Abstract
In comparison with other construction sectors, infrastructure projects are recognized for their relatively longer operation periods, important societal, economic benefits, and extensive consumption of natural resources. The rapid global economic development in the infrastructure industry and rising levels of environmental concerns lead to an increased need for sustainable infrastructure. Despite the fast-growing body of knowledge about sustainable infrastructure and its important role in accomplishing the Sustainable Development Goals which were set forth by the United Nations in 2015, there is a lack of quantitative and comprehensive review studies of sustainable infrastructure. Most of the conducted studies tend to address sustainability issues in infrastructure projects from singular aspects such as society-based design and Public Private Partnerships, among others. Hence, the current research attempts to address this gap by analyzing 1393 peer-reviewed journal papers between 2012 and 2023 using bibliometric analysis through co-authorship, co-occurrence, cluster, theme, trend topics, and citation analyses. The results demonstrate the main scientific contributors, prominent journals, research patterns, and directions for future research about sustainable infrastructure in the field of civil engineering and building construction. Such findings can be thus utilized by interested academic researchers and policymakers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Sustainability concerns have been repeatedly addressed in different contexts and using a vast range of methodologies. For instance, Khan et al. [26] discussed the barriers facing the adoption of green finance systems. The current study is concerned with the construction sector. The sustainable development and operation of construction projects should enable fulfillment of the needs of both present and future generations with respect to the three pillars of sustainability: society, economy, and environment. In this regard, Al-Jawari et al. [4] analyzed the resilience of cities on the social, economic, and environmental levels. Moreover, Yigitcanlar et al. [48] studied the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in urban planning and decision-making to facilitate achieving sustainability benefits.
Adopting a sustainability-based approach in the construction and management of infrastructure projects is essential. On the one hand, these projects present a wide range of societal and economic benefits including accessibility to employment, better connectivity, and access to necessary utilities, development for post-COVID economic recovery [24]. On the other hand, the construction of infrastructure projects involves huge monetary commitments, long durations, major exploitation of natural resources, and numerous negative environmental impacts such as but not limited to traffic and noise pollution which distinguish them from other construction projects [20, 23, 29], and [5]. Consequently, the concept of “sustainable infrastructure” is crucial to maximize benefits to the society, economy, and environment and simultaneously minimize the harmful impact of these projects [10].
The different aspects of sustainable infrastructure have attracted the attention of many researchers over the last 10 years. For instance, Bryce et al. [13] established a decision-making tool to optimize the trade-off between multiple criteria such as cost, pavement condition, and energy consumption in sustainable pavement management by highway agencies. The proposed method was applied to data from Virginia Department of Transportation and was found to be effective at evaluating alternative solutions from the perspective of various stakeholders. Thus, decision-makers can obtain a more complete assessment of the potential implications of each solution for all involved stakeholders. More recently, Rahat et al. [43] presented a front-end planning framework for sustainable infrastructure construction projects that ensures the balance between achieving sustainability goals as well as project objectives. The proposed framework was validated by surveying over 100 stakeholders, and it was concluded that it did enhance the decision-making process in sustainable infrastructure projects and consequently accomplish better outcomes. Additionally, Azzam et al. [9] presented a building information modeling (BIM)-based approach for sustainability assessment of power plant projects. The various criteria were weighted by analytical hierarchy process (AHP), whereas the BIM model provided decision-makers with an accurate and instantaneous assessment tool. The proposed method was validated on a 100 MW power plant, and it successfully saved time and minimized errors owing to its dynamic BIM-based approach. Further, Kambu et al. [25] introduced a model that ensures fast and efficient development of infrastructure projects with maximized local community involvement (human and economic resources) and minimum road conflicts. The developed model can be utilized to assess previous plans as well as guide future projects. Patel and Ruparathna [41] developed a BIM-based life cycle sustainability assessment framework to compare between various road pavement construction methods with respect to the three pillars of sustainability: society, economy, and environment. It was found that the geomembrane road outperformed its competing alternatives.
