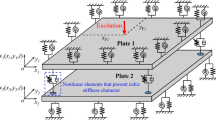
Abstract
This paper introduces the nonlinear vibration response of an eccentrically stiffened porous functionally graded sandwich cylindrical shell panel with simply supported boundary conditions by using a new analytical model. The cylindrical shell has three layers: an FGM core layer and two layers made of isotropic homogeneous material. The FGM core properties are considered to be porosity dependent and varied in the thickness direction according to power-law distribution in terms of the volume fractions index of the constituents. Governing equations for the dynamic response of porous ES-FGM sandwich cylindrical shell panels are derived by combining classical shell theory and nonlinearity von Karman strains. Besides that, the airy stress function and Galerkin approaches are proposed to obtain the resulted equations: Fundamental natural frequency, dynamic response, and amplitude–frequency relation. Comparisons are made to estimate the reliability of the received results. Eventually, the effects of stiffeners, porous coefficient, face sheet thickness, material gradient, FGM core thickness, slenderness ratios, and excitation force on the natural frequency and nonlinear dynamic response of porous FGM sandwich cylindrical shell panels are also clarified in this paper.























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({{\varvec{A}}}_{{\varvec{i}}{\varvec{j}}},{{\varvec{B}}}_{{\varvec{i}}{\varvec{j}}},{{\varvec{D}}}_{{\varvec{i}}{\varvec{j}}}\) :
-
Coefficients described in Appendix N/ m2
- \({{\varvec{A}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},{{\varvec{A}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
Cross-sectional areas of the stiffeners m2
- \({{\varvec{A}}}_{1},{{\varvec{A}}}_{2},{{\varvec{A}}}_{3}\) :
-
Coefficients described in Appendix
- \({{\varvec{E}}}_{^\circ }\) :
-
Elastic modulus for stiffeners N/ m2
- \({{\varvec{E}}}_{\mathbf{c}}\) :
-
Elastic modulus for ceramic N/ m2
- \({{\varvec{E}}}_{\mathbf{m}}\) :
-
Elastic modulus for metal N/ m2
- \({{\varvec{I}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},{{\varvec{I}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
Second moments of the cross-sectional areas for the stiffeners m4
- \({{\varvec{M}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},\boldsymbol{ }{{\varvec{M}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}, {{\varvec{M}}}_{{\varvec{x}}{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
Moment’s resultants N.m
- \({{\varvec{N}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},\boldsymbol{ }{{\varvec{N}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}, {{\varvec{N}}}_{{\varvec{x}}{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
Forces resultants Newton
- \({{\varvec{S}}}_{{\varvec{x}}}{,\boldsymbol{ }{\varvec{S}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
Distance between the transversal and longitudinal stiffeners m
- \({{\varvec{S}}}_{1},{{\varvec{S}}}_{2},{{\varvec{S}}}_{3}\) :
-
Coefficients
- \({{\varvec{Z}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},{{\varvec{Z}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
Eccentricities stiffened m
- \({{\varvec{h}}}_{{\varvec{F}}{\varvec{G}}}\) :
-
Core Thickness m
- \({{\varvec{h}}}_{{\varvec{L}}},{{\varvec{h}}}_{{\varvec{U}}},\) :
-
Skins Thickness m
- \({{\varvec{h}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},{{\varvec{h}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}\), \({{\varvec{d}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},{{\varvec{d}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
Thickness and width of longitudinal and transversal for the rectangle stiffeners m
- a:
-
Panel length m
- b:
-
Span length m
- c:
-
Ceramic
- E:
-
Young modulus N/ m2
- H:
-
Panel thickness m
- m:
-
Metal
- m:
-
Axial wave number unitless
- N:
-
Power law index unitless
- n:
-
Circumferential wave number unitless
- Pr:
-
Effective material properties
- R:
-
Panel radius m
- u, v:
-
Displacement components along x, y directions m
