Abstract
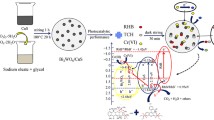
Numerous photocatalysts have been prepared for the photocatalysis of either organic pollutant degradation or Cr(VI) reduction. However, most of the inorganic and organic pollutants usually co-exist in industrial sewage. Simultaneous elimination of mixed inorganic and organic pollutants remains highly challenging. Herein, we report bi-functional Cu-TiO2/CuO photocatalysts by the in-situ doping and heterostructure engineering strategies for large-scale and highly enhanced synergistic photocatalytic elimination of organic pollutants and transitional metallic ions from waste sewage in one shot. Specifically, this bi-functional photocatalyst displays about 2.35 and 3.84 times higher photocatalytic Rhodamine B (RhB) degradation and Cr(VI) reduction rates in the solution with co-existing RhB and Cr(VI) than that in the single RhB or Cr(VI) pollutant solution, respectively. A highly boosted synergetic effect between photocatalytic dye molecule degradation and Cr(VI) reduction is revealed. The bi-functional photocatalyst also displays extraordinary activity and stability in large-scale photocatalytic elimination of mixed pollutants. Moreover, theoretical calculations demonstrate that Cu doping and heterostructure engineering give rise to the narrowed bandgap for enhanced light harvesting, the increased density of states for high charge carrier density, the delocalized electron for fast photoinduced charge carrier separation, and the profitable charge transfer between TiO2 and CuO, thus bringing about the efficient synergetic photocatalysis. The bi-functional photocatalyst concept reported in this study opens a new avenue to construct bi-functional photocatalysts for solar-to-fuel conversion and large-scale industrial waste water treatment and river purification.

摘要
大多数所制备的光催化剂通常只用于单一地降解有机污染物或还原Cr(VI)的光催化. 然而, 无机和有机污染物通常共存于工业污水中.同时消除混合的无机和有机污染物仍然存在着巨大的挑战. 在本文中,我们通过原位掺杂和异质结工程策略, 制备出了新型的双功能Cu-TiO2/CuO光催化剂用于大规模高效协同光催化消除废水中的有机污染物和过渡金属离子. 具体而言, 这种双功能光催化剂在RhB和Cr(VI)共存溶液中的光催化RhB降解率和Cr(VI)还原率分别是在单一RhB或Cr(VI)污染物溶液中对应值的2.35和3.84倍. 光催化染料分子降解和Cr(VI)还原之间存在显著增强的协同效应. 此外, 该双功能光催化剂在大规模光催化消除混合污染物方面也表现出较好的活性和稳定性. 理论计算表明, 铜掺杂和异质结工程促进了高效的光吸收、增高的载流子密度以及快速的光生载流子转移, 从而产生高效的协同光催化作用.这种双功能光催化剂的概念为大规模工业废水处理和净化开辟了新途径.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding Y, Maitra S, Wang C, et al. Vacancy defect engineering in semiconductors for solar light-driven environmental remediation and sustainable energy production. Interdiscip Mater, 2022, 1: 213–255
Ding Y, Huang L, Barakat T, et al. A novel 3DOM TiO2 based multifunctional photocatalytic and catalytic platform for energy regeneration and pollutants degradation. Adv Mater Interfaces, 2021, 8: 2001879
Zu M, Zhang S, Liu C, et al. Portable wastewater treatment system based on synergistic photocatalytic and persulphate degradation under visible light. Sci China Mater, 2021, 64: 1952–1963
Xu M, Chen Y, Qin J, et al. Unveiling the role of defects on oxygen activation and photodegradation of organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol, 2018, 52: 13879–13886
Chen LH, Sun MH, Wang Z, et al. Hierarchically structured zeolites: From design to application. Chem Rev, 2020, 120: 11194–11294
Yang XY, Chen LH, Li Y, et al. Hierarchically porous materials: Synthesis strategies and structure design. Chem Soc Rev, 2017, 46: 481–558
Hou H, Zeng X, Zhang X. 2D/2D heterostructured photocatalyst: Rational design for energy and environmental applications. Sci China Mater, 2020, 63: 2119–2152
Fan X, Zhang L, Li M, et al. a-Ferrous oxalate dihydrate: A simple coordination polymer featuring photocatalytic and photo-initiated Fenton oxidations. Sci China Mater, 2016, 59: 574–580
Zou Y, Wang X, Khan A, et al. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ Sci Technol, 2016, 50: 7290–7304
Zhao Y, Tian G, Duan X, et al. Environmental applications of diatomite minerals in removing heavy metals from water. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2019, 58: 11638–11652
Zai J, Cao F, Liang N, et al. Rose-like I-doped Bi2O2CO3 microspheres with enhanced visible light response: DFT calculation, synthesis and photocatalytic performance. J Hazard Mater, 2017, 321: 464–472