Several review studies were conducted about specific aspects of sustainable infrastructure. Nevertheless, most of these studies have implemented a qualitative approach in interpreting findings, as they tend to address sustainability issues in infrastructure projects from certain aspects such as environmental performance [1, 46], critically reviewing various roadway sustainable rating systems [34], society-based design [19], use of recycled materials in pavement construction [8], and adoption of Public Private Partnerships in the development of sustainable infrastructure [3]. Table 1 shows the focus and objectives of these and other review studies. Accordingly, there is a need for a comprehensive and objective quantitative method for studying the relevant literature to better understand the “Sustainable infrastructure” research domain, identify its most prominent themes and promising topics, highlight its gaps, and propose directions for future research endeavors.
Plenty of research reviewed the importance of sustainable infrastructure in the field of civil engineering and building construction. More advanced review methods are required to keep up with the rapidly growing body of knowledge in all scientific fields [21]. Bibliometrics arose early in the twentieth century, then, was developed to acquaint searchable databases such as Web of Science in the 1960s [38]. Bibliometric analysis uses the metadata of published papers in bibliographic databases (e.g., Scopus, Web of Science Core Collection) to develop a quantitative objective analysis of the literature. This metadata includes publication titles, authors and their affiliations, keywords, abstracts, and citation information. In the current study, performance analysis and science mapping are used to analyze the “Sustainable Infrastructure” research domain. Performance analysis quantifies academic output, while science mapping uncovers the various research field topics and its thematic development over time [16, 18, 21]. To this end, Jin et al., [24] conducted a scientometric review study about sustainable infrastructure with a focus on research topics, trends, and articles citation. However, the current study aims to address the same issues in addition to identifying annual publication trends, leading authors, countries, and institutions, as well as the most prominent academic journals in the field till 2023. These findings can assist interested junior academic researchers in finding potential research opportunities in active institutions with experienced fellow researchers and scientific journals that intensely cover the topic. Additionally, the annual publication trends reveal how publications have increased or decreased over time. Moreover, this research helps in spotting the research gaps and trending topics in the sustainable infrastructure literature, to be exploited by interested academic researchers and policymakers either individually or by initiating collaborations among them. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section “Research objectives and methodology” describes the research objectives and methodology. Section “Bibliometric analysis results” describes the results of the bibliometric analysis, and Sect. “Results interpretation” demonstrates the interpretation of these findings. Finally, Sect. “Conclusion” includes the conclusion and research limitations.
Research objectives and methodology
Aiming to present an objective quantitative method for reviewing the relevant literature, this study provides the academia and policy makers with a general comprehensive review of the research conducted about sustainable infrastructure. This could be achieved through accomplishing the following objectives:
-
1.
Extract all bibliometric data related to sustainable infrastructure area.
-
2.
Perform bibliometric analysis on the extracted data from several perspectives to extract insights about the studied domain.
-
3.
Visualize the results of the bibliometric analysis through VOSviewer and Biblioshiny tools.
-
4.
Provide hot topics and predict future research trends to be utilized by academic researchers and policymakers.
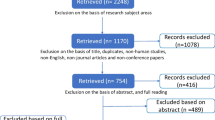
These objectives are accomplished through the following research methodology shown in Fig. 1. The methodology of this research starts with defining the research objectives, which were defined earlier in this section; then, the authors extracted the database using Web of Science (WoS) and performed data preprocessing to be able to analyze this database. Afterward, the authors utilized different bibliometric analysis methods and tools to acquire insights through modeling data which will help in interpreting and visualizing the results.
Bibliometric analysis results
In the current study, bibliometric analysis identifies the following: collaborations between authors, countries, and organizations (co-authorship analysis), citation networks of peer-reviewed journals (citation analysis), and the conceptual structure of the research domain (co-occurrence, cluster, trend topics, and theme analyses). Regarding the software tools, VOSviewer and Biblioshiny were utilized, and both are freely available. VOSviewer was selected for being user-friendly and its ability to produce clear bibliometric visualization networks for scientific collaborators, research domain keywords, as well as prominent journals [45]. On the other hand, Biblioshiny illustrates the thematic evolution and trending topics of a research field using a web interface [7]. The co-authorship analysis is conducted for each of the pioneer authors, organizations/institutes, and countries/regions. On the other hand, the citation analysis is conducted on the sources/journals to examine the citation relations between different sources. In addition, the co-occurrence analysis, trend topic mapping, and thematic evolution are conducted on the keywords.