- Vc:
-
Volume fraction of ceramic
- Vm:
-
Volume fraction of metal
- w:
-
The deflection of the panel m
- x, y, z:
-
Panel coordinates m
- \({\varvec{M}},\boldsymbol{ }{\varvec{H}},\boldsymbol{ }{\varvec{K}}\) :
-
Coefficients
- \({\varvec{Q}}\) :
-
Excitation force N/ m2
- \({\varvec{f}}\) :
-
The stress function
- \({\varvec{q}}\) :
-
Uniformly distributed pressure of intensity Pascal
- \({{\varvec{\gamma}}}_{{\varvec{x}}{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
The shear strain component unitless
- \({{\varvec{\varepsilon}}}_{{\varvec{x}}},\boldsymbol{ }{{\varvec{\varepsilon}}}_{{\varvec{y}}}\) :
-
The normal strains component unitless
- \({{\varvec{\rho}}}_{0}\) :
-
Mass density for stiffeners Kg/ m3
- \({{\varvec{\rho}}}_{1}\) :
-
Coefficient explained in Appendix Kg/ m3
- \({{\varvec{\omega}}}_{{\varvec{L}}}\) :
-
Linear fundamental frequencies Hertz (HZ)
- \({{\varvec{\omega}}}_{{\varvec{N}}{\varvec{L}}}\) :
-
Nonlinear vibration frequency Hertz (HZ)
- \(\boldsymbol{\Omega }\) :
-
Rotational velocity Rad/s
- \({\varvec{\beta}},\boldsymbol{ }\mathbf{B}\mathbf{e}\mathbf{t}\mathbf{a}\) :
-
The factor of the Porosity
- \({\varvec{\eta}}\) :
-
Amplitude of nonlinear vibration m
- \({\varvec{\nu}}\) :
-
Poisson's ratio unitless
- \({\varvec{\rho}}\) :
-
Mass density Kg/ m3
- \({\varvec{\sigma}}\) :
-
Stress component N/ m2
- \({\varvec{\tau}}\) :
-
Shear stress component N/ m2
References
Ahmadi H, Bayat A, Duc ND (2021) Nonlinear forced vibrations analysis of imperfect stiffened FG doubly curved shallow shell in thermal environment using multiple scales method. Compos Struct 256:5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113090
Aris H, Ahmadi H (2021) Nonlinear forced vibration and resonance analysis of rotating stiffened FGM truncated conical shells in a thermal environment. Mech Based Des Struct Mach. https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2021.1950011
Baghlani A, Khayat M, Dehghan SM (2020) Free vibration analysis of FGM cylindrical shells surrounded by Pasternak elastic foundation in thermal environment considering fluid-structure interaction. Appl Math Model 78:550–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.10.023
Bhangale RK, Ganesan N (2006) Thermoelastic buckling and vibration behavior of a functionally graded sandwich beam with constrained viscoelastic core. J Sound Vib 295(1–2):294–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2006.01.026
Chakraverty S, Pradhan KK (2014) Free vibration of exponential functionally graded rectangular plates in thermal environment with general boundary conditions. Aerosp Sci Technol 36:132–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2014.04.005
Chan DQ, van Thanh N, Khoa ND, Duc ND (2020) Nonlinear dynamic analysis of piezoelectric functionally graded porous truncated conical panel in thermal environments. Thin-Walled Struct 154:106837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2020.106837
Cong PH, Duc ND (2021) Nonlinear dynamic analysis of porous eccentrically stiffened double curved shallow auxetic shells in thermal environments. Thin-Walled Structures 163:107748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2021.107748
Cong PH, Duc ND (2022) Nonlinear thermo-mechanical analysis of ES double curved shallow auxetic honeycomb sandwich shells with temperature-dependent properties. Compos Struct 279:114739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114739
Dai HL, Dai T, Zheng HY (2013) Creep buckling and post-buckling analyses for a hybrid laminated viscoelastic FGM cylindrical shell under in-plane loading. Int J Mech Mater Des 9(4):309–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-013-9223-0
Darabi M, Darvizeh M, Darvizeh A (2008) Non-linear analysis of dynamic stability for functionally graded cylindrical shells under periodic axial loading. Compos Struct 83(2):201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.04.014
