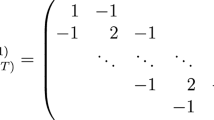Abstract
Spatio-temporal disease mapping models can be used to describe the geographical pattern of disease incidence across space and time. This paper discusses the development and application of spatio-temporal disease models based on generalized linear mixed models (GLMM) incorporating spatially correlated random effects, temporal effects and space–time interaction. Further, the models are fitted within a hierarchical Bayesian framework with Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation (INLA) methodology. The main objectives of this study are to choose the model that best represents the pattern of dengue incidence in Peninsular Malaysia from 2015 to 2017, to estimate the relative risk of disease based on the model selected and to visualize the risk spatial pattern and temporal trend. The models were applied to weekly dengue fever data at the district level in Peninsular Malaysia as reported to the Ministry of Health Malaysia from 2015 to 2017. In conclusion, it can be seen that there was a difference in dengue trend for every district for 2015–2017 and the models used was effective in identifying the high and low risk areas of dengue incidence.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gubler, D.J.: Dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 11(3), 480–496 (1998)
Ong, S.-Q.: Dengue vector control in malaysia: a review for current and alternative strategies. Sains Malaysiana 45(5), 777–785 (2016)
Besag, J., York, J., Mollié, A.: Bayesian image restoration, with two applications in spatial statistics. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 43(1), 1–20 (1991)
Bernardinelli, L., Clayton, D., Pascutto, C., Montomoli, C., Ghislandi, M., Songini, M.: Bayesian analysis of space-time variation in disease risk. Stat. Med. 14(21–22), 2433–2443 (1995)
Assuncao, R.M., Reis, I.A., Oliveira, C.D.L.: Diffusion and prediction of Leishmaniasis in a large metropolitan area in Brazil with a bayesian space-time model. Stat. Med. 20(15), 2319–2335 (2001)
Knorr-Held, L.: Bayesian modelling of inseparable space-time variation in disease risk. Stat. Med. 19(17–18), 2555–2567 (2000)
Ugarte, M., Goicoa, T., Ibanez, B., Militino, A.: Evaluating the performance of spatio-temporal bayesian models in disease mapping. Environ. Official J. Int. Environ. Soc. 20(6), 647–665 (2009)
Martínez-Beneito, M.A., López-Quilez, A., Botella-Rocamora, P.: An autoregressive approach to spatio-temporal disease mapping. Stat. Med. 27(15), 2874–2889 (2008)
Lindgren, F., Rue, H., Lindström, J.: An explicit link between gaussian fields and gaussian markov random fields: the stochastic partial differential equation approach. J. Royal Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 73(4), 423–498 (2011)
Blangiardo, M., Cameletti, M., Baio, G., Rue, H.: Spatial and spatio-temporal models with R-INLA. Spatial Spatio-Temp. Epidemiol. 4, 33–49 (2013)
Coly, S., Charras-Garrido, M., Abrial, D., Yao-Lafourcade, A.-F.: Spatiotemporal disease mapping applied to infectious diseases. Proc. Environ. Sci. 26, 32–37 (2015)
Aswi, A., Cramb, S., Duncan, E., Hu, W., White, G., Mengersen, K.: Climate variability and dengue fever in Makassar, Indonesia: Bayesian spatio-temporal modelling. Spatial Spatio-Temp. Epidemiol. 33, 100335 (2020)
Denis, M., Cochard, B., Syahputra, I., De Franqueville, H., Tisné, S.: Evaluation of spatio-temporal Bayesian models for the spread of infectious diseases in oil palm. Spatial Spatio-Temp. Epidemiol. 24, 63–74 (2018)
Parpia, A.S., Skrip, L.A., Nsoesie, E.O., Ngwa, M.C., Abah, A.S.A., Galvani, A.P., Ndeffo-Mbah, M.L.: Spatio-temporal dynamics of measles outbreaks in Cameroon. Ann. Epidemiol. 42, 64–72 (2020)
Lee, H.: Stochastic and spatio-temporal analysis of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome outbreak in South Korea, 2015. Infect. Disease Modell. 4, 227–238 (2019)
Liao, J., Qin, Z., Zuo, Z., Yu, S., Zhang, J.: Spatial-temporal mapping of hand foot and mouth disease and the long-term effects associated with climate and socio-economic variables in Sichuan Province, China from 2009 to 2013. Sci. Total Environ. 563, 152–159 (2016)
