Abstract
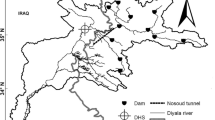
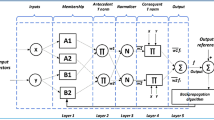
Quantum computer brings many advantages to the world of computations. Also, the tunnel boring machine (TBM) has been industrialized over the prior decades to make the tunneling process safer and more affordable. Several factors such as economic considerations, rock properties, and schedule deadlines play an important role in the use of TBMs mining projects. Hence, future projects are interested in enhanced means for predicting the TBM performance. The TBM penetration is usually an essential factor for the prosperous implementation of a plan for tunneling in a rock situation. In this research, the statistical analyses of rock features and the measured penetration rate of TBMs are presented using the imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) and quantum fuzzy logic. Also, a database has been used that includes the parameters of rock properties of the Queens Water Tunnel. The proposed hybrid method is applied to provide a new predictive model for improving TBM performance. Results demonstrated that this method has a high capability to predict the performance of TBM with R2 = 0.93 and RMSE = 0.09. This shows that the application of the proposed approach is preferable compared to the prior models in terms of penetration rate.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yazdani-Chamzini A, Yakhchali SH (2012) Tunnel boring machine (TBM) selection using fuzzy multicriteria decision making methods. Tunn Undergr Space Tech 30:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.02.021
Liotard P, Robert P (2019) Cutter holder for a tunnel boring machine and an associated cutting set (ed): Google Patents
DiMillo T (2000) Tunnel boring machine with crusher (ed): Google Patents
Cass DT (1999) Tunnel boring machine and method (ed) Google Patents
Koopialipoor M, Nikouei SS, Marto A, Fahimifar A, Armaghani DJ, Mohamad ET (2019) Predicting tunnel boring machine performance through a new model based on the group method of data handling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(5):3799–3813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1349-8
Wijk G (1992) A model of tunnel boring machine performance. Geotech Geol Eng 10(1):19–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00881969
Yagiz S, Karahan H (2015) Application of various optimization techniques and comparison of their performances for predicting TBM penetration rate in rock mass. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 80:308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.09.019
Yagiz S, Gokceoglu C, Sezer E, Iplikci S (2009) Application of two non-linear prediction tools to the estimation of tunnel boring machine performance. Eng Appl Artif Intell 22(4–5):808–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2009.03.007
Ozdemir L, Wang FD (1979) Mechanical tunnel boring prediction and machine design. Nasa Sti/Recon Tech Rep N 80:16239
Jahed Armaghani D, Faradonbeh RS, Momeni E, Fahimifar A, Tahir MM (2018) Performance prediction of tunnel boring machine through developing a gene expression programming equation. Eng Comput 34(1):129–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0526-x
Khorasani E, Zare Naghadehi M, Jimenez R, Tarigh Azali S, Jalali SME, Zare S (2018) Performance analysis of tunnel-boring machine by probabilistic systems approach. P I Civil Eng-Geotec 171(5):422–438. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeen.16.00190
Yagiz S, Karahan H (2011) Prediction of hard rock TBM penetration rate using particle swarm optimization. Int J Rock Mech Min 48(3):427–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.02.013
Gong Q, Zhao J (2009) Development of a rock mass characteristics model for TBM penetration rate prediction. Int J Rock Mech Min 46(1):8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.03.003
Zhao Y, Yang H, Chen Z, Chen X, Huang L, Liu S (2019) Effects of jointed rock mass and mixed ground conditions on the cutting efficiency and cutter wear of tunnel boring machine. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(5):1303–1313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1667-y
Tarkoy PJ, Hendron A (1975) Rock hardness index properties and geotechnical parameters for predicting tunnel boring machine performance
Liao J, Zhu X, Yao B (2018) Dynamic modeling of gripper type hard rock tunnel boring machine. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 71:166–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.08.003
Yagiz S, Ghasemi E, Adoko AC (2018) Prediction of rock brittleness using genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization techniques. Geotech Geol Eng 36(6):3767–3777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0570-3
Gholamnejad J, Tayarani N (2010) Application of artificial neural networks to the prediction of tunnel boring machine penetration rate. Min Sci Technol 20(5):727–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1674-5264(09)60271-4
Ghasemi E, Yagiz S, Ataei M (2014) Predicting penetration rate of hard rock tunnel boring machine using fuzzy logic. B Eng Geol Environ 73(1):23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0497-0
