Abstract
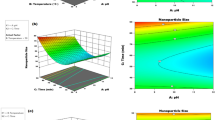
Dyes present a significant environmental challenge as major pollutants in wastewater. Their presence in wastewater not only contaminates surface and groundwater but also poses a threat to human health and disrupts the ecological balance. To address this issue, this study investigates the efficacy of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in removing Eosin Y (Eo-Y) and Erythrosin B (Er-B) from aqueous solutions. The central composite design (CCD) plan combined with response surface methodology (RSM) is employed to assess its predictive capability. Utilizing nZVI as an adsorbent, the maximum adsorption capacity (qmax) is determined to be 10.81 mg/g for Eo-Y and 10.35 mg/g for Er-B. The adsorption process of Eo-Y and Er-B on nZVI follows a pseudo-second-order kinetic model, indicating chemisorption mechanisms. The removal of Eo-Y and Er-B on nZVI is accurately described by Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherm models. Furthermore, density functional theory (DFT) modeling uncovers the presence of hydrogen bonds and dipole–dipole interactions between the dyes and the adsorbent. Based on the calculated DFT-based descriptors, both Eo-Y and Er-B exhibit small chemical hardness values, suggesting their reactivity. Notably, Eo-Y demonstrates higher hardness compared to Er-B. Overall, the study’s findings demonstrate the remarkable effectiveness of nZVI in removing Eo-Y and Er-B from aqueous solutions.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in this article.
Availability of data and materials (data transparency)
All data and materials, as well as the software application, used to support their published claims and comply with field standards.
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Not available.
References
Ahmadi S, Mohammadi L, Igwegbe CA, Rahdar S, Banach AM (2018) Application of response surface methodology in the degradation of reactive Blue 19 using H2O2/MgO nanoparticles advanced oxidation process. Int J Ind Chem 9:241–253
Ahmadi S, Mohammadi L, Rahdar A, Rahdar S, Dehghani R, Adaobi Igwegbe C, Kyzas GZ (2020) Acid dye removal from aqueous solution by using neodymium (III) oxide nanoadsorbents. Nanomaterials 10:556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030556
Ahmadi S, Mesbah M, Igwegbe CA, Ezeliora CD, Osagie C, Khan NA, Dotto GL, Salari M, Dehghani MH (2021) Sono electro-chemical synthesis of LaFeO3 nanoparticles for the removal of fluoride: Optimization and modeling using RSM, ANN and GA tools. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105320
Ahmadi S, Ghosh S, Malloum A, Bornman C, Osagie C, Mohammadi L, Igwegbe CA (2022) Modeling the liquid-phase adsorption of cephalexin onto coated iron nanoparticles using response surface and molecular modeling. Adsorpt Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7619063
Ajemba R, Onukwuli O (2012) Response surface optimization of palm oil bleaching using hydrochloric acid activated Ukpor clay. Eur J Sci Res 82:325–335
Al-Degs YS, Abu-El-Halawa R, Abu-Alrub SS (2012) Analyzing adsorption data of erythrosine dye using principal component analysis. Chem Eng J 191:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.002
Aniagor C, Abdel-Halim E, Hashem A (2021) Evaluation of the aqueous Fe(II) ion sorption capacity of functionalized microcrystalline cellulose. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105703
Aniagor CO, Igwegbe CA, Iwuozor KO, Iwuchukwu FU, Eshiemogie S, Menkiti MC, Ighalo JO (2022) CuO nanoparticles as modifiers for membranes: a review of performance for water treatment. Mat Today Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103896
Bagheri AR, Ghaedi M, Asfaram A, Bazrafshan AA, Jannesar R (2017) Comparative study on ultrasonic assisted adsorption of dyes from single system onto Fe3O4 magnetite nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: experimental design methodology. Ultrason Sonochem 34:294–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.05.047
Balarak D, Chandrika K, Igwegbe CA, Ahmadi S, Umembamalu CJ (2020) Biosorption of phenol using modified barley husk: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamics of interactions. Sigma J Eng & Nat Sci 38:1161–1177
Bhatnagar A, Hogland W, Marques M, Sillanpää M (2013) An overview of the modification methods of activated carbon for its water treatment applications. Chem Eng J 219:499–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.038
Carmen Apostol L, Ghinea C, Alves M, Gavrilescu M (2016) Removal of Erythrosine B dye from water effluents using crop waste pumpkin seed hulls as adsorbent. Desalination Water Treat 57:22585–22608. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1132477
Cashin VB, Eldridge DS, Yu A, Zhao D (2018) Surface functionalization and manipulation of mesoporous silica adsorbents for improved removal of pollutants: a review. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 4:110–128. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00322F
Chatterjee S, Chatterjee S, Chatterjee BP, Das AR, Guha AK (2005) Adsorption of a model anionic dye, eosin Y, from aqueous solution by chitosan hydrobeads. J Colloid Interface Sci 288:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.02.055
Chequer FD, De Oliveira GR, Ferraz EA, Cardoso JC, Zanoni MB, De Oliveira DP (2013) Textile dyes: dyeing process and environmental impact. Eco Friendly Text Dyeing Finish 6:151–176. https://doi.org/10.5772/53659
Egbosiuba TC, Abdulkareem AS, Kovo AS, Afolabi EA, Tijani JO, Bankole MT, Bo S, Roos WD (2021) Adsorption of Cr(VI), Ni(II), Fe(II) and Cd(II) ions by KIAgNPs decorated MWCNTs in a batch and fixed bed process. Sci Rep 11:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79857-z
