Abstract
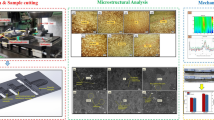
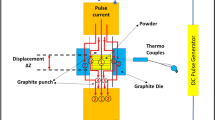
In the present study, the effect of processing temperature on the characteristics of in situ AlSi5Cu3/TiB2 composites is investigated. The AlSi5Cu3/TiB2 composites were synthesized (using K2TiF6 and KBF4) at three different processing temperatures (750, 800, and 850°C) with constant processing time (60 minutes) and cast into the metal mold. The XRD analysis, microscopic examination, and EDS analysis revealed that only TiB2 particles were present in 800°C processed composites without any intermetallics, whereas, the presence of Al3Ti intermetallics along with TiB2 particles was observed in 750 and 850°C processed composites. In 800°C processed composites, significant grain refinement was occurring owing to the presence of more TiB2 particles acting as nuclei as compared to 750 and 850°C processed composites. Due to the presence of more TiB2 particles and the absence of Al3Ti intermetallics, hardness, tensile strength, compressive strength, impact strength, and flexural strength of 800°C processed composites were improved compared to 750 and 850°C processed composites. Considering microstructural characteristics and mechanical behavior, it was observed that in situ AlSi5Cu3/TiB2 composites were effectively developed at 800°C processing temperature.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.P. Barot, R.P. Desai, M.P. Sutaria, Recycling of aluminium matrix composites (AMCs): a review and the way forward. Inter. Metalcast. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00905-7
A. Ramanathan, P.K. Krishnan, R. Muraliraja, A review on the production of metal matrix composites through stir casting–Furnace design, properties, challenges, and research opportunities. J. Manuf. Process. 42, 213–245 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.04.017
S. Poria, P. Sahoo, G. Sutradhar, Tribological characterization of Stir-cast aluminium-TiB2 metal matrix composites. SILICON 8, 591–599 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9437-5
A. Mandal, B.S. Murty, M. Chakraborty, Wear behaviour of near eutectic Al–Si alloy reinforced with in-situ TiB2 particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 506, 27–33 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.11.007
V.S. Ayar, M.P. Sutaria, Comparative evaluation of Ex situ and in situ method of fabricating aluminum/TiB2 composites. Inter. Metalcast. 15, 1047–1056 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00539-7
S. Suresh, N.S.V. Moorthi, S.C. Vettivel, N. Selvakumar, Mechanical behavior and wear prediction of stir cast Al–TiB2 composites using response surface methodology. Mater. Des. 59, 383–396 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.053
Y. Pazhouhanfar, B. Eghbali, Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of TiB2 reinforced Al6061 matrix composites produced using stir casting process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 710, 172–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.10.087
M.K. Akbari, H.R. Baharvandi, K. Shirvanimoghaddam, Tensile and fracture behavior of nano/micro TiB2 particle reinforced casting A356 aluminum alloy composites. Mater. Des. 66, 150–161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.048
M. Manoj, G.R. Jinu, J.S. Kumar, V. Mugendiran, Effect of TiB2 particles on the morphological, mechanical and corrosion behaviour of Al7075 metal matrix composite produced using stir casting process. Inter. Metalcast. 16, 1517–1532 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00696-3
D. Dey, A. Biswas, Comparative study of physical, mechanical and tribological properties of Al2024 alloy and SiC–TiB2 composites. SILICON 13, 1895–1906 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00560-9
S.L. Pramod, S.R. Bakshi, B.S. Murty, Aluminum-based cast in situ composites: a review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24, 2185–2207 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1424-2
M. Emamy, M. Mahta, J. Rasizadeh, Formation of TiB2 particles during dissolution of TiAl3 in Al–TiB2 metal matrix composite using an in situ technique. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 1063–1066 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.04.016
K.L. Tee, L. Lu, M.O. Lai, In situ stir cast Al–TiB2 composite: processing and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Technol. 17, 201–206 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1179/026708301101509863
B. Yang, Y.Q. Wang, B.L. Zhou, The mechanism of formation of TiB2 particulates prepared by in situ reaction in molten aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 29, 635–640 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-998-0098-7
C.S. Ramesh, S. Pramod, R. Keshavamurthy, A study on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al 6061–TiB2 in-situ composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528, 4125–4132 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.024
A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, A metallographic study of grain refining of Sr-modified 356 alloy. Inter. Metalcast. 11, 305–320 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0075-x
A. Changizi, A. Kalkanli, N. Sevinc, Production of in situ aluminum–titanium diboride master alloy formed by slag–metal reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 237–240 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.08.089
V.S. Ayar, M.P. Sutaria, Development and characterization of in situ AlSi5Cu3/TiB2 composites. Inter. Metalcast. 14, 59–68 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00328-x
L. Lü, M. Lai, Y. Su, H. Teo, C. Feng, In situ TiB2 reinforced Al alloy composites. Scr. Mater. 45, 1017–1023 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(01)01128-9
B.S. Murty, S.A. Kori, M. Chakraborty, Grain refinement of aluminium and its alloys by heterogeneous nucleation and alloying. Int. Mater. Rev. 47, 3–29 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1179/095066001225001049
S. Mozammil, J. Karloopia, R. Verma, P.K. Jha, Effect of varying TiB2 reinforcement and its ageing behaviour on tensile and hardness properties of in-situ Al-4.5%Cu-xTiB2 composite. J. Alloys Compd. 793, 454–466 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.137
R.P. Barot, M.P. Sutaria, Effect of casting thickness on mechanical properties of AlSi5Cu3 Aluminium alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 62, 3330–3335 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.243