Yoo C, Kim JM (2007) Tunneling performance prediction using an integrated GIS and neural network. Comput Geotech 34(1):19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2006.08.007
Kim T (2004) Development of a fuzzy logic based utilization predictor model for hard rock tunnel boring machines, Colorado school of mines
Benardos A, Kaliampakos D (2004) Modelling TBM performance with artificial neural networks. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 19(6):597–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2004.02.128
Mahdevari S, Shahriar K, Yagiz S, Shirazi MA (2014) A support vector regression model for predicting tunnel boring machine penetration rates. Int J Rock Mech Min 72:214–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.09.012
Benato A, Oreste P (2015) Prediction of penetration per revolution in TBM tunneling as a function ofintact rock and rock mass characteristics. Int J Rock Mech Min 74:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.12.007
Huo J, Sun W, Su P, Deng L (2009) Optimal disc cutters plane layout design of the full-face rock tunnel boring machine (TBM) using an ant colony optimization algorithm. International conference on intelligent robotics and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 443–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10817-4_44
Yagiz S (2008) Utilizing rock mass properties for predicting TBM performance in hard rock condition. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 23(3):326–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2007.04.011
Oraee K, Salehzade H, Salehi B (2008) Calculation of efficiency and advanced rate TBMs in Karaj-Tehran water transfer project using practical models. In: Proceedings of the 4th national congress on civil engineering
Wu SJ, Qian B, Gong ZB (2006) The time and cost prediction of tunnel boring machine in tunneling. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 11(2):385–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832128
Tarkoy PJ (1973) Predicting Tbm penetration rates in selected rock types
Graham PC (1976) Rock exploration for machine manufacturers. In: Bieniawski ZT (ed) Exploration for rock engineering. Balkema, Johannesburg, pp 173–180
Hughes H (1986) The relative cuttability of coal-measures stone. Min Sci Technol 3(2):95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9031(86)90250-1
Farmer I, Garrity P, Glossop N (1987) Operational characteristics of full face tunnel boring machines. In: Rapid excavation and tunneling conference, pp 188–201
Tatiya RR (2005) Surface and underground excavations: methods, techniques and equipment. CRC Press, Florida
De Silva CW (2018) Intelligent control: fuzzy logic applications. CRC Press, Florida
Ren X, Wu C (2013) The fuzzy riemann-stieltjes integral. Int J Theor Phys 52(6):2134–2151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-013-1511-9
Yager RR, Zadeh LA (2012) An introduction to fuzzy logic applications in intelligent systems. Springer Science & Business Medi, Cham
Zahedi F, Zahedi Z (2015) A review of neuro-fuzzy systems based on intelligent control. J E E 3(1–2):58–61. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jeee.s.2015030201.23
Chen G, Pham TT (2000) Introduction to fuzzy sets, fuzzy logic, and fuzzy control systems. CRC Press, Florida. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420039818
Bisht DCS, Srivastava PK, Ram M (2018) Role of fuzzy logic in flexible manufacturing system. In: Ram M, Davim J (eds) Diagnostic techniques in industrial engineering. Management and industrial engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65497-3_9
Liu Z, Li HX (2005) A probabilistic fuzzy logic system for modeling and control. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 13(6):848–859. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2005.859326
Karnik NN, Mendel JM (1998) Introduction to type-2 fuzzy logic systems. In: 1998 IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems proceedings. IEEE world congress on computational intelligence (Cat. No. 98CH36228), pp 915–920. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/FUZZY.1998.686240
Venkatrama R, Sergioli G, Freytes H, Leporini R (2017) Fuzzy type representation of the Fredkin gate in quantum computation with mixed states. Int J Theor Phys 56(12):3860–3868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-017-3362-2
Ross TJ (2010) Fuzzy logic with engineering applications, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119994374
Luo G, Zhou RG, Liu X, Hu W, Luo J (2018) Fuzzy matching based on gray-scale difference for quantum images. Int J Theor Phys 57(8):2447–2460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3766-7
Mayburov S (2015) Fuzzy topology and geometric formalism of quantum mechanics. Int J Theor Phys 54(12):4272–4282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-014-2480-3
Varghese A, George JS, George J (2018) A continuous assessment strategy using fuzzy logic. In: Learning strategies and constructionism in modern education settings: IGI Global, pp 69–86. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-5430-1.ch005
Yazdanbakhsh O, Dick S (2018) A systematic review ofcomplex fuzzy sets and logic. Fuzzy Set Syst 338:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2017.01.010