Ekpotu WF, Ighalo JO, Nkundu K-aB, Onu PO, Adeniyi AG (2020) Analysis of factor effects and interactions in a conventional drilling operation by response surface methodology and historical data design. Pet Coal 62:356–1368
Eletta OA, Adeniyi AG, Ighalo JO, Onifade DV, Ayandele FO (2020) Valorisation of Cocoa (Theobroma cacao) pod husk as precursors for the production of adsorbents for water treatment. Environ Technol Rev 9:20–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2020.1730983
Elhami S, Abrishamkar M, Esmaeilzadeh L (2013) Preparation and characterization of diethylentriamine-montmorillonite and its application for the removal of Eosin Y dye: optimization, kinetic and isotherm studies. J Sci Ind Res 7:461–466
Ezzatahmadi N, Ayoko GA, Millar GJ, Speight R, Yan C, Li J, Li S, Zhu J, Xi Y (2017) Clay-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composite materials for the remediation of contaminated aqueous solutions: a review. Chem Eng J 312:336–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.154
Fazlzadeh M, Ansarizadeh M, Leili M (2018) Data of furfural adsorption on nano zero valent iron (NZVI) synthesized from Nettle extract. Data Brief 16:341–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.035
Hacıosmanoğlu GG, Mejías C, Martín J, Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2022) Antibiotic adsorption by natural and modified clay minerals as designer adsorbents for wastewater treatment: a comprehensive review. J Environ Manag 317:115397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115397
Haoyu SY, He X, Li SL, Truhlar DG (2016) MN15: a Kohn–Sham global-hybrid exchange–correlation density functional with broad accuracy for multi-reference and single-reference systems and noncovalent interactions. Chem Sci 7:5032–5051. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00705H
Hashem A, Aniagor CO, Nasr MF, Abou-Okeil A (2021) Efficacy of treated sodium alginate and activated carbon fibre for Pb(II) adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 176:201–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.067
Hevira L, Ighalo JO, Aziz H, Zein R (2021) Terminalia catappa shell as low-cost biosorbent for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. J Ind Eng Chem 97:188–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.01.028
Ighalo JO, Igwegbe CA, Aniagor CO, Oba SN (2021) A review of methods for the removal of penicillins from water. J Water Process Eng 39:101886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101886
Igwegbe CA, Umembamalu CJ (2022) Synthetic anthraquinone vat dye removal on NaCl-activated agro biomass: process characterisation and modelling. Trop J Eng Sci Technol 1:149–167
Igwegbe CA, Mohmmadi L, Ahmadi S, Rahdar A, Khadkhodaiy D, Dehghani R, Rahdar S (2019) Modeling of adsorption of methylene blue dye on Ho-CaWO4 nanoparticles using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) techniques. MethodsX 6:1779–1797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.07.016
Igwegbe CA, Onukwuli OD, Ighalo JO, Okoye PU (2020a) Adsorption of cationic dyes on Dacryodes edulis seeds activated carbon modified using phosphoric acid and sodium chloride. Environ Process 7:1151–1171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00467-y
Igwegbe CA, Onukwuli OD, Onyechi KK, Ahmadi S (2020b) Equilibrium and kinetics analysis on vat yellow 4 uptake from aqueous environment by modified rubber seed shells: nonlinear modelling. J Mater Environ Sci 11:1424–1444
Jeevanandam J, Barhoum A, Chan YS, Dufresne A, Danquah MK (2018) Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:1050–1074. https://doi.org/10.3762/2Fbjnano.9.98
Kyzas GZ, Kostoglou M, Lazaridis NK, Bikiaris DN (2013) Decolorization of dyeing wastewater using polymeric absorbents—an overview. Eco-friendly textile dyeing and Finishing ed Intech, M Günay, pp 177–206
Lee X, Lee L, Foo L, Tan K, Hassell D (2012) Evaluation of carbon-based nanosorbents synthesised by ethylene decomposition on stainless steel substrates as potential sequestrating materials for nickel ions in aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 24:1559–1568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60987-X
Leili M, Fazlzadeh M, Bhatnagar A (2018) Green synthesis of nano-zero-valent iron from Nettle and Thyme leaf extracts and their application for the removal of cephalexin antibiotic from aqueous solutions. Environ Technol 39:1158–1172
Mahvi AH, Rahdar A, Igwegbe CA, Rahdar S, Ahmadi S (2020) Fluoride removal from aqueous solutions by zinc oxide nanoparticles. Fluoride 53:531–541
Mesbah M, Hamedshahraki S, Ahmadi S, Sharifi M, Igwegbe CA (2020) Hydrothermal synthesis of LaFeO3 nanoparticles adsorbent: Characterization and application of error functions for adsorption of fluoride. MethodsX 7:100786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2020.100786
Mohamed OA, Masood SH, Bhowmik JL (2016) Optimization of fused deposition modeling process parameters for dimensional accuracy using I-optimality criterion. Measurement 81:174–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2015.12.011
Mohebbi P, Parvini M, Zavar Mousavi H (2014) Removal of erythrosine dyes from aquatic environment using Ziziphus nummularia kernel. Iran (iranica) J Energy Environ 5:400–406. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ijee.2014.05.04.08
Mouni L, Belkhiri L, Bollinger J-C, Bouzaza A, Assadi A, Tirri A, Dahmoune F, Madani K, Remini H (2018) Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solutions by adsorption on Kaolin: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Appl Clay Sci 153:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.034