Xue C, Zhang T, Ding S, et al. Anchoring tailored low-index faceted BiOBr nanoplates onto TiO2 nanorods to enhance the stability and visible-light-driven catalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9: 16091–16102
Padhi D, Pradhan GK, Parida KM, et al. Facile fabrication of Gd(OH)3 nanorod/RGO composite: Synthesis, characterisation and photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI). Chem Eng J, 2014, 255: 78–88
Feng Y, Li H, Ling L, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation performance by fluid-induced piezoelectric field. Environ Sci Technol, 2018, 52: 7842–7848
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Lu J, et al. Synergistic photoelectrochemical reduction of Cr(VI) and oxidation of organic pollutants by g-C3N4/TiO2-NTs electrodes. Chemosphere, 2016, 162: 55–63
Guo S, Yang W, You L, et al. Simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by a novel iron-modified rectorite composite through heterogeneous photo-Fenton processes. Chem Eng J, 2020, 393: 124758
Zheng R, Li J, Zhu R, et al. Enhanced Cr(VI) reduction on natural chalcopyrite mineral modulated by degradation intermediates of RhB. J Hazard Mater, 2022, 423: 127206
Sakaguchi N, Miyamoto R, Giamello E, et al. Evaluation of coexistent metal ions with TiO2: An EPR approach. Res Chem Intermed, 2018, 44: 4563–4575
Zhao H, Li CF, Hu ZY, et al. Size effect of bifunctional gold in hierarchical titanium oxide-gold-cadmium sulfide with slow photon effect for unprecedented visible-light hydrogen production. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2021, 604: 131–140
Zhao H, Hu Z, Liu J, et al. Blue-edge slow photons promoting visible-light hydrogen production on gradient ternary 3DOM TiO2-Au-CdS photonic crystals. Nano Energy, 2018, 47: 266–274
Choudhury B, Choudhury A, Borah D. Interplay of dopants and defects in making Cu doped TiO2 nanoparticle a ferromagnetic semiconductor. J Alloys Compd, 2015, 646: 692–698
Zalfani M, van der Schueren B, Mahdouani M, et al. ZnO quantum dots decorated 3DOM TiO2 nanocomposites: Symbiose of quantum size effects and photonic structure for highly enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Appl Catal B-Environ, 2016, 199: 187–198
Jin J, Wang C, Ren XN, et al. Anchoring ultrafine metallic and oxidized Pt nanoclusters on yolk-shell TiO2 for unprecedentedly high photocatalytic hydrogen production. Nano Energy, 2017, 38: 118–126
Choudhury B, Dey M, Choudhury A. Defect generation, d-d transition, and band gap reduction in Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Int Nano Lett, 2013, 3: 25
Yang Y, Yin LC, Gong Y, et al. An unusual strong visible-light absorption band in red anatase TiO2 photocatalyst induced by atomic hydrogen-occupied oxygen vacancies. Adv Mater, 2018, 30: 1704479
Qi D, Lu L, Xi Z, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of TiO2 based on synergistic effect of Ti3+ self-doping and slow light effect. Appl Catal B-Environ, 2014, 160–161: 621–628
Hao R, Wang G, Tang H, et al. Template-free preparation of macro/mesoporous g-C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction photocatalysts with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B-Environ, 2016, 187: 47–58
Xu J, Wang W, Sun S, et al. Enhancing visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity by coupling with wide-band-gap semiconductor: A case study on Bi2WO6/TiO2. Appl Catal B-Environ, 2012, 111–112: 126–132
Wei Z, Liu D, Wei W, et al. Ultrathin TiO2 (B) nanosheets as the inductive agent for transfrering H2O2 into superoxide radicals. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9: 15533–15540
Shi Q, Ping G, Wang X, et al. CuO/TiO2 heterojunction composites: An efficient photocatalyst for selective oxidation of methanol to methyl formate. J Mater Chem A, 2019, 7: 2253–2260
Wang S, Chen P, Bai Y, et al. New BiVO4 dual photoanodes with enriched oxygen vacancies for efficient solar-driven water splitting. Adv Mater, 2018, 30: 1800486
Feng C, Tang L, Deng Y, et al. Synthesis of leaf-vein-like g-C3N4 with tunable band structures and charge transfer properties for selective photocatalytic H2O2 evolution. Adv Funct Mater, 2022, 30: 2001922
Ding Y, Maitra S, Wang C, et al. Hydrophilic bi-functional B-doped g-C3N4 hierarchical architecture for excellent photocatalytic H2O2 production and photoelectrochemical water splitting. J Energy Chem, 2022, 70: 236–247
