Abstract
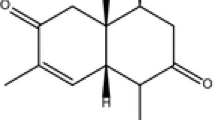
Entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) are the main microbiological control agents of insect pests. One of the key factors in the pathogenicity of EPF is the production of insecticidal bioactive compounds. Therefore, the metabolites of two isolates of EPF, Cladosporium cladosporioides (Fresen.) G.A. de Vries (AF98) and Acremonium zeylanicum (Petch) W. Gams & H.C. Evans (IR87), were analyzed. The presence of insecticidal toxic cyclic peptides such as Bassianolide in C. cladosporioides AF98 metabolites was detected by HPLC. Moreover, GC–MS analysis showed some toxic compounds, including 3,4-Dihydro-7,12-Dihydroxy-7,12-Imethylbenz[A]Anthracene, 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-1,1,4,4,6-Pentamethyl-5,7-Dinitronaphthalene, and 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-1,1,4,4,6-Pentamethyl-5,7-Dinitronaphthalene in the metabolites purified from A. zeylanicum IR87. Also, a few hazardous compounds, including 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-trimethylsiloxytoluene, bis(2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate, di-n-octyl phthalate, 1-pentadecene, and 1-eicosene were found which might be toxic against insects. This is the first report on the detection of toxic peptides from C. cladosporioides. These results showed that multiple compounds are likely contributed to the insecticidal effects of the EPF.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdelaziz O, Senoussi MM, Oufroukh A, Birgücü AK, Karaca İ, Kouadri F, Bensegueni A (2018) Pathogenicity of three entomopathogenic fungi, to the aphid species, Metopolophium dirhodum (Walker) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), and their Alkaline protease activities. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 28(1):1–5
Arnaud L, Lognay G, Verscheure M, Leenaers L, Gaspar C, Haubruge E (2002) Is dimethyldecanal a common aggregation pheromone of Tribolium flour beetles? J Chem Ecol 28(3):523–532
Boguś MI, Wrońska AK, Kaczmarek A, Boguś-Sobocińska M (2021) In vitro screening of 65 mycotoxins for insecticidal potential. PLoS ONE 16(3):e0248772
Bräse S, Encinas A, Keck J, Nising CF (2009) Chemistry and biology of mycotoxins and related fungal metabolites. Chem Rev 109(9):3903–3990. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr050001f
Butt TM, Ibrahim L, Ball BV, Clark SJ (1994) Pathogenicity of the entomogenous fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana against crucifer pests and the honey bee. Biocontrol Sci Technol 4:207–214
de Maciel MHC, do Amaral ACT, da Silva TD, Bezerra JD, de Souza-Motta CM, da Costa AF, Tiago PV, de Oliveira NT (2021) Evaluation of mycotoxin production and phytopathogenicity of the entomopathogenic fungi Fusarium caatingaense and F. pernambucanum from Brazil. Curr Microbiol 78(4):1218–1226
Đukić N, Andrić G, Glinwood R, Ninkovic V, Andjelković B, Radonjić A (2021) The effect of 1-pentadecene on Tribolium castaneum behaviour: repellent or attractant? Pest Manag Sci 77(9):4034–4039
El-Sawy M, Mostafa EH, Ismail NAER (2019) Secondary metabolites of the entomopathogenic fungus, Cladosporium cladosporioides and its relation to toxicity of cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Glov.). Int J 5(1):115–120
Fraga BM (2013) Natural sesquiterpenoids. Nat Prod Rep 30(9):1226–1264
Hu Q, Dong T (2015) Non-ribosomal peptides from entomogenous fungi. In: Sree KS, Varma A (eds) Biocontrol of Lepidopteran pests. Springer, Germany
Hu Q, Li F, Zhang Y (2016) Risks of mycotoxins from mycoinsecticides to humans. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3194321
Ibrahim HY (2017) Biodiversity of Entomopathogenic fungi naturally infecting cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae L. J Plant Prot Pathol 8(12):631–634
Isaka M, Kittakoop P, Kirtikara K, Hywel-Jones NL, Thebtaranonth Y (2005) Bioactive substances from insect pathogenic fungi. Acc Chem Res 38:813–823
Jaquet C, Stohler HR, Chollet J, Peters W (1994) Antimalarial activity of the bicyclic peroxide Ro 42–1611 (arteflene) in experimental models. Trop Med Parasitol 45(3):266–271