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Tian X (2019) A novel fuzzy logic system with consequents as fuzzy weighted averages of antecedents. In: Proceedings of 2018 Chinese intelligent systems conference, chapter in lecture notes in electrical engineering. Springer, Cham, p 571–582. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2291-4_56
Raghuvanshi A, Perkowski M (2010) Fuzzy quantum circuits to model emotional behaviors of humanoid robots. In: IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, p 1–8. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2010.5586038
Schmitt I, Nürnberger A, Lehrack S (2009) On the relation between fuzzy and quantum logic. In: Seising R. (eds) Views on fuzzy sets and systems from different perspectives. Studies in fuzziness and soft computing. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-93802-6_20
Liao HC, Wu X, Keikha A, Hafezalkotob A (2018) Power average-based score function and extension rule of hesitant fuzzy set and the hesitant power average operators. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35(3):3873–3882. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-18794
Khaled AA, Hosseini S (2015) Fuzzy adaptive imperialist competitive algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput Appl 26(4):813–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1752-4
Atashpaz-Gargari E, Lucas C (2007) Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. In: 2007 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, p 4661–4667. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2007.4425083
Kaveh A, Talatahari S (2010) Imperialist competitive algorithm for engineering design problems. Asian J Civ Eng 11(6):675–697
Talatahari S, Azar BF, Sheikholeslami R, Gandomi A (2012) Imperialist competitive algorithm combined with chaos for global optimization. Commun Nonlinear Sci 17(3):1312–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.08.021
Mollajan A, Memarian H, Quintal B (2019) Imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) optimization method for nonlinear AVA inversion. Geophysics 84(3):81–92. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2018-0507.1
Abdechiri M, Faez K, Bahrami H (2010) Adaptive imperialist competitive algorithm (AICA). In: 9th IEEE international conference on cognitive informatics (ICCI'10), pp 940–945. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/COGINF.2010.5599776
Yazdani M, Jolai F, Taleghani M, Yazdani R (2018) A modified imperialist competitive algorithm for a two-agent single-machine scheduling under periodic maintenance consideration. Int J Oper Res 32(2):127–155. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJOR.2018.092011
Mikaeil R, Haghshenas SS, Haghshenas SS, Ataei M (2018) Performance prediction of circular saw machine using imperialist competitive algorithm and fuzzy clustering technique. Neural Comput Appl 29(6):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2557-4
Tashayo B, Behzadafshar K, Tehrani MS, Banayem HA, Hashemi MH, Nezhad SST (2019) Feasibility of imperialist competitive algorithm to predict the surface settlement induced by tunneling. Eng Comput 35(3):917–923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0641-3
Hasanipanah M, Amnieh HB, Khamesi H, Armaghani DJ, Golzar SB, Shahnazar A (2018) Prediction of an environmental issue of mine blasting: an imperialistic competitive algorithm-based fuzzy system. Int J Environ Sci Te 15(3):551–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1395-y
Afradi A, Ebrahimabadi A, Hallajian T (2019) Prediction of the penetration rate and number of consumed disc cutters of tunnel boring machines (TBMs) using artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector machine (svm)-case study: beheshtabad water conveyance tunnel in Iran. Asian j water environ pollut 16(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.3233/AJW190006
Afradi A, Ebrahimabadi A, Hallajian T (2020) Prediction of tunnel boring machine penetration rate using ant colony optimization, bee colony optimization and the particle swarm optimization, case study: Sabzkooh water conveyance tunnel . M M D 14:75–84. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.33271/mining14.02.075
Afradi A, Ebrahimabadi A, Hallajian T (2020) Prediction of TBM penetration rate using support vector machine. Geosaberes 11:467–479
ZareNaghadehi M, Samaei M, Ranjbarnia M, Nourani V (2018) State-of-the-art predictive modeling of TBM performance in changing geological conditions through gene expression programming. Measurement 126:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.05.049
Adoko AC, Gokceoglu C, Yagiz S (2017) Bayesian prediction of TBM penetration rate in rock mass. Eng Geol 226:245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.06.014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afradi, A., Ebrahimabadi, A. Prediction of TBM penetration rate using the imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) and quantum fuzzy logic. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 6, 103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-021-00467-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-021-00467-3