Mutuk T, Mesci B (2014) Analysis of mechanical properties of cement containing boron waste and rice husk ash using full factorial design. J Clean Prod 69:128–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.01.051
Nwobi-Okoye CC, Uzochukwu CU (2020) RSM and ANN modeling for production of Al 6351/egg shell reinforced composite: multi objective optimization using genetic algorithm. Mat Today Commun 22:100674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100674
Oba SN, Ighalo JO, Aniagor CO, Igwegbe CA (2021) Removal of ibuprofen from aqueous media by adsorption: a comprehensive review. Sci Total Environ 780:146608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146608
Ohale P, Uzoh C, Onukwuli O (2017) Optimal factor evaluation for the dissolution of alumina from Azaraegbelu clay in acid solution using RSM and ANN comparative analysis. S Afr J Chem Eng 24:43–54
Onokwai A, Owamah H, Ibiwoye M, Ayuba G, Olayemi O (2022) Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for the optimization of energy generation from Jebba hydro-power plant, Nigeria. ISH J Hydraul Eng 28:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2020.1806120
Othmani A, Kesraoui A, Seffen M (2021) Removal of phenol from aqueous solution by coupling alternating current with biosorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:46488–46503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09976-7
Oyelude EO, Awudza JA, Twumasi SK (2017) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study of removal of eosin yellow from aqueous solution using teak leaf litter powder. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12424-1
Ponnusamy SK, Subramaniam R (2013) Process optimization studies of Congo red dye adsorption onto cashew nut shell using response surface methodology. Int J Ind Chem 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5547-4-17
Porkodi K, Kumar KV (2007) Equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism modeling and simulation of basic and acid dyes sorption onto jute fiber carbon: Eosin yellow, malachite green and crystal violet single component systems. J Hazard Mater 143:311–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.029
Qu X, Alvarez PJ, Li Q (2013) Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res 47:3931–3946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.058
Rahdar S, Taghavi M, Khaksefidi R, Ahmadi S (2019) Adsorption of arsenic (V) from aqueous solution using modified saxaul ash: isotherm and thermodynamic study. Appl Water Sci 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0974-0
Rani MJ, Murugan M, Subramaniam P, Subramanian E (2016) Study of water soluble dyes adsorption from aqueous solution by Prosopis spicigera L. wood (PSLW) carbon. Indian J Chem Technol. https://doi.org/10.56042/ijct.v23i1.4019
Rashtbari Y, Afshin S, Hamzezadeh A, Gholizadeh A, Ansari FJ, Poureshgh Y, Fazlzadeh M (2022) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon prepared from walnut peel extract for the removal of Eosin Y and Erythrosine B dyes from aqueous solution: Experimental approaches, kinetics models, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16006-7
Ruan Y, Kong L, Zhong Y, Diao Z, Shih K, Wang S, Chen D (2021) Review on the synthesis and activity of iron-based catalyst in catalytic oxidation of refractory organic pollutants in wastewater. J Clean Prod 321:128924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128924
Sarmah D, Karak N (2020) Double network hydrophobic starch based amphoteric hydrogel as an effective adsorbent for both cationic and anionic dyes. Carbohydr Polym 242:116320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116320
Sivashankar R, Sathya A, Vasantharaj K, Sivasubramanian V (2014) Magnetic composite an environmental super adsorbent for dye sequestration—a review. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 1:36–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2014.06.001
Tetteh E, Rathilal S, Chollom M (2017) Treatment of industrial mineral oil wastewater-optimisation of coagulation flotation process using response surface methodology (RSM). Int J Appl Eng Res 12:13084–13091
Zhang L, Hu P, Wang J, Huang R (2016) Adsorption of Amido Black 10B from aqueous solutions onto Zr (IV) surface-immobilized cross-linked chitosan/bentonite composite. Appl Surf Sci 369:558–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.217
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr. Swagata Ghosh, Assistant Professor of English, Kumaraguru College of Arts and Science, Coimbatore, India for editing this manuscript.
Funding
The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SG: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and validation; SA: conceptualization, data curation, methodology, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing; AM: writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing; LM: writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing; CAI: conceptualization, investigation, data curation, software analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, supervision, and validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Compliance with ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies involving human or animal subjects.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Ahmadi, S., Malloum, A. et al. Liquid-phase adsorption modeling of Eosin Y and Erythrosin B dyes onto nanoscale zero-valent iron using response surface and computational methodologies. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 9, 160 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00940-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00940-0