Dat ND, Quan TQ, Duc ND (2021) “Nonlinear thermal dynamic buckling and global optimization of smart sandwich plate with porous homogeneous core and carbon nanotube reinforced nanocomposite layers.” Eur J Mech A/Solids 90:104351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2021.104351
Dinh Duc N, Hong Cong P (2015) Nonlinear vibration of thick FGM plates on elastic foundation subjected to thermal and mechanical loads using the first-order shear deformation plate theory. Cogent Eng. 2:104522. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2015.1045222
Dinh Duc N, Dinh Nguyen P, Dinh Khoa N (2017) “Nonlinear dynamic analysis and vibration of eccentrically stiffened S-FGM elliptical cylindrical shells surrounded on elastic foundations in thermal environments. Thin-Walled Struct 117:178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2017.04.013
Duc ND (2013) Nonlinear dynamic response of imperfect eccentrically stiffened FGM double curved shallow shells on elastic foundation. Compos Struct 99:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.11.017
Duc ND, Cong PH (2015) Nonlinear thermal stability of eccentrically stiffened functionally graded truncated conical shells surrounded on elastic foundations. Eur J Mech, A/Solids 50:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2014.11.006
Duc ND, Quan TQ (2013) Nonlinear postbuckling of imperfect eccentrically stiffened P-FGM double curved thin shallow shells on elastic foundations in thermal environments. Compos Struct 106:590–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.07.010
Duc ND, Quan TQ (2014) Nonlinear response of imperfect eccentrically stiffened FGM cylindrical panels on elastic foundation subjected to mechanical loads. Eur J Mech, A/Solids 46:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2014.02.005
Duc ND, Thang PT (2014) Nonlinear response of imperfect eccentrically stiffened ceramic-metal-ceramic FGM thin circular cylindrical shells surrounded on elastic foundations and subjected to axial compression. Compos Struct 110(1):200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.11.015
Duc ND, Thang PT (2015) Nonlinear dynamic response and vibration of shear deformable imperfect eccentrically stiffened S-FGM circular cylindrical shells surrounded on elastic foundations. Aerosp Sci Technol 40:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2014.11.005
Duc ND, Vuong PM (2022) ‘Nonlinear vibration response of shear deformable FGM sandwich toroidal shell segments.’ Meccanica 57:1083–1103
Duc ND, Cong PH, Quang VD (2016) Nonlinear dynamic and vibration analysis of piezoelectric eccentrically stiffened FGM plates in thermal environment. Int J Mech Sci 115–116:711–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2016.07.010
Duc ND, Quang VD, Nguyen PD, Chien TM (2018) Nonlinear dynamic response of functionally graded porous plates on elastic foundation subjected to thermal and mechanical loads. J Appl Comput Mech 4(4):245–259. https://doi.org/10.22055/jacm.2018.23219.1151
Eipakchi H, Nasrekani FM (2022) Response investigation of viscoelastic cylindrical shells with geometrical nonlinearity effect under moving pressure: an analytical approach. Mech Adv Mater Struct 29(8):1124–1137. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2020.1808916
Foroutan K, Shaterzadeh A, Ahmadi H (2020) Nonlinear static and dynamic hygrothermal buckling analysis of imperfect functionally graded porous cylindrical shells. Appl Math Model 77:539–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.07.062
Foroutan K, Carrera E, Ahmadi H (2021) Static and dynamic hygrothermal postbuckling analysis of sandwich cylindrical panels with an FG-CNTRC core surrounded by nonlinear viscoelastic foundations. Compos Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113214
Fu T, Wu X, Xiao Z, Chen Z, Li J (2021) Vibro-acoustic characteristics of eccentrically stiffened functionally graded material sandwich cylindrical shell under external mean fluid. Appl Math Model 91:214–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2020.09.061
