Abstract
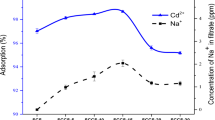
Naturally occurring low-rank Pakistani coal was studied for the adsorptive removal of silver ions from aqueous solutions. A series of essential physico-chemical conditions were optimized as a function of concentration of electrolytes (\({\mathrm{HNO}}_{3}, {\mathrm{H}}_{2}{\mathrm{SO}}_{4},\mathrm{ and }{\mathrm{HClO}}_{4}\)), weight of coal, equilibration time, temperature, initial concentration of adsorbate, and the quantification of silver was made by atomic absorption spectrometric technique. Maximum sorption of silver ions i.e., 96% (percentage efficiency of coal) was achieved at 0.0001 mol/L \({\mathrm{HNO}}_{3}\) solution, with 0.75 g of coal for 10 mL of 9.271 × 10−5 mol/L of silver ion concentration using 30 min equilibration time. The sorption of silver followed pseudo-second order kinetics with overall intra-particle/film diffusion process. The determined rate constant \({\mathrm{K}}_{2}\) was 14.303 g/mg min. Sorption data obeyed Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms over the silver concentration range of 9.271 × 10−5 to 1.391 × 10−3 mol/L. The Langmuir constants Q = 9.366 × 10−3 m mol/g and b = 20.238 × 103 \({\mathrm{dm}}^{3}/\mathrm{ mol}\) have been computed for the sorption system. The determined sorption energy from the Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm was 12.91 kJ/mol indicating chemisorption phenomena. The sorption of silver was increased with the rise in temperature (278–333 K) indicating endothermic process. Thermodynamic parameters i.e., ΔG, ΔH and ΔS have also been computed and discussed for the system. The low-rank Pakistani coal was characterized using FTIR and SEM both before and after sorption of silver ions. The influence of various foreign ions on the sorption of silver in solution and desorption has also been studied.
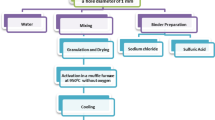
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Akgül M, Karabakan A, Acar O, Yürüm Y (2006) Removal of silver (I) from aqueous solutions with clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 94(1–3):99–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2006.02.023
Ardejani FD, Badii K, Limaee NY, Mahmoodi N, Arami M, Shafaei S, Mirhabibi A (2007) Numerical modelling and laboratory studies on the removal of direct red 23 and direct red 80 dyes from textile effluents using orange peel, a low-cost adsorbent. Dyes Pigm 73(2):178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.11.011
Ardejani FD, Badii K, Limaee NY, Shafaei SZ, Mirhabibi A (2008) Adsorption of Direct Red 80 dye from aqueous solution onto almond shells: effect of pH, initial concentration and shell type. J Hazard Mater 151(2–3):730–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.048
Arslan G, Cetin S, Pehlivan E (2007) Removal of Cu (II) and Ni (II) from aqueous solution by lignite-based humic acids. Energy Sourc Part a: Recovery, Util Environ Effects 29(7):619–630. https://doi.org/10.1080/009083190957711
Baruah MK, Upreti MC (1994) Preferential uptake of Fe (III) by humic acid extracted from lignite. Fuel 73(2):273–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(94)90124-4
Batool M, Javed T, Wasim M, Zafar S, Din MI (2021) Exploring the usability of Cedrus deodara sawdust for decontamination of wastewater containing crystal violet dye. Desalin Water Treat 224:433–448. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27192
Begum S (2003) Silver removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on concrete particles. Turk J Chem 27(5):609–618
Behbahani M, Najafi F, Amini MM, Sadeghi O, Bagheri A, Hassanlou PG (2014) Solid phase extraction using nanoporous MCM-41 modified with 3, 4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde for simultaneous preconcentration and removal of gold (III), palladium (II), copper (II) and silver (I). J Ind Eng Chem 20(4):2248–2255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.09.057
Behnamfard A, Salarirad MM, Veglio F (2013) Process development for recovery of copper and precious metals from waste printed circuit boards with emphasize on palladium and gold leaching and precipitation. Waste Manag 33(11):2354–2363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.07.017
Benedetti MF, Milne CJ, Kinniburgh DG, Van Riemsdijk WH, Koopal LK (1995) Metal ion binding to humic substances: application of the non-ideal competitive adsorption model. Environ Sci Technol 29(2):446–457. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00002a022