Bibliometric data acquisition and analysis acquisition
The bibliographic data were extracted from the Web of Science and includes papers related to the “Construction and Building Technology” and “Civil Engineering” categories only. However, it contains a large collection of journals in the engineering field [36]. The search was conducted with the following search statement: (“sustainability” AND “infrastructure”) OR “sustainable infrastructure.” The results were further refined by setting the date to 2012–2023 and limiting the search process to peer-reviewed journals. Thus, this resulted in 1393 peer-reviewed research publications for the subsequent analysis.
Annual publication trends
Figure 2 illustrates the resulting publication trend of literature conducted about sustainable infrastructure. Publications were steadily increasing from 2013 to 2018. Then, there was a minor drop in publications number between 2018 and 2019. Afterward, the number continued to increase again up until 2021. In 2022, an abrupt increase in the number of publications about sustainable infrastructure from 160 articles in 2021 to 224 articles was found. This increase could be attributed to the decline of the impact of the world pandemic COVID-19 as researchers carry on with producing research studies. Finally, up until 2023, 113 papers were found. These results show that sustainable infrastructure is a promising research field expecting to have a higher number of publications in the upcoming years.
Most cited articles
Citations of the Sustainable Infrastructure publications are assessed globally (Global Citation Score) as well as within the extracted bibliographic database (Local Citation Score). The Global Citation Score represents the total number of citations received by an article from publications found in different sources (i.e., Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science). However, the Local Citation Score demonstrates the number of citations a document received from other documents in an executed search [39]. Table 2 shows the ten most globally cited publications in the database. References [12] and [17] are the most locally cited articles.
Collaboration networks
This type of knowledge structure is used to explore scientific collaboration structures which can accordingly facilitate access to expertise by analyzing the co-authorship networks [47]. This analysis can be beneficial for junior researchers to explore and widen their networks and find opportunities for future collaborations while selecting the most influencing contributors and institutions in a certain field [27]. VOSviewer is used to perform co-authorship analysis for authors, organizations, and countries.
Leading authors
This analysis helps in determining the pioneer authors or the major knowledge producers while determining their number of publications, the level of production, as well as their activeness in the field of sustainable infrastructure. In this study, there are 3994 authors for the 1393 article paper, and only 95 authors have authored more than three publications in the field of sustainable infrastructure. The authors’ collaboration network is shown in Fig. 3. This network focused on authors who published at least three publications in the area of sustainable infrastructure. Thus, in this network, there are 95 nodes and 77 links, where each node identifies a different author, and the links between the nodes represent the collaboration relations between the authors. The size of the nodes emphasizes the number of publications, and the thickness of the links represents the researchers’ collaboration strength in terms of mutual documents [33]. Figure 4 illustrates the average publication year for each author which subsequently manifests the activeness of the authors.
Leading institutions
Figure 5 illustrates the collaboration network of different organizations in the field of sustainable infrastructure. The nodes represent a certain organization, while the edges manifest the collaboration relation between the different organizations. The thickness of the edges illustrates the strength of the relations between the different organizations in terms of mutual documents. In the network shown in Fig. 5, the organizations with a minimum of five publications are shown and studied to give a total of 108 organizations that published a minimum of five publications. The number of publications, average publication years, and the average number of citations of the top 15 universities are shown in Table 3, having Swinburne University Technology in Australia as the most active university publishing articles with an average publication year of 2021, and Lehigh University in the USA is having the highest average citations of 55.11 citations for each publication. On the other hand, both Khon Kaen University in Thailand and the University of Birmingham in England have the highest number of publications of 21 publications but have a low average number of citations.
