. Phys. 42, 846–855 (2015). doi:10.1118/1.4905489
J. Wang, X. Pei, R.F. Cao et al., A multiphase direct aperture optimization for inverse planning in radiotherapy. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 26, 010502 (2015). doi:10.13538/j.1001-8042/nst.26.010502
M.C. Frese, V.K. Yu, R.D. Stewart et al., A mechanism-based approach to predict the relative biological effectiveness of protons and carbon ions in radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 83, 442–450 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.06.1983
S. Agostinelli, J. Allison, K. Amako et al., GEANT4—a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 506, 250–303 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(03)01368-8
N. Zahra, T. Frisson, L. Grevillot et al., Influence of Geant4 parameters on dose distribution and computation time for carbon ion therapy simulation. Phys. Med. 26, 202–208 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2009.12.001
Q.I.N. Xue, Z.H.O.U. Rong, H.A.N. Ji-Feng et al., GEANT4 simulation of the characteristic gamma-ray spectrum of TNT under soil induced by DT neutrons. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 26, 010501 (2015). doi:10.13538/j.1001-8042/nst.26.010501
T.T. Böhlen, F. Cerutti, M. Dosanjh et al., Benchmarking nuclear models of FLUKA and GEANT4 for carbon ion therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 55, 5833–5847 (2010). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/55/19/014
I. Pshenichnov, I. Mishustin, W. Greiner, Distributions of positron-emitting nuclei in proton and carbon-ion therapy studied with GEANT4. Phys. Med. Biol. 51, 6099–6112 (2006). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/51/23/011
M.D. Napoli, F. Romano, D. D’Urso et al., Nuclear reaction measurements on tissue-equivalent materials and GEANT4 Monte Carlo simulations for hadrontherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 59, 7643–7652 (2014). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/59/24/7643
I. Pshenichnov, I. Mishustin, W. Greiner, Comparative study of depth-dose distributions for beams of light and heavy nuclei in tissue-like media. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 266, 1094–1098 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2008.02.025
Y.-P. Liu, X.-B. Tang, Z.-H. Xu et al., Energy deposition, parameter optimization, and performance analysis of space radiation voltaic batteries. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 25, S010402 (2014). doi:10.13538/j.1001-8042/nst.25.S010402
G. Santin, D. Strul, D. Lazaro et al., GATE: a Geant4-based simulation platform for PET, SPECT integrating movement and time management. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 50, 1516–1521 (2003). doi:10.1109/TNS.2003.817974
D. Sarrut, M. Bardiès, N. Boussion et al., A review of the use and potential of the GATE Monte Carlo code for radiation therapy and dosimetry applications. Med. Phys. 41, 1–14 (2014). doi:10.1118/1.4871617
S. Jan, D. Benoit, E. Becheva et al., GATE V6: a major enhancement of the GATE simulation platform enabling modelling of CT and radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 56, 881–901 (2011). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/56/4/001
C.O. Thiam, V. Breton, D. Donnarieix et al., Validation of a dose deposited by low-energy photons using GATE/GEANT4. Phys. Med. Biol. 53, 3039–3056 (2008). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/53/11/019
L. Grevillot, T. Frisson, D. Maneval et al., Simulation of a 6 MV Elekta Precise Linac photon beam using GATE/GEANT4. Phys. Med. Biol. 56, 903–918 (2011). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/56/4/002
L. Grevillot, D. Bertrand, F. Dessy et al., GATE as a GEANT4-based Monte Carlo platform for the evaluation of proton pencil beam scanning treatment plans. Phys. Med. Biol. 57, 4223–4244 (2012). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/57/13/4223
K. Kurosu, M. Takashina, M. Koizumi et al., Optimization of GATE and PHITS Monte Carlo code parameters for uniform scanning proton beam based on simulation with FLUKA general-purpose code. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 336, 45–54 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2014.06.009
L. Grevillot, T. Frisson, N. Zahra et al., Optimization of GEANT4 settings for Proton Pencil Beam Scanning simulations using GATE. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 268, 3295–3305 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2010.07.011
E. Haettner, H. Iwase, M. Krämer et al., Experimental study of nuclear fragmentation of 200 and 400 MeV/u 12C ions in water for applications in particle therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 58, 8265–8279 (2013). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/58/23/8265
N. Matsufuji, M. Komori, H. Sasaki et al., Spatial fragment distribution from a therapeutic pencil-like carbon beam in water. Phys. Med. Biol. 50, 3393–3403 (2005). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/50/14/014
Y. Kusano, T. Kanai, Y. Kase et al., Dose contributions from large-angle scattered particles in therapeutic carbon beams. Med. Phys. 34, 193–198 (2007). doi:10.1118/1.2402328
B. Braunn, M. Labalme, G. Ban et al., Nuclear reaction measurements of 95 MeV/u 12C interactions on PMMA for hadrontherapy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 269, 2676–2684 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2011.08.010
Z. Francis, E. Seif, S. Incerti et al., Carbon ion fragmentation effects on the nanometric level behind the Bragg peak depth. Phys. Med. Biol. 59, 7691–7702 (2014). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/59/24/7691
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. H1809).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, HF., Zhang, B. & Zhao, SJ. Gate/Geant4-based Monte Carlo simulation for calculation of dose distribution of 400 MeV/u carbon ion beam and fragments in water. NUCL SCI TECH 27, 83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0097-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0097-3