Abstract
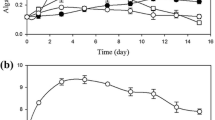
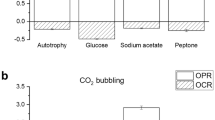
Growing nutrient content of surface waters causes environmental concerns about eutrophication due to the immethodical release of nutrient containing effluent. The potential of microorganisms to decrease nitrogen and phosphorus concentration has drawn increasing attention. The present study is performed to evaluate the nutrient removal potential of cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus in different trophic cultivations. For this purpose, 15 experiments were designed by the Box-Behnken method using modified BG-11, including the initial concentrations of phosphorus, nitrogen, and glucose up to 10 mg L−1, 600 mg L−1, and 10 g L−1, respectively. Different trophic conditions were applied by changing carbon sources and light–dark cycles. The maximal removal of phosphorus and nitrogen were obtained in mixotrophic condition with 85.1% and 87.4%, respectively, and the specific growth rate of microalga was 0.99 day−1. Besides, its nutrient removal efficiency in dairy effluent was about 92% in mixotrophic culture, while the heterotrophic condition was not efficient. Based on the obtained results, mixotrophic cultivation of the cyanobacteria S. elongatus would be useful for application in N-riched and P-riched effluents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alketife AM, Znad H, Judd S (2016) Synergistic effects and optimization of nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth and nutrient uptake of a freshwater Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Technol 38(1):94–102
Arbib Z, Ruiz J, Álvarez-Díaz P, Garrido-Pérez C, Perales JA (2014) Capability of different microalgae species for phytoremediation processes: Wastewater tertiary treatment, CO2 bio-fixation and low cost biofuels production. Water Res 49:465–474
Arias DM, Solé-Bundó M, Garfí M, Ferrer I, García J, Uggetti E (2018) Integrating microalgae tertiary treatment into activated sludge systems for energy and nutrients recovery from wastewater. Biores Technol 247:513–519
Babaei A, Mehrnia MR, Shayegan J, Sarrafzadeh MH (2016) Comparison of different trophic cultivations in microalgal membrane bioreactor containing N-riched wastewater for simultaneous nutrient removal and biomass production. Proc Biochem 51(10):1568–1575
Bhatnagar A, Chinnasamy S, Singh M, Das KC (2011) Renewable biomass production by mixotrophic algae in the presence of various carbon sources and wastewaters. Appl Energy 88(10):3425–3431
Cai T, Park SY, Li Y (2013) Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: status and prospects. Renew Sust Energy 19:360–369
Cai W, Zhao Z, Li D, Lei Z, Zhang Z, Lee DJ (2019) Algae granulation for nutrients uptake and algae harvesting during wastewater treatment. Chemos 214:55–59
Chojnacka K, Noworyta A (2004) Evaluation of Spirulina sp. growth in photoautotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic cultures. Enzyme Microb Technol 34(5):461–465
Fawzy MA, Issa AA (2016) Bioremoval of heavy metals and nutrients from sewage plant by Anabaena oryzae and Cyanosarcina fontana. Int J Phytorem 18(4):321–328
Gao F, Yang ZH, Li C, Zeng GM, Ma DH, Zhou L (2015) A novel algal biofilm membrane photobioreactor for attached microalgae growth and nutrients removal from secondary effluent. Biores Technol 179:8–12
González LE, Cañizares RO, Baena S (1997) Efficiency of ammonia and phosphorus removal from a colombian agroindustrial wastewater by the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus dimorphus. Bioresour Technol 60(3):259–262
González-Camejo J, Barat R, Pachés M, Murgui M, Seco A, Ferrer J (2018) Wastewater nutrient removal in a mixed microalgae–bacteria culture: effect of light and temperature on the microalgae–bacteria competition. Environ Technol 39(4):503–515
Hajimahmoodi M, Faramarzi MA, Mohammadi N, Soltani N, Oveisi MR, Nafissi-Varcheh N (2010) Evaluation of antioxidant properties and total phenolic contents of some strains of microalgae. J Appl Phycol 22(3):43–50
Hanifzadeh M, Sarrafzedeh MH, Nabatu Z, Tavakoli O, Feyzizarnagh H (2018) The technical, economic and energy assessment of an alternative strategy for mass production of biomass and lipid from microalgae. J Environ Chem Eng 6(1):866–873
Hu Q, Westerhoff P, Vermaas W (2000) Removal of nitrate from groundwater by cyanobacteria : quantitative assessment of factors influencing nitrate uptake removal of nitrate from groundwater by cyanobacteria: quantitative assessment of factors influencing nitrate uptake. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(1):133–139
