Abstract
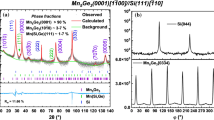
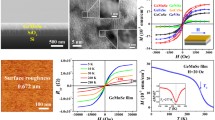
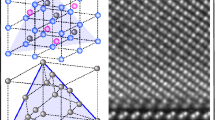
In this work, silicon-germanium (SiGe) thin films are epitaxially grown on Ge substrates by ultra-high vacuum chemical vapor deposition and then doped with Mn element by ion-implantation and subsequent rapid thermal annealing (RTA). The characterizations show that the epitaxial SiGe thin films are single-crystalline with uniform tensile strain and then become polycrystalline after the ion implantation and following RTA. The magnetization measurements indicate that the annealed thin films exhibit Mn concentration-dependent ferromagnetism up to 309 K and the X-ray magnetic circular dichroism characterizations reveal the spin and orbital magnetic moments from the substitutional Mn element. To minimize the influence of anomalous Hall effect, magneto-transport measurements at a high magnetic field up to 31 T at 300 K are performed to obtain the hole mobility, which reaches a record-high value of ∼1230 cm2 V−1 s−1, owing to the crystalline quality and tensile strain-induced energy band modulation of the samples. The first demonstration of Mn-doped SiGe thin films with room-temperature ferromagnetism and high carrier mobility may pave the way for practical semiconductor spintronic applications.
摘要
本文采用超高真空化学气相沉积系统在锗衬底上外延生长了第 IV族硅锗薄膜, 然后通过离子注入和快速热退火进行锰元素掺杂. 结构 测试表明, 外延的硅锗薄膜是具有均匀拉伸应变的单晶, 随后的离子注 入和快速热退火使其变为多晶. 磁性测试表明, 退火后的薄膜表现出依 赖于锰掺杂浓度的铁磁性, 居里温度最高可达309 K; X射线磁圆二色谱 揭示了替代位锰元素的自旋和轨道磁矩. 为最大限度地减少反常霍尔 效应的影响, 磁输运测试在高达31 T的强磁场下进行, 该薄膜在300 K 温度下空穴迁移率达到创纪录的∼1230 cm2 V−1 s−1. 此高迁移率归因于 样品较高的结晶质量和拉伸应变对能带的调制. 本文首次展示了具有 室温铁磁性和高载流子迁移率的锰掺杂硅锗薄膜, 有望促进基于第IV 族半导体的自旋电子材料与器件的实际应用.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohno H, Shen A, Matsukura F, et al. (Ga,Mn)As: A new diluted magnetic semiconductor based on GaAs. Appl Phys Lett, 1996, 69: 363–365
Chen L, Yang X, Yang F, et al. Enhancing the Curie temperature of ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As to 200 K via nanostructure engineering. Nano Lett, 2011, 11: 2584–2589
Jungwirth T, Wang KY, Masek J, et al. Prospects for high temperature ferromagnetism in (Ga,Mn)As semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72: 165204
Cui JB, Gibson UJ. Electrodeposition and room temperature ferromagnetic anisotropy of Co and Ni-doped ZnO nanowire arrays. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87: 133108
Fan JP, Li XL, Quan ZY, et al. Tunable magnetic and transport properties of p-type ZnMnO films with n-type Ga, Cr, and Fe codopants. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102: 102407
Brieler FJ, Grundmann P, Fröba M, et al. Formation of Zn1−xMnxS nanowires within mesoporous silica of different pore sizes. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126: 797–807
Zhao GQ, Lin CJ, Deng Z, et al. Single crystal growth and spin polarization measurements of diluted magnetic semiconductor (BaK)-(ZnMn)2As2. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 14473
Gu G, Zhao G, Lin C, et al. Asperomagnetic order in diluted magnetic semiconductor (Ba,Na)(Zn,Mn)2As2. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112: 032402
Zhao K, Deng Z, Wang XC, et al. New diluted ferromagnetic semiconductor with Curie temperature up to 180 K and isostructural to the ‘122’ iron-based superconductors. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 1442
Bolduc M, Awo-Affouda C, Stollenwerk A, et al. Above room temperature ferromagnetism in Mn-ion implanted Si. Phys Rev B, 2005, 71: 33302
Collins BA, Chu YS, He L, et al. Dopant stability and strain states in Co and Mn-doped Ge (001) epitaxial films. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77: 193301
Wang H, Sun S, Lu J, et al. High Curie temperature ferromagnetism and high hole mobility in tensile strained Mn-doped SiGe thin films. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30: 2002513
Kazakova O, Kulkarni JS, Holmes JD, et al. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Ge1−xMnx nanowires. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72: 094415
Xiu F, Wang Y, Kim J, et al. Electric-field-controlled ferromagnetism in high-Curie-temperature Mn0.05Ge0.95 quantum dots. Nat Mater, 2010, 9: 337–344
