Abstract
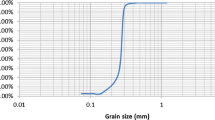
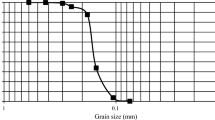
In this study, an alternative and environmentally friendly method for the reinforcement of dune sand is proposed. This technique consists of using randomly distributed rubber fibers to improve the engineering properties of sand. Rubber fibers are added to the sand with different percentages: 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75 and 2% of dry weight of sand. The experimental program carried out consists of investigating the effect of rubber fibers on the shear strength properties of sand. Reinforced and unreinforced samples are tested in the dense as well as loose state. The results obtained showed that the inclusion of rubber fibers in dune sand will improve the engineering properties of various civil engineering applications such as shallow foundations and slope. Therefore, incorporation of rubber fibers can enhance the shear strength characteristics, peak and residual strengths, and introduce more ductility to the mechanical behavior of sand. In addition to the technical effect, this paper emphasizes another environmentally attractive option, which is the use of rubber fibers as reinforcements for granular soils as this helps to remove some parts of these wastes and protect the environment.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ateş A (2016) Mechanical properties of sandy soils reinforced with cement and randomly distributed glass fibers (GRC). Compos Part B: Eng 96:295–304. Available at: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1359836816304437. Accessed 13 June 2016
Balunaini U et al (2014) Pullout response of uniaxial geogrid in tire shred-sand mixtures. Geotech Geol Eng 32(2):505–523
Botero E et al (2015) Stress–strain behaviour of a silty soil reinforced with polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Geotext Geomembr 43(4):363–369. doi:10.1016/j.geotexmem.2015.04.003
Cecich V et al (1996) Use of shredded tires as lightweight backfill. Waste Manag Res 14:433–451
Eldesouky HM, Morsy MM, Mansour MF (2014) Fiber-reinforced sand strength and dilation characteristics. Ain Shams Eng J. doi:10.1016/j.asej.2015.06.003
Gray DH, Ohashi H (1983) Mechanics of fiber reinforcement in sand. 109(3):335–353
Güneyisi E, Gesoğlu M, Özturan T (2004) Properties of rubberized concretes containing silica fume. Cem Concr Res 34(12):2309–2317
Ibraim E et al (2012) Assessment of laboratory sample preparation for fibre reinforced sands. Geotext Geomemb 34:69–79. doi:10.1016/j.geotexmem.2012.03.002
Jingfu K, Chuncui H, Zhenli Z (2008) Strength and shrinkage behaviours of roller-compacted concrete with rubber additives. Mater Struct 42(8):1117–1124
Krishna Rao SV, Nasr AMA (2012) Laboratory study on the relative performance of silty-sand soils reinforced with linen fiber. Geotech Geol Eng 30(1):63–74
Kyser D, Ravichandran N (2016) Properties of chipped rubber roofing membrane and sand mixtures for civil engineering applications. J Build Eng 7:103–113. Available at: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2352710216300547. Accessed 13 June 2016
Maity J, Chattopadhyay BC, Mukherjee SP (2012) Behaviour of different types of sand randomly mixing with various natural fibers. J Inst Eng (India) Ser A 93(2):97–104. doi:10.1007/s40030-012-0014-7
Meddah A (2015) Characterization or roller compacted concrete containing rubber-tire wastes. National Polytechnic School of Algiers, Algiers
Meddah A, Beddar M, Bali A (2014a) Experimental study of compaction quality for roller compacted concrete pavement containing rubber tire wastes. In: Sustainability, eco-efficiency, and conservation in transportation infrastructure asset management. CRC Press, New York, pp 273–278
Meddah A, Beddar M, Bali A (2014b) Use of shredded rubber tire aggregates for roller compacted concrete pavement. J Clean Product 72:187–192. Available at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095965261400198X. Accessed 13 Sept 2014
Meddah A, Sahli M, Safer S (2015) Etude de l’effet de la rugosité des renforcements sur le comportement des massifs en terre armée. Journées d’étude de Génie Civil. M’sila University, Algeria, pp 54–59
Naik BTR, Singh SS (1991) Utilization of discarded tires as transportation facilities. Report N. CBU-1991-02
Onuaguluchi O, Panesar DK (2014) Hardened properties of concrete mixtures containing pre-coated crumb rubber and silica fume. J Clean Product 82:125–131. Available at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652614006568. Accessed 13 Sept 2014
Shao W et al (2014) Experimental investigation of mechanical properties of sands reinforced with discrete randomly distributed fiber. Geotech Geol Eng 32:901–910
Tang C-S, Shi B, Zhao L-Z (2010) Interfacial shear strength of fiber reinforced soil. Geotext Geomemb 28(1):54–62. doi:10.1016/j.geotexmem.2009.10.001
Thomas BS, Gupta RC (2015) Long term behaviour of cement concrete containing discarded tire rubber. J Clean Product 102:78–87
Yetimoglu T, Salbas O (2003) A study on shear strength of sands reinforced with randomly distributed discrete fibers. Geotext Geomemb 21(2):103–110
Yoon S et al (2006) Construction of a test embankment using a sand-tire shred mixture as fill material. Waste Manag 26(9):1033–1044
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meddah, A., Merzoug, K. Feasibility of using rubber waste fibers as reinforcements for sandy soils. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2, 5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-017-0053-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-017-0053-z