Heidari Y, Arefi M, Irani Rahaghi M (2020) Nonlocal vibration characteristics of a functionally graded porous cylindrical nanoshell integrated with arbitrary arrays of piezoelectric elements. Mech Based Des Struct Mach 50:4246. https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2020.1830799
Hong Cong P, Anh VM, Dinh Duc N (2017) “Nonlinear dynamic response of eccentrically stiffened FGM plate using Reddy’s TSDT in thermal environment. J Therm Stresses 40(6):704–732. https://doi.org/10.1080/01495739.2016.1261614
Hosseini-Hashemi S, Rokni Damavandi Taher H, Akhavan H, Omidi M (2010) Free vibration of functionally graded rectangular plates using first-order shear deformation plate theory. Appl Math Model 34:1276–1291
Husain M, Al-shammari M (2020) Effect of cracks on the natural frequency of cylindrical shell structures. Eng Technol J 38(12):1808–1817. https://doi.org/10.30684/etj.v38i12a.1513
Huy Bich D, van Dung D, Nam VH, Thi Phuong N (2013) Nonlinear static and dynamic buckling analysis of imperfect eccentrically stiffened functionally graded circular cylindrical thin shells under axial compression. Int J Mech Sci 74:190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.06.002
Huy Bicil D, do Long V (2007) “Non-linear dynamical analysis of laminated reinforced composite doubly curved shallow shells. Vietnam J Mech 29:257
Jweeg MJ, Mohammed AD and AAlshamari M (2010) “Theoretical and experimental investigations of vibration characteristics of a combined composite cylindrical-conical shell structure,” “Eng Technol J [Online]. Available: www.pdffactory.com
Kadum Njim E, Bakhy SH, Al-Waily M (2021) Analytical and numerical investigation of buckling load of functionally graded materials with porous metal of sandwich plate. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.557
Karakoti A, Pandey S, Kar VR (2022) Nonlinear transient analysis of porous P-FGM and S-FGM sandwich plates and shell panels under blast loading and thermal environment. Thin-Walled Struct 173:108985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2022.108985
Kumar A, Kumar D (2020) Vibration analysis of functionally graded stiffened shallow shells under thermo-mechanical loading. Mater Today: Proc 44:4590–4595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.826
Li H, Pang F, Chen H, Du Y (2019) Vibration analysis of functionally graded porous cylindrical shell with arbitrary boundary restraints by using a semi analytical method. Compos B Eng 164:249–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.11.046
Liu Y, Qin Z, Chu F (2020) Analytical study of the impact response of shear deformable sandwich cylindrical shell with a functionally graded porous core. Mech Adv Mater Struct. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2020.1818904
Liu Y, Qin Z, Chu F (2021) Nonlinear forced vibrations of FGM sandwich cylindrical shells with porosities on an elastic substrate. Nonlinear Dyn 104(2):1007–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06358-7
Liu Y, Qin Z, Chu F (2021) Nonlinear forced vibrations of functionally graded piezoelectric cylindrical shells under electric-thermo-mechanical loads. Int J Mech Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106474
Liu Y et al (2022) “‘Dynamic responses of corrugated cylindrical shells subjected to nonlinear low-velocity impact. Aerosp Sci Technol 121:107321
Meksi R, Benyoucef S, Mahmoudi A, Tounsi A, Adda Bedia EA, Mahmoud SR (2019) An analytical solution for bending, buckling and vibration responses of FGM sandwich plates. J Sandwich Struct Mater 21(2):727–757. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636217698443
Mirjavadi SS, Forsat M, Barati MR, Hamouda AMS (2020) Geometrically nonlinear vibration analysis of eccentrically stiffened porous functionally graded annular spherical shell segments. Mech Based Des Struct Mach. https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2020.1771729
“Mouthanna A, Hamad MH, and Khalid BN (2018) ‘Nonlinear Vibration Analysis of Functionally Graded Imperfection of Cylindrical Panels Reinforced with Different Types of Stiffeners.’ 2018 11th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE). IEEE, 2018.”.