Benyahya L, Garnier J-M (1999) Effect of salicylic acid upon trace-metal sorption (CdII, ZnII, CoII, and MnII) onto alumina, silica, and kaolinite as a function of pH. Environ Sci Technol 33(9):1398–1407. https://doi.org/10.1021/es980509i
Berrima B, Maatar W, Mortha G, Boufi S, El Aloui L, Belgacem M (2016) Adsorption of heavy metals on charcoal from lignin. Cellul Chem Technol 50:701–709
Bhattacharyya KG, Gupta SS (2007) Adsorptive accumulation of Cd (II), Co (II), Cu (II), Pb (II), and Ni (II) from water on montmorillonite: Influence of acid activation. J Colloid Interface Sci 310(2):411–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.01.080
Bhattacharyya KG, Sen Gupta S (2007) Influence of acid activation of kaolinite and montmorillonite on adsorptive removal of Cd (II) from water. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(11):3734–3742. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie061475n
Bowe CA, Poore DD, Benson RF, Martin DF (2003) Extraction of heavy metals by amines adsorbed onto silica gel. J Environ Sci Health, Part A 38(11):2653–2660. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-120024454
Bukhari A, Javed T, Haider MN (2022) Adsorptive exclusion of crystal violet dye from wastewater by using fish scales as an adsorbent. J Dispers Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2022.2059506
Calace N, Nardi E, Petronio B, Pietroletti M, Tosti G (2003) Metal ion removal from water by sorption on paper mill sludge. Chemosphere 51(8):797–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00864-0
Carolin CF, Kumar PS, Saravanan A, Joshiba GJ, Naushad M (2017) Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 5(3):2782–2799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.029
Davarnejad R, Panahi P (2016) Cu (II) removal from aqueous wastewaters by adsorption on the modified Henna with Fe3O4 nanoparticles using response surface methodology. Sep Purif Technol 158:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.12.018
Długosz O, Banach M (2018) Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic investigations of the adsorption of Ag+ and Cu2+ on vermiculite. J Mol Liquids. 258:295–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.041
Doulati Ardejani F, Badii K, Farhadi F, Aziz Saberi M, Jodeiri Shokri B (2012) A computational fluid dynamic model for prediction of organic dyes adsorption from aqueous solutions. Environ Model Assess 17(5):505–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-012-9310-x
Elkady M, Shokry H, Hamad H (2020) New activated carbon from mine coal for adsorption of dye in simulated water or multiple heavy metals in real wastewater. Materials 13(11):2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112498
Elwakeel KZ, Al-Bogami AS, Guibal E (2021) 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole derivative of chitosan for silver sorption–contribution of magnetite incorporation and sonication effects on enhanced metal recovery. Chem Eng J 403:126265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126265
Etale A, Tavengwa NT, Pakade VE (2018) Metal adsorption by coal fly ash: the role of nano-sized materials. Coal fly ash beneficiation-treatment of acid mine drainage with coal fly ash. Intechopen, pp 1–24. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.69426
Ghassabzadeh H, Mohadespour A, Torab-Mostaedi M, Zaheri P, Maragheh MG, Taheri H (2010) Adsorption of Ag, Cu and Hg from aqueous solutions using expanded perlite. J Hazard Mater 177(1–3):950–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.010
Gode F, Pehlivan E (2005) Adsorption of Cr (III) ions by Turkish brown coals. Fuel Process Technol 86(8):875–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2004.10.006
Green-Ruiz C (2009) Effect of salinity and temperature on the adsorption of Hg (II) from aqueous solutions by a Ca-montmorillonite. Environ Technol 30(1):63–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330802503859
Guo D, Guo Q, Zheng K, Wang E, Bao X (2007) Initial growth and oxygen adsorption of silver on Al2O3 film. J Phys Chem C 111(10):3981–3985. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp066842n
Güvenç A, Karabacakolu B (2005) Use of electrodialysis to remove silver ions frommodel solutions and wastewater. Desalination 172(1):7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2004.06.193
Hasany SM, Saeed MM, Ahmed M (2001) Sorption of traces of silver ions onto polyurethane foam from acidic solution. Talanta 54(1):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(00)00634-2
Hayat K (2017) Studies on sorption of methylene blue over Cedrus deodara saw