Leading countries
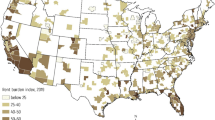
This study also includes an analysis of the leading countries in relation to their publications in the area of sustainable infrastructure. Figure 6 illustrates the countries’ collaboration network; the nodes represent the countries, while the edges represent the collaboration relation between the different countries. The strength of the edges illustrates the collaboration strength between the different countries. Under this study, there are a total of 87 different countries working in the field of sustainable infrastructure. Table 4 shows publication and citation data about the top five countries. The USA, England, the People’s Republic of China, Australia, and Canada are considered the top five countries in publishing articles related to sustainable infrastructure and in having the greatest number of citations among the 87 countries in the extracted database. The USA has the highest number of publications equal 457 publications with average citations of 16.98 citations per publication. However, China is considered the top country with respect to the average number of citations. On the other hand, the strongest collaboration exists between USA and China having the highest link strength; the edge thickness is higher in these two countries than others.
Sources Citation Networks
Citation analysis is conducted to distinguish reliable sources of information. Figure 7 shows 84 out of the 169 peer-reviewed journals, which have a minimum of three publications and three citations in “Sustainable Infrastructure.” In this figure, each node represents a journal, the node size corresponds to the number of publications, and the edges represent the collaboration relations between the different journals.
Conceptual knowledge structures
Conceptual knowledge structures enable the visualization of the relationships between keywords/topics within publications in a given research field [21]. Thus, it helps interested researchers to better understand the landscape of the research field. This is achieved via co-occurrence analysis, cluster analysis, theme analysis, and trend topic analyses of the published research over the 10-year study period.
Co-occurrence and cluster analyses
Keyword co-occurrence analysis is considered a type of conceptual analysis that could be used to determine the prime interest in a certain domain. Thus, keyword co-occurrence analysis is implemented to recognize the mostly used keywords and their co-occurrences with other keywords. Figure 8 illustrates the co-occurrence network for the keywords that are repeated at least 6 times. Thus, this network contains 93 keywords with a total of ten clusters, and each cluster is related to a certain topic. This network consists of nodes (keywords) whose size reflects the keyword frequency and edges (strength of co-occurrence between these keywords indicated by thickness). Furthermore, the network is color-coded, where each color represents a different cluster. The most frequently used keywords as concluded by the analysis were sustainability, infrastructure, green infrastructure management, resilience, sustainable development, sustainable infrastructure, climate change, concrete durability, life cycle assessment, and smart cities. Table 5 shows an example of the co-occurrence of the term “Sustainability” with other corresponding keywords to extract the clusters and provide clusters’ analyses. Table 6 shows the ten clusters and their associated keywords.
Theme analysis
The main themes in the extracted database were identified using Biblioshiny software. Themes are classified with respect to centrality and density. Centrality reflects the value of themes, while density demonstrates the extent of their development [18]. The different categories are illustrated in Table 7 [18]. Figure 9 shows the strategic diagram for sustainable infrastructure research themes between 2012 and 2023. The analysis concluded the following themes to be worthy of further exploration: “Green Infrastructure, Sustainable Infrastructure, Resilience, Data Science, Climate Change, Renewable Energy, Optimization, and Urban Sustainability.”
Trend topic analysis
Burst words are keywords that are used at a considerably high frequency over a short period implying that an issue has drawn a lot of attention [28]. The outcomes of the conducted citation burst analysis are shown in Fig. 10, which lists the burst strength and duration for the top keywords. In this figure, the straight line indicates the start and end of the keyword’s timeline, and the circle is drawn at the year of peak for each keyword. Several remarks can be made about Fig. 10. Topics related to “Life Cycle Assessment” (Peak Year 2020), “Climate Change” (Peak Year 2018), and “Asset Management” (Peak Year 2018) have already been included in many studies. Moreover, publications about “Optimization” and “COVID-19” were intently studied around 2020 and 2021, respectively. However, they are still addressed in publications up until 2023. Finally, the trend topics analysis identified “Smart Cities,” “Sustainability and Resilience,” and “Transportation and Sustainability” as the hot topics peaking in 2022 and 2023.
