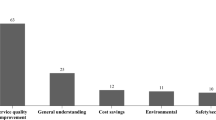
Abstract
Indian Railways has one of the most extensive rail systems in the world which covers 68,000 km of rail track, and 7318 stations with over 23 million passengers daily. This public transport system is one of the cheapest modes of travel for millions of Indians daily. Railways play a vital role in transportation from origin to destination. A methodology for classifying railway passenger stations was developed in this study. The classification is done in four buckets: the position of the railway station within the network, the position of the Railway Station relative to Settlement (Attractiveness), Railway Station Infrastructure and Passenger Importance. This categorization aims to classify railway stations in the railway network according to accessibility, infrastructure and importance of the station on the network and the region. The research is based on an investigation of 7 parameters on 40 passenger railway stations of the Indian railway's northern division. Two techniques are evaluated for the classification which are general ranking rule and AHP (analytic hierarchy process) and then cluster analysis is conducted for categorization.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data associated with Indian Railways in the research are collected through primary surveys. Due to the nature of this research, participants of this study did not agree for their data to be shared publicly.
References
Bertolini L (1996) Nodes and places: complexities of railway station redevelopment. Eur Plan Stud 4(3):331–345
Mohajeri NAGRA (2010) Railway station site selection using analytical hierarchy process and data envelopment analysis. Comput Industrial Eng 1(59):107–114
Zemp S (2011) Classifying railway stations for strategic transport and land use planning: context matters! J Transp Geogr 19(4):670–679
Havlena O (2014) Parameters of passenger facilities according to railway station characteristics. Transport Problems 9(4):97–104
S. S. A. R. Nikolova, (2016) Classifying railway passenger stations for use transport planning–application to bulgarian railway network., Transport Problems 11
C. Xu, “Application of hierarchical clustering based on principal component analysis to railway station classification,” American Society of Civil Engineers, no. ICTE 2019, pp. 162-171, 2020.
Yücel NASET (2019) The selection of railway system projects with multi creteria decision making methods: a case study for Istanbul. Procedia Computer Sci 158:382–393
T. H. A. C. Y. Oum, (1994) “Economic efficiency of railways and implications for public policy: a comparative study of the OECD countries’ railways,” Journal of transport Economics and Policy, 121–138
Coelli TASP (1999) A comparison of parametric and non-parametric distance functions: with application to European railways. Eur J Operational Res 117(2):326–339
P. L. S. A. J. M. P. Cantos, (2002) “Cost and revenue inefficiences in the European railways,” Cost and revenue inefficiences in the European railways 1000–1030
Growitsch CAHW (2009) Testing for economies of scope in European railways: an efficiency analysis. J Trans Eco Policy (JTEP) 43(1):1–24
G. M. G. L. a. M. M. Driessen, (2006) “The impact of competition on productive efficiency in European railways,” The Hague, the Netherlands: CPB Netherlands Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis
Cantos PJMPALS (2010) Vertical and horizontal separation in the European railway sector and its effects on productivity. J Trans Eco Policy (JTEP) 44(2):139–160
Tomeš Z (2014) Competition in the railway passenger market in the Czech Republic. Res Transp Econ 48:270–276
Khadem Sameni M, Kashi Mansouri MR (2017) Analyzing Efficiency of Railway Transportation by Considering Quality of Services: New Data Envelopment Analysis Models. Int J Railway Res 4(1):47–55
Irg-Rail, (2016) “Overview on charging principles for passenger,” Irg-Rail
T. R. Board, (2012) “Transit cooperative research program (Tcrp),” Washington, D.C
N. Rail, (2011) “Station design principles for network rail,” United Kingdom
“Tran slink public transport infrastructure manual”, Washington, 2012.
Charles RGAP (2013) Improving Rail Station Access in Australia. CRC for Rail Innovation, Queensland
D. R. Yogita Rani, (2013) “A Study of Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm” International Journal of Information and Computation Technology 3 (5)1225–1232
Saaty RW (1987) The analytic hierarchy process—what it is and how it is used. Mathematical Modelling 9(3–5):161–176
Boroushaki SMJ (2008) Implementing an extension of the analytical hierarchy process using ordered weighted averaging operators with fuzzy quantifiers in ArcGIS. Computers Geosci 34(4):399–410
Forman EHGSI (2001) The analytical hierarchy process—an exposition. Oper Res 49(4):469–487
W. D. J. S. F. P. C. S. R. E. Z. S. D. K. Jyrki, (2008) “Multiple criteria decision making, multiattribute utility theory: recent accomplishments and what lies ahead,” Management Science,54(7) 1339–1340
I. S. F. K. S. J. F. E. P. R. C. Linkov, (2007)"Multi criteria decision analysis and environmental risk assessment for nanomaterials," Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 9(4) 543–544
H. X. M. &. B. A. C. Raharjo, "On modeling dynamic priorities in the analytic hierarchy process using compositional data analysis," European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 194 , no. 3, pp. 843–846, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The current classification criteria in Indian Railway are based on the income generated by the station and proposed annual passenger flow through the stations, these criteria of selection do not include the importance of the station in its surrounding urban setting Fand also on the network. The proposed criteria in this paper will categorize stations in a way so that infrastructure can be developed for better station accessibility and the development of multimodal transit hubs. As the transit demand increases in the future railway stations need to be developed in a phased manner to work efficiently and have better travel time reliability for the passengers.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatnagar, R.V., Ram, S. Classifying Indian Railway Passenger Stations Using a Multi-criteria Framework. Transp. in Dev. Econ. 9, 3 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40890-022-00173-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40890-022-00173-4