Qiao S, Hou D, Tang G The structure and magnetic properties in heavily Mn-doped MnxSi1−x films. Solid State Commun, 2015, 203: 21–25
Jamet M, Barski A, Devillers T, et al. High-Curie-temperature ferromagnetism in self-organized Ge1−xMnx nanocolumns. Nat Mater, 2006, 5: 653–659
Park YD, Hanbicki AT, Erwin SC, et al. A Group-IV ferromagnetic semiconductor: MnxGe1−x. Science, 2002, 295: 651–654
Gambardella P, Claude L, Rusponi S, et al. Surface characterization of MnxGe1−x and CryMnxGe1−x−y dilute magnetic semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75: 125211
Dietl T, Sato K, Fukushima T, et al. Spinodal nanodecomposition in semiconductors doped with transition metals. Rev Mod Phys, 2015, 87: 1311–1377
Dietl T, Ohno H. Dilute ferromagnetic semiconductors: Physics and spintronic structures. Rev Mod Phys, 2014, 86: 187–251
Park S, Kim P, Lee YP, et al. Realization of room-temperature ferromagnetism and of improved carrier mobility in Mn-doped ZnO film by oxygen deficiency, introduced by hydrogen and heat treatments. Adv Mater, 2007, 19: 3496–3500
Matsukura F, Ohno H, Shen A, et al. Transport properties and origin of ferromagnetism in (Ga,Mn)As. Phys Rev B, 1998, 57: R2037–R2040
Sverdlov V, Selberherr S. Silicon spintronics: Progress and challenges. Phys Rep, 2015, 585: 1–40
Wang K, Xu G, Gao F, et al. Ultrafast coherent control of a hole spin qubit in a germanium quantum dot. Nat Commun, 2022, 13: 206
Wang J, Shen L, Lin G, et al. Homoepitaxy of Ge on ozone-treated Ge (100) substrate by ultra-high vacuum chemical vapor deposition. J Cryst Growth, 2019, 507: 113–117
Denton AR, Ashcroft NW. Vegard’s “law”. Phys Rev A, 1991, 43: 3161–3164
Woodbury HH, Tyler WW. Properties of germanium doped with manganese. Phys Rev, 1955, 100: 659–662
Bulavchenko OA, Vinokurov ZS, Afonasenko TN, et al. Reduction of mixed Mn-Zr oxides: In situ XPS and XRD studies. Dalton Trans, 2015, 44: 15499–15507
Myers CE, Franzen HF, Anderegg JW. X-ray photoelectron spectra and bonding in transition-metal phosphides. Inorg Chem, 1985, 24: 1822–1824
Kim SK, Cho YC, Jeong SY, et al. High-temperature ferromagnetism in amorphous semiconductor Ge3Mn thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 192505
Qiao S, Hou D, Wei Y, et al. Ferromagnetism in MnxGe1−x films prepared by magnetron sputtering. J Magn Magn Mater, 2009, 321: 2446–2450
Zhou S, Schmidt H. Mn-doped Ge and Si: A review of the experimental status. Materials, 2010, 3: 5054–5082
Li AP, Zeng C, van Benthem K, et al. Dopant segregation and giant magnetoresistance in manganese-doped germanium. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75: 201201
Zhou S, Potzger K, Zhang G, et al. Structural and magnetic properties of Mn-implanted Si. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75: 085203
Awo-Affouda C, Bolduc M, Huang MB, et al. Observation of crystallite formation in ferromagnetic Mn-implanted Si. J Vacuum Sci Tech A-Vacuum Surfs Films, 2006, 24: 1644–1647
Wang H, Sun S, Xu J, et al. Microstructure and ferromagnetism of heavily Mn doped SiGe thin flims. Chin Phys B, 2020, 29: 057504
Wang Y, Zou J, Zhao Z, et al. Direct structural evidences of Mn11Ge8 and Mn5Ge2 clusters in Ge0.96Mn0.04 thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 101913
Biegger E, Stäheli L, Fonin M, et al. Intrinsic ferromagnetism versus phase segregation in Mn-doped Ge. J Appl Phys, 2007, 101: 103912
Passacantando M, Ottaviano L, D’Orazio F, et al. Growth of ferromagnetic nanoparticles in a diluted magnetic semiconductor obtained by Mn+implantation on Ge single crystals. Phys Rev B, 2006, 73: 19520
Ottaviano L, Continenza A, Profeta G, et al. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Mn-implanted amorphous Ge. Phys Rev B, 2011, 83: 134426
Ishiwata Y, Watanabe M, Eguchi R, et al. Manganese concentration and low-temperature annealing dependence of Ga1−xMnxAs by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Phys Rev B, 2002, 65: 233201
Ottaviano L, Passacantando M, Verna A, et al. Mn L2,3 X-ray absorption spectra of a diluted Mn-Ge alloy. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 242105
van der Laan G, Kirkman IW. The 2p absorption spectra of 3d transition metal compounds in tetrahedral and octahedral symmetry. J Phys-Condens Matter, 1992, 4: 4189–4204