He Y, Liu Q, Hu J, Zhao C, Peng C, Yang Q, Wang H, Liu H (2017) Efficient removal of Pb (II) by amine functionalized porous organic polymer through post-synthetic modification. Sep Purif Technol 180:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.01.026
Hefne J, Mekhemer W, Alandis N, Aldayel O, Alajyan T (2010) Removal of silver (I) from aqueous solutions by natural bentonite. JKAU Sci 22(1):155–176. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/240844542
Ibarra J, Osácar J, Gavilán J (1979) Retention of metallic cations by lignites and humic acids. Fuel 58(11):827–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(79)90191-1
Ida S, Eva T (2021) Removal of heavy metals during primary treatment of municipal wastewater and possibilities of enhanced removal: a review. Water 13(8):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081121
Imran MS, Javed T, Areej I, Haider MN (2022) Sequestration of crystal violet dye from wastewater using low-cost coconut husk as a potential adsorbent. Water Sci Technol 85(8):2295–2317. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2022.124
Janoš P, Sypecká J, Mlčkovská P, Kuráň P, Pilařová V (2007) Removal of metal ions from aqueous solutions by sorption onto untreated low-rank coal (oxihumolite). Sep Purif Technol 53(3):322–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.08.004
Javed T, Khalid N, Mirza ML (2017) Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics for thorium ions adsorption from aqueous solutions by coal. Desalin Water Treat 92:291–300
Jeon C (2017) Adsorption of silver ions from industrial wastewater using waste coffee grounds. Korean J Chem Eng 34(2):384–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0253-9
Jintakosol T, Nitayaphat W (2016) Adsorption of silver (I) from aqueous solution using chitosan/montmorillonite composite beads. Mater Res 19:1114–1121. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2015-0738
Karabakan A, Karabulut S, Denizli A, Yürüm Y (2004) Removal of silver (I) from aqueous solutions with low-rank Turkish coals. Adsorpt Sci Technol 22(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1260/026361704323150917
Karabulut S, Karabakan A, Denizli A, Yürüm Y (2000) Batch removal of copper (II) and zinc (II) from aqueous solutions with low-rank Turkish coals. Sep Purif Technol 18(3):177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5866(99)00067-2
Kausar F, Khalid N, Mirza M, DINc M (2017) Influence of electrolytes on decontamination of Cu (II) ions by surface of coconut coir. J Optoelectron Biomed Mater 9(2):107–119
Kazy SK, Dsouza S, Sar P (2009) Uranium and thorium sequestration by a Pseudomonas sp: mechanism and chemical characterization. J Hazard Mater 163(1):65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.076
Khalid N, Daud M (2014) Adsorption of arsenic from aqueous media using lateritic minerals: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Radiochim Acta 102(5):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2013-2129
Madrakian T, Afkhami A, Zolfigol MA, Solgi M (2006) Separation, preconcentration and determination of silver ion from water samples using silica gel modified with 2, 4, 6-trimorpholino-1, 3, 5-triazin. J Hazard Mater 128(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.07.031
Manunza B, Deiana S, Maddau V, Gessa C, Seeber R (1995) Stability constants of metal-humate complexes: titration data analyzed by bimodal gaussian distribution. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59(6):1570–1574. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1995.03615995005900060009x
Manzoori JL, Karim-Nezhad G (2003) Selective cloud point extraction and preconcentration of trace amounts of silver as a dithizone complex prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Anal Chim Acta 484(2):155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00343-X
Martyniuk H, Więckowska J (2003) Adsorption of metal ions on humic acids extracted from brown coals. Fuel Process Technol 84(1–3):23–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3820(02)00246-1
Mondal NK, Samanta A, Chakraborty S, Shaikh WA (2018) Enhanced chromium (VI) removal using banana peel dust: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics study. Sustain Water Resourc Manag 4(3):489–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0130-7
Murakami K, Ozaki J-I, Nishiyama Y (1995) Effects of surface treatment on cation exchange properties of Australian brown coals. Fuel Process Technol 43(1):95–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3820(95)00009-V
Nemeş LN, Bulgariu L (2016) Optimization of process parameters for heavy metals biosorption onto mustard waste biomass. Open Chem 14(1):175–187. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2016-0019
