Abstract
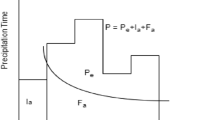
This article shows that there occur systematic errors and omissions in water management design while using the existing water balance equation by Perrault (De l'origine des fontainesm, 1674). The existing balance equation does not include all water balance parameters. Such parameters as infiltration capacity of the bedrock and loss by runoff recession are meant here. In order to calculate water balance parameters more precisely, the author of the article presents the linear correlation model (Iofin in Bull Admir Makarov State Univ Marit Inland Shipp 3:18–27, 2013). The core of the model is the linear correlation equation which shows the dependence between the river runoff depth and precipitation depth in the river basin. The members of the equation are supported by the genetic runoff theory (Befany in Issues of regional hydrology, Peakflow UMKVO, Kiev, 1989). The point is that the part of the graph which is placed on the x-axis before the beginning of the runoff is related to the absorption into the soil. The part of the graph which is placed on the x-axis after the beginning of the runoff is related to the loss by runoff recession. This loss results in specific water movement down the slope. The part of the graph on the y-axis represents the river runoff depth loss by infiltration into the ground water. Every type of the slope runoffs contains these parts of the graph. The article contains mathematical expressions for perched and banked-upslope runoffs. In addition, the method of least rectangles introduced by Alekseev (In: Errors of measurement and empirical relationships. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad, 1962) is used in the work while graphing. This method differs from the method of least squares because it takes into account any deviation from the middle both in y-direction and x-direction. Such an approach helps to receive more precise correlation parameters. As for the method of least squares, it takes into account deviation from the middle in one direction only. The usage of the three methods together—the linear correlation model, the genetic runoff theory and the method of least rectangles—helps to calculate the necessary water balance parameters and to introduce the complete water balance equation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekseev GA, Velikanov MA (1962) Search for forms of relations between random variables quantile method. In: Errors of measurement and empirical relationships. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad
Andreyanov VG (1960) Applying the equations of water balance and heat balance to the investigation and calculation of the annual runoff mode. In: Proceedings of GGI, vol 73. Leningrad, pp 3–54
Babkin VI, Vuglinsky VS (1982) Water balance of river basins. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad
Befany AN (1989) Issues of regional hydrology. In: Peakflow. UMKVO, Kiev
Budyko MI (1956) Evaporation in vivo. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad
Bulavko AG (1971) Water balance of river basins. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad
Iofin ZK (2013) Theoretical underpinning of linear-correlation model of water balance. Saint Petersburg, The Scientific Journal “Vestnik Gosudarstvennogo Universiteta Morskogo I Rechnogo Flota Imeni Admirala S.O. Makarova”. Bulle Admir Makarov State Univ Marit Inland Shipp 3:18–27
Koronkevich NI (1990) Water balance of the Russian Plain and its anthropogenic changes. Science, Moscow
Mezentsev VS, Karnatsevich IV (1969) Moistening of the west Siberian plain. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad
Perrault P (1674). De l'origine des fontaines
Velikanov MA (1940) Water balance of the land. Gidrometeoizdat, Moscow
Voeikov AI (1884) Climates of the world, Russia in particular. In: Selected works, vol 1. Moscow-Leningrad, pp 163–750
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iofin, Z.K. Water balance theory is more than 340 years old. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 6, 32 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00388-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00388-6