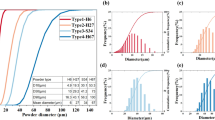
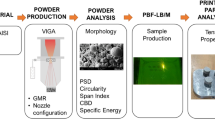
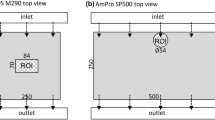
Abstract
In the laser-based powder bed fusion process (L-PBF), the used powder is exposed to a multitude of mechanical and atmospheric parameters along the entire process chain, beginning with the production of the powder, over transportation, storage and processing and ending with the recycling of the material. The chemical composition and shape of individual powder particles, for example, as well as the characteristic properties of the entire powdered material change depending on the duration and intensity of the effects of, among other things, the atmosphere, temperature, humidity and external forces. Once the influencing variables and their effects are known, the changes in the powder can be counteracted in a targeted manner. In this way, it is possible to restore or maintain the powder properties relevant to the L-PBF process, making the overall process more robust and reliable. This paper discusses the results of investigations on significant influencing factors that cause a change in the powder material during L-PBF, representing the cost-intensive titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. The results can be used to derive powder handling and management recommendations that can ensure powder quality throughout the service life.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford S, Despeisse M (2016) Additive manufacturing and sustainability: an exploratory study of the advantages and challenges. J Clean Prod 137:1573–1587
Alcisto J, Enriquez A, Garcia H, Hinkson S, Steelman T, Silverman E, Valdovino P, Gigerenzer H, Foyos J, Ogren J, Dorey J, Karg K, McDonald T, Es-Said OS (2011) Tensile properties and microstructures of laser-formed Ti-6Al-4V. J Mater Eng Perform 20:203–212
Shipley H, McDonnell D, Culleton M, Coull R, Lupoi R, O’Donnell G, Trimble D (2018) Optimisation of process parameters to address fundamental challenges during selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V: a review. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 128:1–20
Günther ML, Schwer F, Seidel C, Reinhart G (2016) Effects on properties of metal powders for laser beam melting along the powder process chain. In: Proceedings of the Fraunhofer direct digital manufacturing conference DDMC 2016, pp 1–8
Lutter-Günther M, Horn M, Seidel C, Reinhart G (2017) Einfluss der Korngrößenverteilung auf Fließfähigkeit und Bauteilqualität beim Laserstrahlschmelzen. Rapid Tech Int Trade Show Conf Addit Manuf.:297–311
Sutton AT, Kriewall CS, Leu MC, Newkirk JW (2017) Powder characterisation techniques and effects of powder characteristics on part properties in powder-bed fusion processes. Virtual Phys Prototyp 12:3–29
Matthes S, Kahlenberg R, Jahn S, Straube C (2016) About the influence of powder properties on the selective laser melting process. Fraunhofer Direct Digital Manufacturing Conference pp 1–5
Dietrich K, Messé OMDM, Schobert A, Arunprasad T, Szost B, Foret P, Gerd W, Gmbh OAM (2019) Influence of humidity in Ti-6Al-4V powder during storage—part 1. Euro PM, pp 2–8
Dietrich K, Messé OMDM, Schobert A, Arunprasad T, Szost B, Foret P, Gerd W, Gmbh OAM (2019) Influence of humidity in Ti-6Al-4V powder during storage—part 2. Euro PM, pp 1–6
Lutter-Günther M, Bröker M, Mayer T, Lizak S, Seidel C, Reinhart G (2018) Spatter formation during laser beam melting of AlSi10Mg and effects on powder quality. Procedia CIRP 74:33–38
DIN 65122 (2017) Luft- und Raumfahrt—Pulver zur Verwendung für die additive Fertigung mittels Pulverbettverfahren—Technische Lieferbedingungen
Acknowledgements
The presented results were part of a research project (IGF- project 19204 BG) carried out in the framework of the industrial collective research programme. It was supported by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi) through the AiF (German Federation of Industrial Research Associations eV) based on a decision taken by the German Bundestag.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matthes, S., Kluge, M., Jahn, S. et al. Factors influencing powder-properties of TiAl6V4 along the L-PBF process chain. Prog Addit Manuf 5, 33–39 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-020-00120-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-020-00120-y