Norton L, Baskaran K, McKenzie T (2004) Biosorption of zinc from aqueous solutions using biosolids. Adv Environ Res 8(3–4):629–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(03)00035-2
Olaosebikan AO, Victor EB, Kehinde OA, Adebukola MB (2022) Isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of methylene blue adsorption on chitosan flakes derived from African giant snail shell. Afr J Environ Sci Technol. 16(1): 37–70. http://www.academicjournals.org/AJEST
Oubagaranadin JUK, Murthy Z (2009) Adsorption of divalent lead on a montmorillonite—illite type of clay. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(23):10627–10636. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie9005047
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kriz GS, Vyvyan JA (2014) Introduction to spectroscopy: Cengage learning
Pilśniak-Rabiega M, Wolska J (2021) Novel functional polymers for recovery of silver. Physicochem Probl Min Process. https://doi.org/10.37190/ppmp/142453
Popoola LT (2019) Characterization and adsorptive behaviour of snail shell-rice husk (SS-RH) calcined particles (CPs) towards cationic dye. Heliyon 5(1):e01153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01153
Praus P, Turicová M, Valásková M (2008) Study of silver adsorption on montmorillonite. J Braz Chem Soc 19(3):549–556. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532008000300025
Purcell TW, Peters JJ (1998) Sources of silver in the environment. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(4):539–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620170404
Qing Y, Hang Y, Wanjaul R, Jiang Z, Hu B (2003) Adsorption behavior of noble metal ions (Au, Ag, Pd) on nanometer-size titanium dioxide with ICP-AES. Anal Sci 19(10):1417–1420. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19.1417
Randle K, Hartmann E (1995) Applications of the continuous-flow stirred-cell (CFSC) technique: II. The adsorption behaviour of Na, Cs, Sr, Cu, Ni and Pb on humic acids. Eur J Soil Sci 46(2):303–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1995.tb01837.x
Reichenberg D (1953) Properties of ion-exchange resins in relation to their structure. III. Kinetics of exchange. J Am Chem Soc 75(3):589–597. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01099a022
Ríos CA, Williams CD, Mohan D (2011) Kinetic study of metal ion adsorption from wastewater onto coal industry by-products. Ingeniería y Competitividad. 13(2):9–21. http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=291323530001
Salehi R, Arami M, Mahmoodi NM, Bahrami H, Khorramfar S (2010) Novel biocompatible composite (chitosan–zinc oxide nanoparticle): preparation, characterization and dye adsorption properties. Colloids Surf, B 80(1):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.05.039
Shafiabadi M, Dashti A, Tayebi H-A (2016) Removal of Hg (II) from aqueous solution using polypyrrole/SBA-15 nanocomposite: experimental and modeling. Synth Metals. 212:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2015.12.020
Shen W, Li Z, Liu Y (2008) Surface chemical functional groups modification of porous carbon. Recent Patents Chem Eng 1(1):27–40. https://doi.org/10.2174/2211334710801010027
Song X, Gunawan P, Jiang R, Leong SSJ, Wang K, Xu R (2011) Surface activated carbon nanospheres for fast adsorption of silver ions from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 194:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.076
Srivastava VC, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2006) Characterization of mesoporous rice husk ash (RHA) and adsorption kinetics of metal ions from aqueous solution onto RHA. J Hazard Mater 134(1–3):257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.052
Stejskal J, Trchová M, Brožová L, Prokeš J (2009) Reduction of silver nitrate by polyaniline nanotubes to produce silver-polyaniline composites. Chem Pap 63(1):77–83. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-008-0086-z
Stuart AD (1986) Selective cation exchange using acidic groups in coals and oxidised coals. Fuel 65(7):1003–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(86)90212-7
Sultana S, Islam K, Hasan MA, Khan HJ, Khan MAR, Deb A, Al Raihan M, Rahman MW (2022) Adsorption of crystal violet dye by coconut husk powder: isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics perspectives. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100651
Sun Q, Li Y, Tang T, Yuan Z, Yu C-P (2013) Removal of silver nanoparticles by coagulation processes. J Hazard Mater 261:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.066