Results interpretation
The conducted bibliometric analysis aims to visualize and quantitatively analyze the “Sustainable Infrastructure” research field. For instance, several insights can be concluded about the main contributors and academic sources of information. To start with, Table 8 summarizes the top 10 researchers in the field of sustainable infrastructure. It could be concluded that Frangopol, Dan M. is the most productive author contributing to 17 publications with an average publication year of 2017. This author is also having the highest number of citations compared to the other researchers following him such as Dong who authored 11 publications with an average year of publication of 2016 with 697 total citations. However, these two top authors are not active as of today, which is clearly shown in Fig. 4 illustrating the activeness of the authors according to their average publication year. The most active authors are Musonda, Innocent, Nematollahi, Behzad, Nielsen, Linda, Wongsa, Ampol, Gravina, Rebecca J., Sarkar, Debases, Xie, Tianyu, Maghool, and Farshid. These authors are publishing their papers in 2021 and 2022 and correspond to seven different clusters as shown in Table 9. In this network, there is a total of 45 clusters, where most of the productive authors are categorized under cluster 3, and most of the active authors are categorized under clusters 1, 4, 6, 21, 36, 37, and 44.
Additionally, the top two institutions with respect to the number of publications are Khon Kaen University in Thailand and University Birmingham in England with 21 research studies on this topic. This is particularly interesting since Thailand is not among the most active countries. Nevertheless, Khon Kaen University is found to produce more articles than other universities with average publication year 2019. Following them are University of Illinois and Lehigh University in the USA with 19 publications. However, Lehigh University in the USA, the University of Michigan in the USA, Tongji University in China, the University of California Berkeley in the USA, and Columbia University in the USA are the top five universities with respect to the number of citations having a total number of citations of 1047, 612, 548, 489, and 387, respectively. Thus, the top university with respect to both the number of publications and the number of citations is Lehigh University with an average publication year of 2017. The average publication years, number of publications, and average number of citations of the top 15 universities are shown in Table 4. Chongqing University in China, RMIT University in Australia, and Mcmaster University in Canada are the top three active universities publishing in the field of sustainable infrastructure. However, Swinburne University Technology which is located in Australia is the top active university with respect to the total number of publications.
Table 10 lists the top journals ranked based on number of publications, citation score, and average publication year. The top 5 journals “Sustainable Cities and Society, Transportation Research Record, Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Engineering, Construction and Building Materials, and Journal of Infrastructure Systems” collectively have 392 publications, which is approximately 30% of the extracted database found in 3% of the journals (5/169). Further, only three of those most productive journals have some of the highest citation scores of 2,303, 1,295, and 794 for “Sustainable Cities and Society, Construction and Building Materials, and Journal of Infrastructure Systems,” respectively. The journal with the most recent average publication year (2021) in the extracted bibliographic database is “Innovative Infrastructure Solutions.”
On another account, the bibliometric analysis offers a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape of the Sustainable Infrastructure research domain.
First, co-authorship analysis illustrated that collaborations among institutions and countries are stronger than those found between authors’ clusters. Therefore, researchers are encouraged to explore studies and form relationships outside their cluster border.
Second, the bibliometric analysis resulted in the identification of the following topics for the most cited studies in the extracted database: resilience and sustainability analysis of infrastructure impact on the society, economy, and environment [12], building energy consumption [22], the role of big data in improving the environmental sustainability in smart cities [11], building information modeling (BIM) and green buildings [31], studying the environmental aspect of construction materials of sustainable infrastructure projects [6, 30, 35], and sustainability assessment of bridge projects with respect to society, economy, and environment [17].
Interested researchers can tackle the understudied topics in the field. Jin et al. [24] recommended conducting studies about sustainable infrastructure that address social and economic sustainability, interdisciplinary collaboration, and use of building information modeling and Internet of Things. In the present study, it is concluded that most of the research studies are primarily focused on only the environmental aspect of sustainability [6, 11, 30, 35], with much fewer studies focused on the social aspect of sustainability [19] or the economic aspect.