Edmonds KW, Farley NRS, Campion RP, et al. Surface effects in Mn L3,2 X-ray absorption spectra from (Ga,Mn)As. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84: 4065–4067
Picozzi S, Ottaviano L, Passacantando M, et al. X-ray absorption spectroscopy in MnxGe1−x diluted magnetic semiconductor: Experiment and theory. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 062501
Hirai C, Sato H, Kimura A, et al. Mn 2p–3d soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism study of Mn5Ge3. Physica B-Condensed Matter, 2004, 351: 341–343
Sangaletti L, Magnano E, Bondino F, et al. Interface formation and growth of ferromagnetic thin layers in the Mn:Ge(111) system probed by dichroic soft X-ray spectroscopies. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75: 153311
de Padova P, Ayoub JP, Berbezier I, et al. Mn0.06Ge0.94 diluted magnetic semiconductor epitaxially grown on Ge(001): Influence of Mn5Ge3 nanoscopic clusters on the electronic and magnetic properties. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77: 045203
Thole BT, Carra P, Sette F, et al. X-ray circular dichroism as a probe of orbital magnetization. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 68: 1943–1946
Carra P, Thole BT, Altarelli M, et al. X-ray circular dichroism and local magnetic fields. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 70: 694–697
Weng H, Dong J. First-principles investigation of transition-metal-doped group-IV semiconductors: RxY1−x (R = Cr, Mn, Fe; Y = Si, Ge). Phys Rev B, 2005, 71: 035201
Nagaosa N, Sinova J, Onoda S, et al. Anomalous Hall effect. Rev Mod Phys, 2010, 82: 1539–1592
Nie T, Tang J, Kou X, et al. Enhancing electric-field control of ferromagnetism through nanoscale engineering of high-Tc MnxGe1−x nanomesh. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 12866
Mchedlidze T, Yonenaga I. Hall effect measurements on SixGe1−x bulk alloys. MRS Proc, 1997, 442: 381–384
Shen L, Zhang X, Lu J, et al. The effect of vacancy defects on the conductive properties of SiGe. Phys Lett A, 2021, 386: 126993
Fischetti MV, Laux SE. Band structure, deformation potentials, and carrier mobility in strained Si, Ge, and SiGe alloys. J Appl Phys, 1996, 80: 2234–2252
Chu M, Sun Y, Aghoram U, et al. Strain: A solution for higher carrier mobility in nanoscale MOSFETs. Annu Rev Mater Res, 2009, 39: 203–229
Prince MB. Drift mobilities in semiconductors. I. Germanium. Phys Rev, 1953, 92: 681–687
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFB0405702) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52172272). The authors thank the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of Chinese Academy of Sciences for the help in the high magnetic field transport measurements of the samples, and the Analytical & Testing Center of Sichuan University for the TEM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shen L prepared the samples and performed the experiments; Zhang X and Li C provided the resources and supervised the project; Wang JQ and Wang JY prepared the samples; Shen L, Zhang X, and Xiang G wrote the paper; Xiang G designed and supervised the project. All authors contributed to the general discussion.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Limeng Shen is a PhD student at Sichuan University under the supervision of Prof. Gang Xiang. His current research interests focus on the diluted magnetic semiconductors based on group-IV as well as the related functional devices.
Gang Xiang earned his PhD degree in condensed matter physics from Pennsylvania State University-University Park in 2006. Then he worked at Pennsylvania State University-University Park (2006–2007) and also at Ohio State University-Columbus (2007–2010) as a postdoctoral researcher. He joined Sichuan University in 2010. His research interests include the design and fabrication of magnetic materials including diluted magnetic semiconductors and transition metal chalcogenides, and their spintronic and electronic applications.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Zhang, X., Wang, J. et al. Mn-doped SiGe thin films grown by UHV/CVD with room-temperature ferromagnetism and high hole mobility. Sci. China Mater. 65, 2826–2832 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-022-2025-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-022-2025-x