Kim HC, Choi WJ, Chae AN, Park J, Kim HJ (2016) Treating high-strength saline piggery wastewater using the heterotrophic cultivation of Acutodesmus obliquus. Biochem Eng J 110:51–58
Kim S, Park J, Cho YB, Hwang SJ (2013) Growth rate, organic carbon and nutrient removal rates of Chlorella sorokiniana in autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic conditions. Biores Technol 144:8–13
Li C, Yu Y, Zhang D, Liu J, Ren N, Feng Y (2015) Combined effects of carbon, phosphorus and nitrogen on lipid accumulation of Chlorella vulgaris in mixotrophic culture. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:680–684
Liang Y, Sarkany N, Cui Y (2009) Biomass and lipid productivities of Chlorella vulgaris under autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic growth conditions. Biotechnol Let 31(7):1043–1049
Lu W, Wang Z, Wang X, Yuan Z (2015) Cultivation of Chlorella sp. using raw diary wastewater for nutrient removal and biodiesel production: characteristics comparison of indoor bench-scale and outdoor pilot-scale cultures. Biores Technol 192:382–388
Mahdavi HR, Azizi N, Mohammadi T (2017) Performance evaluation of a synthesized and characterized Pebax1657/PEG1000/γ-Al2O3 membrane for CO2/CH4 separation using response surface methodology. J Polym Res 24:1–15
Martínez M, Sánchez S, Jiménez JM, Yousfi F, Muñoz L (2000) Nitrogen and phosphorus removal from urban wastewater by the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. Bioresour Technol 73(3):263–272
Mashayekhi M, Sarrafzadeh MH, Tavakoli O, Soltani N, Faramarzi MA (2017) Potential for biodiesel production and carbon capturing from Synechococcus Elongatus: an isolation and evaluation study. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 9:230–235
Mastala Z, Herodek S, V-Balogh K, Borbely G, Shafik HM, Voros L (1996) Nutrient requirement and growth of a Synechococcus species isolated from Lake Balaton. Int Rev Hydrobiol 81(4):503–512
Mogharabi M, Faramarzi MA (2016) Are algae the future source of enzymes? Tren Pept Prot Sci 1(1):1–6
Órpez R, Martínez ME, Hodaifa G, Yousfi FE, Jbari N, Sánchez S (2009) Growth of the microalga Botryococcus braunii in secondarily treated sewage. Desalination 246(1–3):625–630
Perez-Garcia O, de-BashanHernandezBashan LEJPY (2010) Efficiency of growth and nutrient uptake from wastewater by heterotrophic, autotrophic, and mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris immobilized with Azospirillum brasilense. J Phycol 46(4):800–812
Perez-Garcia O, Escalante FME, de-BashanBashan ELY (2011) Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: metabolism and potential products. Water Res 45(1):11–36
Praveen P, Loh KC (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus removal from tertiary wastewater in an osmotic membrane photobioreactor. Biores Technol 206:180–187
Ruiz-Güereca DA, Pilar Sánchez-Saavedra M (2016) Growth and phosphorus removal by Synechococcus elongatus co-immobilized in alginate beads with Azospirillum brasilense. J Appl Phycol 28(3):1501–1507
Salama ES, Kurade MB, Abou-Shanab RAI, El-Dalatony MM, Yang IS, Min B, Jeon BH (2017) Recent progress in microalgal biomass production coupled with wastewater treatment for biofuel generation. Renew Sust Energy 79:1189–1211
Sarrafzadeh MH, La HJ, Lee JY, Cho DH, Shin SY, Kim WJ, Oh HM (2014) Microalgae biomass quantification by digital image processing and RGB color analysis. J Appl Phycol 27(1):205–209
Xin L, Hong-ying H, Ke G, Jia Y (2010) Growth and nutrient removal properties of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. LX1 under different kinds of nitrogen sources. Ecol Eng 36(4):379–381
Yan R, Zhu D, Zhang Z, Zeng Q, Chu J (2012) Carbon metabolism and energy conversion of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 under mixotrophic conditions: comparison with photoautotrophic condition. J Appl Phycol 24(4):657–668
Yu G, Shi D, Cai Z, Cong W, Ouyang F (2011) Growth and physiological features of Cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 in a glucose-mixotrophic culture. Chin J Chem Eng 19(1):108–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pishbin, M., Sarrafzadeh, MH. & Faramarzi, M.A. Nitrate and Phosphate Removal Efficiency of Synechococcus elongatus Under Mixotrophic and Heterotrophic Conditions for Wastewater Treatment. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 45, 1831–1843 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00514-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00514-6