Future research ought to aim to achieve a balanced approach to successfully incorporate the three pillars of sustainability in infrastructure projects. The cluster and co-occurrence analyses showed that there are few studies incorporating system dynamics and public–private partnerships (PPPs) with sustainable infrastructure. System dynamics and PPPs can help deal with highly interconnected systems [40] and distribute the economic burden of infrastructure development between the private and public sectors, respectively [2]. This can lead to better handling of the three pillars of sustainability. Consequently, more research should be conducted about their use in sustainable infrastructure development. Finally, the emerging data science should be further explored by policymakers, especially for governmental decisions concerning infrastructure as well as sustainability rating systems. State-of-the-art data-driven decision-making can lead to a balance between economic, social, and environmental aspects.
Conclusion
This research is implemented to study the area of sustainable infrastructure academically. This research manifested an integrated quantitative–qualitative literature review on the sustainable infrastructure in both civil engineering and building construction areas by analyzing a total of 1393 journal articles from 2012 to 2023. The findings of this research could be summarized as follows:
-
In 2022, an increase in the number of publications about sustainable infrastructure from 160 articles in 2021 to 224 articles in 2022 took place. These results that sustainable infrastructure is a promising research field worthy of further exploration.
-
“Resilience and Sustainability of Civil Infrastructure: Toward a Unified Approach” is the most cited article having a local citation score of 25 and a global citation score of 270.
-
Frangopol, Dan M. is considered the most productive author in this field publishing a total of 17 publications related to sustainable infrastructure. On the other hand, Musonda, Innocent is considered the most active researcher in the area of sustainable infrastructure having three publications with an average publication year of 2022.
-
Lehigh University in the USA has the highest average citation per publication and is the university is one of the top institutions publishing papers related to sustainable infrastructures, while the USA is considered the pioneer country in publications in this area having a total number of publications of 457 and a total number of citations of 7762.
The performed bibliometric analysis represents an alternative to the subjective review of the body of knowledge about sustainable infrastructure. It provides interested researchers with insights that would not be achieved otherwise such as annual publication trends, leading authors, countries, and institutions, the most prominent academic journals in the field till 2023, promising topics, research gaps, and directions for future research endeavors. It also enables policymakers to enhance their decision-making process regarding how sustainability can be achieved and assessed in infrastructure systems. The present study recommends utilizing System Dynamics, Public Private Partnerships, and/or Data Science to reach an effective balance between the three pillars of sustainability. However, there are some limitations. For example, only one database is used in the analysis. In addition, the bibliometric analysis in the present study does not consider full paper content and relies on abstracts, keywords, and titles of journal publications only. Therefore, the scope and results of this paper can be expanded by including more databases, different search criteria, and a more detailed content analysis of the extracted bibliographic data.
References
Abhijith KV, Kumar P, Gallagher J, McNabola A, Baldauf R, Pilla F, Broderick B, Di Sabatino S, Pulvirenti B (2017) Air pollution abatement performances of green infrastructure in open road and built-up street canyon environments–a review. Atmos Environ 162:71–86
Agarchand N, Laishram B (2017) Sustainable infrastructure development challenges through PPP procurement process: Indian perspective. Int J Manag Proj Bus 10(3):642–662