R.P. Barot, M.P. Sutaria, Effect of multiple remelting on behaviour of AlSi5Cu3 Aluminium alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 62, 4046–4051 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.608
Y. Zhang, N. Ma, H. Wang, Y. Le, X. Li, Damping capacity of in situ TiB2 particulates reinforced aluminium composites with Ti addition. Mater. Des. 28, 628–632 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2005.07.015
Z. Chen, T. Wang, Y. Zheng, Y. Zhao, H. Kang, L. Gao, Development of TiB2 reinforced aluminum foundry alloy based in situ composites–Part I: an improved halide salt route to fabricate Al–5 wt%TiB2 master composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 605, 301–309 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.02.088
C.F. Feng, L. Froyen, Microstructures of in situ Al/TiB2 MMCs prepared by a casting route. J. Mater. Sci. 35, 837–850 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004729920354
S. Kumar, M. Chakraborty, V.S. Sarma, B.S. Murty, Tensile and wear behaviour of in situ Al–7Si/TiB2 particulate composites. Wear 265, 134–142 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2007.09.007
G.K. Sigworth, T.A. Kuhn, Grain refinement of aluminum casting alloys. Inter. Metalcast. 1, 31–40 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355416
H.B.M. Rajan, S. Ramabalan, I. Dinaharan, S.J. Vijay, Synthesis and characterization of in situ formed titanium diboride particulate reinforced AA7075 aluminum alloy cast composites. Mater. Des. 44, 438–445 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.08.008
H.B.M. Rajan, S. Ramabalan, I. Dinaharan, S.J. Vijay, Effect of TiB2 content and temperature on sliding wear behavior of AA7075/TiB2 in situ aluminum cast composites. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 14, 72–79 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2013.05.005
Y. Birol, An improved practice to manufacture Al–Ti–B master alloys by reacting halide salts with molten aluminium. J. Alloys Compd. 420, 71–76 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.10.017
X. Liu, Y. Liu, D. Huang, Q. Han, X. Wang, Tailoring in-situ TiB2 particulates in aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 705, 55–61 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.08.047
N. El-Mahallawy, M.A. Taha, A.E. Jarfors, H. Fredriksson, On the reaction between aluminium, K2TiF6 and KBF4. J. Alloys Compd. 292, 221–229 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(99)00294-7
T. Wang, Z. Chen, Y. Zheng, Y. Zhao, H. Kang, L. Gao, Development of TiB2 reinforced aluminum foundry alloy based in situ composites–Part II: enhancing the practical aluminum foundry alloys using the improved Al–5 wt%TiB2 master composite upon dilution. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 605, 22–32 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.03.021
Y. Yu, Z. Cao, J. Wang, G. Tu, Y. Mu, Compressive behavior of Al-TiB2 composite foams fabricated under increased pressure. Materials. 14, 5112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14175112
V. Mohanavel, K.R. Kumar, T. Sathish, P. Velmurugan, A. Karthick, M. Ravichandran, S. Alfarraj, H.S. Almoallim, S.S. Kumar, J.I.J. Lalvani, Investigation on inorganic salts K2TiF6 and KBF4 to develop nanoparticles based TiB2 reinforcement aluminium composites. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 1–13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8559402
J.V. Christy, R. Arunachalam, A.H.I. Mourad, P.K. Krishnan, S. Piya, M. Al-Maharbi, Processing, properties, and microstructure of recycled aluminum alloy composites produced through an optimized stir and squeeze casting processes. J. Manuf. Process. 59, 287–301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.09.067
P.K. Krishnan, J.V. Christy, R. Arunachalam, A.H.I. Mourad, R. Muraliraja, M. Al-Maharbi, V. Murali, M.M. Chandra, Production of aluminum alloy-based metal matrix composites using scrap aluminum alloy and waste materials: influence on microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 784, 1047–1061 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.115
E. Samuel, B. Golbahar, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Effect of grain refiner on the tensile and impact properties of Al–Si–Mg cast alloys. Mater. Des. 56, 468–479 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.058
X. Zhang, X.Y. Yue, H.Q. Ru, Effect of in-situ synthesized TiB2 on microstructure and mechanical property of Al/TiB2 -SiC interpenetrating phase composites. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 10, 531–544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/21870764.2022.2082643
T. Wang, Y. Zheng, Z. Chen, Y. Zhao, H. Kang, Effects of Sr on the microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ TiB2 reinforced A356 composite. Mater. Des. 64, 185–193 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.07.040
A. Pineau, A.A. Benzerga, T. Pardoen, Failure of metals I: brittle and ductile fracture. Acta Mater. 107, 424–483 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.12.034
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India sponsored SMART Foundry project (DST/TSG/AMT/2015/332 dated 17/08/2016). The authors acknowledge Charotar University of Science and Technology (CHARUSAT) for providing technical support and facilities. The authors are grateful to the editor-in-chief for assigning competitive reviewers to evaluate the manuscript. Moreover, the authors acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for providing comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RPB contributed to conceptualization, methodology, experimentation, investigation, data curation, original draft preparation. RPD contributed to conceptualization, analysis, review, editing, supervision. MPS contributed to conceptualization, overall review, editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. No funding was received for conducting this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barot, R.P., Desai, R.P. & Sutaria, M.P. Effect of Processing Temperature on the Synthesis of In Situ AlSi5Cu3/TiB2 Composites Cast in Metal Mold: Structural and Mechanical Characterizations. Inter Metalcast 18, 915–932 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01067-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01067-w