Kanaoka M, Isogai A, Uakoshi SM, Ichinoe M, Suzuki A, Tamura S (1978) Bassianolide, a new insecticidal cyclodepsipeptide from Beauveria bassiana and Verticillium lecanii. Agric Biol Chem 42:629–635
Kishore Varma P, Chandra Sekhar V, Bhavani B, Upendhar S (2019) Cladosporium cladosporioides: A new report of parasitism on sugarcane woolly aphid, Ceratovacuna lanigera Zehntner. J Entomol Zool Stud 7(6):1122–1126
Kramer R, Abraham WR (2012) Volatile sesquiterpenes from fungi: what are they good for? Phytochem Rev 11(1):15–37
Liu W, Xie Y, Xue J, Gao Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Tan J (2009) Histopathological changes of Ceroplastes japonicus infected by Lecanicillium lecanii. J Invertebr Pathol 101(2):96–105
Lovett B, Leger RJ (2017) The insect pathogens. Microbiol Spectr 5(2):5
Molnar I, Gibson DM, Krasnoff SB (2010) Secondary metabolites from entomopathogenic Hypocrealean fungi. Nat Prod Rep 27:1241–1275
Mousavi K, Rajabpour A, Ghodoum Parizipour MH, Yarahmadi F (2022) Biological and molecular characterization of Cladosporium cladosporioides (Fresen.) G.A. de Vries and Acremonium zeylanicum (Petch) W. Gams & H.C. Evans as biocontrol agents of Aphis fabae Scop in a tri-trophic system. Entomol Exp Appl 170(10):877–886
Qasim M, Islam SU, Islam W, Noman A, Khan KA, Hafeez M, Hussain D, Dash CK, Bamisile BS, Akutse KS, Rizwan M, Nisar MS, Jan S, Wang L (2020) Characterization of mycotoxins from entomopathogenic fungi (Cordyceps fumosorosea) and their toxic effects to the development of asian citrus psyllid reared on healthy and diseased citrus plants. Toxicon 188:39–47
Ravindran K, Sivaramakrishnan S, Hussain M, Dash CK, Bamisile BS, Qasim M, Liande W (2018) Investigation and molecular docking studies of Bassianolide from Lecanicillium lecanii against Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 206:65–72
Schoepe KB, Friesel H, Schurdak ME, Randerath K, Hecker E (1986) Comparative DNA binding of 7, 12-dimethylbenz [a] anthracene and some of its metabolites in mouse epidermis in vivo as revealed by the 32 P-postlabeling technique. Carcinogenesis 7(4):535–540
Shah PA, Pell JK (2003) Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61(5–6):413–423
Sinha KK, Choudhary AK, Kumari P (2016) Entomopathogenic fungi. In: Omkar A (ed) Ecofriendly pest management for food security. Academic Press, pp 475–505
Vey A, Hoagland RE, Butt TM (2001) Toxic metabolites of fungal biocontrol agents. In: Butt TM, Jackson CW, Magan N (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents: progress, problems and potential. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp 311–346
Wang X, Gong X, Li P, Lai D, Zhou L (2018) Structural diversity and biological activities of cyclic Depsipeptides from fungi. Molecules 23:169
Zhang L, Fasoyin OE, Molnár I, Xu Y (2020) Secondary metabolites from hypocrealean entomopathogenic fungi: novel bioactive compounds. Nat Prod Rep 37(9):1181–1206
Zhou WS, Xu XX (1994) Total synthesis of the antimalarial sesquiterpene peroxide qinghaosu and yingzhaosu A. Acc Chem Res 27(7):211–216
Zimmermann G (2007) Review on safety of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii. Biocontrol Sci Technol 17:553–596
Acknowledgements
We thank staffs of Citrus and Subtropical Fruits Research Center of Iran for their technical supports.
Funding
The research was financially supported by Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources University of Khuzestan (Grant No. 9428412).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR, MHGP and FY designed the experiments. KM performed the experiments. AR wrote the manuscript. The manuscript studied and certificated by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi, K., Rajabpour, A., Parizipour, M.H.G. et al. Insecticidal bioactive compounds derived from Cladosporium cladosporioides (Fresen.) G.A. de Vries and Acremonium zeylanicum (Petch) W. Gams & H.C. Evans. J Plant Dis Prot 130, 543–549 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-022-00701-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-022-00701-9