Akomea-Frimpong I, Jin X, Osei-Kyei R, Kukah AS (2023) Public–private partnerships for sustainable infrastructure development in Ghana: a systematic review and recommendations. Smart Sustain Built Environ 12(2):237–257
Al-Jawari SM, Albasri NAH, Al-Mosherefawi OJ (2022) Using CRF tool for analyzing the resilience of cities. Civ Eng J 8(10):2220–2234
Andreas G, Allen J, Farley L, Kao JK, Mladenova I (2010) Towards the development of a rating system for sustainable infrastructure: a checklist or a decision-making tool? In: Proceedings of the water environment federation; Boston, MA, pp 379–391
Angst UM (2018) Challenges and opportunities in corrosion of steel in concrete. Mater Struct 51(1):1–20
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Inform 11(4):959–975
Aytekin B, Mardani-Aghabaglou A (2022) Sustainable materials: a review of recycled concrete aggregate utilization as pavement material. Transp Res Rec 2676(3):468–491
Azzam A, El Zayat M, Marzouk M (2022) Integrated approach for sustainability assessment in power plant projects using building information modeling. Energy Sustain Dev 66:222–237
Bhattacharya A, Meltzer JP, Oppenheim J, Qureshi Z, Stern N (2016) Delivering on sustainable infrastructure for better development and better climate. Washington (DC): Global economy and development, The Brookings Institution
Bibri SE (2018) The IoT for smart sustainable cities of the future: an analytical framework for sensor-based big data applications for environmental sustainability. Sustain Cities Soc 38:230–253
Bocchini P, Frangopol DM, Ummenhofer T, Zinke T (2014) Resilience and sustainability of civil infrastructure: toward a unified approach. J Infrastruct Syst 20(2):04014004
Bryce JM, Flintsch G, Hall RP (2014) A multi criteria decision analysis technique for including environmental impacts in sustainable infrastructure management business practices. Transp Res Part D Transp Environ 32:435–445
Buehler R, Pucher J (2012) Cycling to work in 90 large American cities: new evidence on the role of bike paths and lanes. Transportation 39(2):409–432
Castro C, Sabogal D, Fernández W (2022) A review of emissions on pavement materials and sustainability rating systems. Rev ingeniería de constr 37(2):280–291
Darko A, Chan APC, Adabre MA, Edwards DJ, Reza Hosseini M, Ameyaw EE (2020) Artificial intelligence in the AEC industry: scientometric analysis and visualization of research activities. Autom Constr 112(2020):103081
Dong Y, Frangopol DM, Saydam D (2013) Time-variant sustainability assessment of seismically vulnerable bridges subjected to multiple hazards. Earthq Eng Struct Dynam 42(10):1451–1467
Garcia-Buendia N, Moyano-Fuentes J, Maqueira-Marín JM, Cobo MJ (2021) 22 years of lean supply chain management: a science mapping-based bibliometric analysis. Int J Prod Res 59(6):1901–1921
Gardoni P, Murphy C (2020) Society-based design: promoting societal well-being by designing sustainable and resilient infrastructure. Sustain Resil Infrastruct 5(1–2):4–19
Gibson Jr GE, Bingham E, Stogner CR (2010) Front end planning for infrastructure projects. In: Construction research congress 2010: innovation for reshaping construction practice; May 8–10; Banff, Alberta, Canada: Construction Research Congress 2010, pp 1125–1135
Gutiérrez-Salcedo M, Martínez MÁ, Moral-Munoz JA, Herrera-Viedma E, Cobo MJ (2018) Some bibliometric procedures for analyzing and evaluating research fields. Appl Intell 48(5):1275–1287
Howard B, Parshall L, Thompson J, Hammer S, Dickinson J, Modi V (2012) Spatial distribution of urban building energy consumption by end use. Energy Build 45:141–151
Jalaei F, Zoghi M, Khoshand A (2019) Life cycle environmental impact assessment to manage and optimize construction waste using building information modeling (BIM). Int J Construct Manag 21(8):784–718
Jin H, Chan M, Morda R, Lou CX, Vrcelj Z (2023) A scientometric review of sustainable infrastructure research: visualization and analysis. Int J Construct Manag 23(11):1847–1855
Kambu Z, Jinca MY, Pallu MS, Ramli MI (2022) Meta synthesis of community participation model on Trans-Papua road development. Civ Eng J 8(11):2476–2489
Khan KI, Mata MN, Martins J, Nasir A, Dantas RM, Correia AB, Saghir US (2022) Impediments of green finance adoption system: linking economy and environment. Emerg Sci J 6:217–237
Khodabandelu A, Park J (2021) Agent-based modeling and simulation in construction. Autom Constr 131:103882