Wang S, Pan L, Song JJ, et al. Titanium-defected undoped anatase TiO2 with p-type conductivity, room-temperature ferromagnetism, and remarkable photocatalytic performance. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137: 2975–2983
Wang D, Liu ZP, Yang WM. Revealing the size effect of platinum cocatalyst for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on TiO2 support: A DFT study. ACS Catal, 2018, 8: 7270–7278
Hou H, Shang M, Gao F, et al. Highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution in ternary hybrid TiO2/CuO/Cu thoroughly mesoporous nanofibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8: 20128–20137
Wei F, Liu Y, Zhao H, et al. Oxygen self-doped g-C3N4 with tunable electronic band structure for unprecedentedly enhanced photocatalytic performance. Nanoscale, 2018, 10: 4515–4522
Xia P, Zhu B, Cheng B, et al. 2D/2D g-C3N4/MnO2 nanocomposite as a direct Z-scheme photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic activity. ACS Sustain Chem Eng, 2018, 6: 965–973
Ding Y, Maitra S, Esteban DA, et al. Photochemical production of hydrogen peroxide by digging pro-superoxide radical carbon vacancies in porous carbon nitride. Cell Rep Phys Sci, 2022, 3: 100874
Wan S, Xu J, Cao S, et al. Promoting intramolecular charge transfer of graphitic carbon nitride by donor-acceptor modulation for visible-light photocatalytic H2 evolution. Interdiscip Mater, 2022, 1: 294–308
Wang C, Weng B, Keshavarz M, et al. Photothermal Suzuki coupling over a metal halide perovskite/Pd nanocube composite catalyst. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2022, 14: 17185–17194
Zhao H, Jin Q, Khan MA, et al. Rational design of carbon nitride for remarkable photocatalytic H2O2 production. Chem Catal, 2022, 2: 1720–1733
Zhao H, Zalfani M, Li CF, et al. Cascade electronic band structured zinc oxide/bismuth vanadate/three-dimensional ordered macroporous titanium dioxide ternary nanocomposites for enhanced visible light photocatalysis. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2019, 539: 585–597
Lu Y, Cheng X, Tian G, et al. Hierarchical CdS/m-TiO2/G ternary photocatalyst for highly active visible light-induced hydrogen production from water splitting with high stability. Nano Energy, 2018, 47: 8–17
Zhao H, Li CF, Liu LY, et al. n-p Heterojunction of TiO2-NiO core-shell structure for efficient hydrogen generation and lignin photoreforming. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2021, 585: 694–704
Yang JX, Yu WB, Li CF, et al. PtO nanodots promoting Ti3C2 MXene in-situ converted Ti3C2/TiO2 composites for photocatalytic hydrogen production. Chem Eng J, 2021, 420: 129695
Chen LH, Li Y, Su BL. Hierarchy in materials for maximized efficiency. Natl Sci Rev, 2020, 7: 1626–1630
Zhao H, Liu J, Li C, et al. Meso-microporous nanosheet-constructed 3DOM perovskites for remarkable photocatalytic hydrogen production. Adv Funct Mater, 2022, 32: 2112831
Wang YY, Chen YX, Barakat T, et al. Recent advances in non-metal doped titania for solar-driven photocatalytic/photoelectrochemical water-splitting. J Energy Chem, 2022, 66: 529–559
Wu L, Li Y, Fu Z, et al. Hierarchically structured porous materials: Synthesis strategies and applications in energy storage. Natl Sci Rev, 2020, 7: 1667–1701
Ding Y, Maitra S, Halder S, et al. Emerging semiconductors and metal-organic-compounds-related photocatalysts for sustainable hydrogen peroxide production. Matter, 2022, 5: 2119–2167
Wang C, Huang H, Weng B, et al. Planar heterojunction boosts solar-driven photocatalytic performance and stability of halide perovskite solar photocatalyst cell. Appl Catal B-Environ, 2022, 301: 120760
Maitra S, Pal S, Maitra T, et al. Solvothermal etching-assisted phase and morphology tailoring in highly porous CuFe2O4 nanoflake photocathodes for solar water splitting. Energy Fuels, 2021, 35: 14087–14100
Maitra S, Halder S, Maitra T, et al. Superior light absorbing CdS/vanadium sulphide nanowalls@TiO2 nanorod ternary heterojunction photoanodes for solar water splitting. New J Chem, 2021, 45: 7353–7367
Li Y, Zhang D, Qiao W, et al. Nanostructured heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for green synthesis of valuable chemicals. Chem Synth, 2022, 2: 9