Tariq J, Nasir K, Mirza ML (2017) Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics of cerium removal by adsorption on low-rank coal. Desalin Water Treat 89:240–249. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.21357
Tauanov Z, Shah D, Inglezakis V (2018) Silver nanoparticles impregnated zeolites derived from coal fly ash: effect of the silver loading on adsorption of mercury (II). Multidiscip Digit Publ Inst Proc 2(11):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110647
Usmani TH, Ahmed TW, Ahmed SZ, Yousufzai A (1996) Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from a low rank coal. Carbon 34(1):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(95)00137-9
Vasconcelos IF, Bunker BA, Cygan RT (2007) Molecular dynamics modeling of ion adsorption to the basal surfaces of kaolinite. J Phys Chem C 111(18):6753–6762. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp065687+
Vimonses V, Jin B, Chow CW, Saint C (2010) An adsorption–photocatalysis hybrid process using multi-functional-nanoporous materials for wastewater reclamation. Water Res 44(18):5385–5397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.033
Virolainen S, Tyster M, Haapalainen M, Sainio T (2015) Ion exchange recovery of silver from concentrated base metal-chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy 152:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.12.011
Wang S, Li H, Chen X, Yang M, Qi Y (2012) Selective adsorption of silver ions from aqueous solution using polystyrene-supported trimercaptotriazine resin. J Environ Sci 24(12):2166–2172. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)61052-8
Weber WJ Jr, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89(2):31–59. https://doi.org/10.1061/JSEDAI.0000430
Wibowo N, Setyadhi L, Wibowo D, Setiawan J, Ismadji S (2007) Adsorption of benzene and toluene from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon and its acid and heat treated forms: influence of surface chemistry on adsorption. J Hazard Mater 146(1–2):237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.011
Xiong Y, Wan L, Xuan J, Wang Y, Xing Z, Shan W, Lou Z (2016) Selective recovery of Ag (I) coordination anion from simulate nickel electrolyte using corn stalk based adsorbent modified by ammonia–thiosemicarbazide. J Hazard Mater 301:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.003
Yao S, Zhang K, Jiao K, Hu W (2011) Evolution of coal structures: FTIR analyses of experimental simulations and naturally matured coals in the Ordos Basin China. Energy Explor Exploit 29(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1260/0144-5987.29.1.1
Yao Q-L, Xia Z, Tang C-J, Zhu L, Wang W-N, Chen T, Tan Y-M (2020) Characteristics of heavy metal ion adsorption by silty mudstones in coal mine goafs. Geofluids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8560151
Yin X, Long J, Xi Y, Luo X (2017) Recovery of silver from wastewater using a new magnetic photocatalytic ion-imprinted polymer. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(3):2090–2097. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01871
Zhang R, Wang B, Ma H (2010) Studies on chromium (VI) adsorption on sulfonated lignite. Desalination 255(1–3):61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.01.016
Zhang Y, Ghaly A, Li B (2012) Physical properties of rice residues as affected by variety and climatic and cultivation conditions in three continents. Am J Appl Sci 9(11): 1757–1768. http://thescipub.com/abstract/10.3844
Zhang L, Zhang G, Wang S, Peng J, Cui W (2017) Sulfoethyl functionalized silica nanoparticle as an adsorbent to selectively adsorb silver ions from aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 71:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.001
Zouboulis A (1995) Silver recovery from aqueous streams using ion flotation. Miner Eng 8(12):1477–1488. https://doi.org/10.1016/0892-6875(95)00112-3
Acknowledgements
One of the authors i.e., Mr. Tariq Javed, would like to acknowledge Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan, for awarding an indigenous Ph. D. fellowship and Pakistan Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, for providing research facilities for the present work.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contribute equally to the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Javed, T., Khalid, N. & Mirza, M.L. Adsorption modeling and thermodynamic characteristics of silver ions on to low-rank Pakistani coal. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 9, 3 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00779-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00779-x