Ngo Dinh D, Tran Quoc Q, Nguyen Dinh D (2022) Vibration analysis of auxetic laminated plate with magneto-electro-elastic face sheets subjected to blast loading. Compos Struct 280:114925
Nguyen DD (2018) Nonlinear thermo- electro-mechanical dynamic response of shear deformable piezoelectric sigmoid functionally graded sandwich circular cylindrical shells on elastic foundations. J Sandwich Struct Mater 20(3):351–378. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636216653266
Njim E, Bakhi S, Al-Waily M (2022) Experimental and numerical flexural properties of sandwich structure with functionally graded porous materials. Eng Technol J 40(1):137–147. https://doi.org/10.30684/etj.v40i1.2184
Njim EK, Bakhy SH, Al-Waily M (2021) Free vibration analysis of imperfect functionally graded sandwich plates: analytical and experimental investigation. Arch Mater Sci Eng 111(2):49–65. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0015.5805
Njim EK, Bakhy SH, Al-Waily M (2021) Analytical and numerical free vibration analysis of porous functionally graded materials (Fgpms) sandwich plate using rayleigh-ritz method. Arch Mater Sci Eng 110(1):27–41. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0015.3593
Njim EK, Bakhy SH, Al-Waily M (Jul.2021) Analytical and numerical investigation of free vibration behavior for sandwich plate with functionally graded porous metal core. Pertanika J Sci Technol 29(3):1655–1682. https://doi.org/10.47836/pjst.29.3.39
Quan TQ, van Quyen N, Duc ND (2021) “An analytical approach for nonlinear thermo-electro-elastic forced vibration of piezoelectric penta – Graphene plates. Europ J Mech, A/Solids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2020.104095
Quan TQ, Ha DTT, Duc ND (2022) Analytical solutions for nonlinear vibration of porous functionally graded sandwich plate subjected to blast loading. Thin-Walled Struct 170:2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2021.108606
Ruzzene M and Baz A (2001) “Dynamic stability of periodic shells with moving loads,”. [Online]. Available: http://proceedings.spiedigitallibrary.org/
Setoodeh AR, Shojaee M, Malekzadeh P (2019) Vibrational behavior of doubly curved smart sandwich shells with FG-CNTRC face sheets and FG porous core. Compos B Eng 165:798–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.022
Soleimani-Javid Z, Arshid E, Amir S, Bodaghi M (2021) On the higher-order thermal vibrations of FG saturated porous cylindrical micro-shells integrated with nanocomposite skins in viscoelastic medium. Defence Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2021.07.007
Vu HN, Nguyen TP, Ho SL, Vu MD, Cao VD (2021) Nonlinear buckling analysis of stiffened FG-GRC laminated cylindrical shells subjected to axial compressive load in thermal environment. Mech Based Des Struct Mach. https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2021.1932522
Wattanasakulpong N, Chaikittiratana A (2015) Flexural vibration of imperfect functionally graded beams based on Timoshenko beam theory: Chebyshev collocation method. Meccanica 50(5):1331–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-014-0094-8
Yunfei L, Zhaoye Q, Fulei C (2022) Investigation of magneto-electro-thermo-mechanical loads on nonlinear forced vibrations of composite cylindrical shells. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 107:106146
Yun-fei L, Zhao-Ye Q, Fl Liu C (2022) “Nonlinear free vibration of graphene platelets reinforced composite corrugated plates. J Cent South Univ 29:3054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5086-6
Zhang Y, Jin G, Chen M, Ye T, Yang C, Yin Y (2020) Free vibration and damping analysis of porous functionally graded sandwich plates with a viscoelastic core. Compos Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112298
Zhao X, Lee YY, Liew KM (2009) Free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates using the element-free kp-Ritz method. J Sound Vib 319(3–5):918–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2008.06.025
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mouthanna, A., Bakhy, S.H. & Al-Waily, M. Analytical Investigation of Nonlinear Free Vibration of Porous Eccentrically Stiffened Functionally Graded Sandwich Cylindrical Shell Panels. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 47, 1035–1053 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-022-00555-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-022-00555-4