Wang H, Wang L, Luo Q, et al. Two-dimensional manganese oxide on ceria for the catalytic partial oxidation of hydrocarbons. Chem Synth, 2022, 2: 2
Roy K, Maitra S, Ghosh D, et al. 2D-heterostructure assisted activation of MoS2 basal plane for enhanced photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Eng J, 2022, 435: 134963
Ghosh D, Roy K, Maitra S, et al. Unravelling Rashba-Dresselhaus splitting assisted magneto-photoelectrochemical water splitting in asymmetric MoSSe-GaN heterostructures. J Phys Chem Lett, 2022, 13: 1234–1240
Liu J, Guo YH, Hu ZY, et al. Slow photon-enhanced heterojunction accelerates photocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction to unprecedented rates. CCS Chem, 2022,: 1–13
Zhao H, Liu P, Wu X, et al. Plasmon enhanced glucose photoreforming for arabinose and gas fuel co-production over 3DOM TiO2-Au. Appl Catal B-Environ, 2021, 291: 120055
Acknowledgements
Ding Y thanks the financial support from the China Scholarship Council (201808310127). Chen LH acknowledges Hubei Provincial Department of Education for the “Chutian Scholar” program. This work was financially supported by the Foundation of Natural Science (61905159), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1663225) Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team (IRT_15R22), and the project “DepollutAir” of Interreg V France-Wallonie-Vlaanderen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ding Y carried out all experiments and wrote the paper; Maitra S and Roy S conducted the DFT calculations; Wang C and Zheng R helped with the characterizations of photoluminescence, photoluminescence lifetime and EPR spectra; Chen LH and Barakat T guided the experiments, discussed the results and revised the paper; Su BL established the research direction, conceived the project, provided the scientific guidance and project realization ideas, revised and finalized the paper.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary information
Supporting data are available in the online version of the paper.
Yang Ding received his MSc degree from the College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Shanghai Normal University in 2018. He is currently a PhD student in the Laboratory of Inorganic Materials Chemistry (CMI) of the University of Namur under the supervision of Prof. Bao-Lian Su. His research interests include the synthesis and characterization of porous materials, photocatalytic pollutant elimination and sustainable energy production.
Li-Hua Chen obtained his PhD degrees, one in inorganic chemistry from Jilin University, China (2009), and another in inorganic materials chemistry from the University of Namur, FUNDP, Belgium (2011). In 2011–2012, he held a project-researcher position at the University of Namur with Professor Bao-Lian Su, working on hierarchically porous zeolites. He is currently a full professor at Wuhan University of Technology, China. His research is aimed at new porous materials with designed hierarchically porosity.
Bao-Lian Su founded the CMI at the University of Namur, Belgium in 1995. He is full professor, Member of the European Academy of Sciences, Member of the Royal Academy of Belgium, Fellow of the Royal of Society of Chemistry, UK and Life Member of Clare Hall College, University of Cambridge. He is also a strategy scientist at Wuhan University of Technology, China. His research fields include the synthesis, the property study and the molecular engineering of organized, hierarchically porous materials and bio-organisms for artificial photosynthesis, (photo)catalysis, energy conversion and storage, biotechnology, cell therapy and biomedical applications.
Supplementary Information
40843_2022_2148_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Bi-functional Cu-TiO2/CuO photocatalyst for large-scale synergistic treatment of waste sewage containing organics and heavy metal ions
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Maitra, S., Wang, C. et al. Bi-functional Cu-TiO2/CuO photocatalyst for large-scale synergistic treatment of waste sewage containing organics and heavy metal ions. Sci. China Mater. 66, 179–192 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-022-2148-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-022-2148-4