Kou WJ, Wang XQ, Li Y, Ren XH, Sun JR, Lei SY, Wang MX (2021) Research trends of posttraumatic growth from 1996 to 2020: a bibliometric analysis based on web of science and citespace. J Affect Disord Rep 3:100052
Krajangsri T, Pongpeng J (2017) Effect of sustainable infrastructure assessments on construction project success using structural equation modeling. J Manag Eng 33(3):04016056
Li VC, Herbert E (2012) Robust self-healing concrete for sustainable infrastructure. J Adv Concr Technol 10(6):207–218
Lu Y, Wu Z, Chang R, Li Y (2017) Building information modeling (BIM) for green buildings: a critical review and future directions. Autom Construct 83:134–148
Mandić Ivanković A, Strauss A, Sousa H (2019) European review of performance indicators towards sustainable road bridge management. Proc Ins Civ Eng-Eng Sustain 173(3):109–124
Martinez P, Al-Hussein M, Ahmad R (2019) A scientometric analysis and critical review of computer vision applications for construction. Autom Constr 107:102947
Mattinzioli T, Sol-Sánchez M, Martínez G, Rubio-Gámez M (2020) A critical review of roadway sustainable rating systems. Sustain Cities Soc 63:102447
Miller SA, John VM, Pacca SA, Horvath A (2018) Carbon dioxide reduction potential in the global cement industry by 2050. Cem Concr Res 114:115–124
Mongeon P, Paul-Hus A (2016) The journal coverage of web of science and scopus: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 106(1):213–228
Navarro IJ, Yepes V, Marti JV (2019) A review of multicriteria assessment techniques applied to sustainable infrastructure design. Adv Civ Eng 2019:1–16
Nettle D, Frankenhuis WE (2019) The evolution of life-history theory: a bibliometric analysis of an interdisciplinary research area. Proc R Soc B 286(1899):20190040
Batista-Canino RM, Santana-Hernández L, Medina-Brito P (2023) A scientometric analysis on entrepreneurial intention literature: delving deeper into local citation. Heliyon 9:e13046
Nguyen T, Cook S, Ireland V (2017) Application of system dynamics to evaluate the social and economic benefits of infrastructure projects. Systems 5(2):29
Patel K, Ruparathna R (2023) Life cycle sustainability assessment of road infrastructure: a building information modeling-(bim) based approach. Int J Constr Manag 23(11):1837–1846
Plati C (2019) Sustainability factors in pavement materials, design, and preservation strategies: a literature review. Constr Build Mater 211:539–555
Rahat R, Ferrer V, Pradhananga P, ElZomor M (2023) Developing an effective front-end planning framework for sustainable infrastructure projects. Int J Constr Manag 23(16):2841–2858
Upadhyaya JK, Biswas N, Tam E (2014) A review of infrastructure challenges: assessing stormwater system sustainability. Can J Civ Eng 41(6):483–492
Van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84(2):523–538
Wang Y, Bakker F, De Groot R, W€ortche H (2014) Effect of ecosystem services provided by urban green infrastructure on indoor environment: a literature review. Build Environ 77:88–100
Xue J, Reniers G, Li J, Yang M, Wu C, van Gelder PHAJM (2021) A bibliometric and visualized overview for the evolution of process safety and environmental protection. Int J Environ Res Pub Health 18(11):5985
Yigitcanlar T, Li RYM, Inkinen T, Paz A (2022) Public perceptions on application areas and adoption challenges of AI in urban services. Emerg Sci J 6(6):1199–1236
Yu C, Feng Y, Liu HX, Ma W, Yang X (2018) Integrated optimization of traffic signals and vehicle trajectories at isolated urban intersections. Transp Res Part B Methodol 112:89–112
Funding
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB). Open access funding provided by Faculty of Engineering, Cairo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
The paper is neither published nor under review elsewhere. There are no human or animal participants involved in the conducted study.
Informed consent
All authors are aware of the paper.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Elkhayat, Y., Mohamed, B., Zayat, M.E. et al. Bibliometric analysis and visualization of sustainable infrastructure. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 9, 14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-023-01319-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-023-01319-y