Abd Naeeim, N.S., Rahman, N.A.: Estimating relative risk for dengue disease in Peninsular Malaysia using INLA. Malays. J. Fund. Appl. Sci 13, 721–727 (2017)
Blangiardo, M., Cameletti, M.: Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Bayesian Models with R-INLA, 1st edn. John Wiley & Sons, United Kingdom (2015)
Clayton, D., Kaldor, J.: Empirical bayes estimates of age-standardized relative risks for use in disease mapping. Biometrics, 671–681 (1987)
Marshall, R.J.: Mapping disease and mortality rates using empirical bayes estimators. Appl. Stat. 283–294 (1991)
Lahiri, P., Maiti, T.: Empirical bayes estimation of relative risks in disease mapping. Calcutta Statist. Assoc. Bull. 53(3–4), 213–224 (2002)
MacNab, Y.C., Farrell, P.J., Gustafson, P., Wen, S.: Estimation in bayesian disease mapping. Biometrics 60(4), 865–873 (2004)
Wakefield, J.: Disease mapping and spatial regression with count data. Biostatistics 8(2), 158–183 (2006)
Rue, H., Martino, S., Chopin, N.: Approximate Bayesian inference for latent Gaussian models by using integrated nested Laplace approximations. J. Royal Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 71(2), 319–392 (2009)
Bakka, H., Rue, H., Fuglstad, G.A., Riebler, A., Bolin, D., Illian, J., Krainski, E., Simpson, D., Lindgren, F.: Spatial modeling with r-inla: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 10(6), 1443 (2018)
Aswi, A., Cramb, S., Moraga, P., Mengersen, K.: Bayesian spatial and spatio-temporal approaches to modelling dengue fever: a systematic review. Epidemiol. Infect. 147(33), 1–14 (2019)
Lowe, R., Bailey, T.C., Stephenson, D.B., Graham, R.J., Coelho, C.A.S., Sá Carvalho, M., Barcellos, C.: Spatio-temporal modelling of climate-sensitive disease risk: Towards an early warning system for dengue in Brazil. Comput. Geosci. 37(3), 371–381 (2011). (Geoinformatics for Environmental Surveillance)
Jaya, I., Abdullah, A.S., Hermawan, E., Ruchjana, B.: Bayesian spatial modeling and mapping of dengue fever: a case study of dengue Feverin the city of Bandung, Indonesia. Int. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 54(3), 94–103 (2016)
Kikuti, M., Cunha, G.M., Paploski, I.A., Kasper, A.M., Silva, M.M., Tavares, A.S., Cruz, J.S., Queiroz, T.L., Rodrigues, M.S., Santana, P.M., et al.: Spatial distribution of dengue in a Brazilian urban slum setting: Role of socioeconomic gradient in disease risk. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9(7), 0003937 (2015)
Wijayanti, S.P., Porphyre, T., Chase-Topping, M., Rainey, S.M., McFarlane, M., Schnettler, E., Biek, R., Kohl, A.: The importance of socio-economic versus environmental risk factors for reported dengue cases in Java. Indonesia. PLoS Neglected Trop. Diseases 10(9), 0004964 (2016)
Martínez-Bello, D., López-Quílez, A., Prieto, A.T.: Spatiotemporal modeling of relative risk of dengue disease in colombia. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk Assess. 32(6), 1587–1601 (2018)
Sani, A., Abapihi, B., Mukhsar, M., Kadir, K.: Relative risk analysis of dengue cases using convolution extended into spatio-temporal model. J. Appl. Stat. 42(11), 2509–2519 (2015)
Martínez-Bello, D.A., Lopez-Quilez, A., Prieto, A.T.: Relative risk estimation of dengue disease at small spatial scale. Int. J. Health Geogr. 16(1), 1–15 (2017)
Abd Naeeim, N.S., Rahman, N.A.: Fitting spatio-temporal model with different choice of dependence matrices: A case study of dengue incidence in Peninsular Malaysia. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2184, p. 050033 (2019). AIP Publishing LLC
Abd Naeeim, N.S., Abdul Rahman, N., Muhammad Fahimi, F.A.: A spatial-temporal study of dengue in Peninsular Malaysia for the year 2017 in two different space-time model. J. Appl. Stat. 47(4), 739–756 (2020)
Shaddick, G., Zidek, J.V.: Spatio-Temporal Methods in Environmental Epidemiology. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London (2015)
Leroux, B.G., Lei, X., Breslow, N.: Estimation of disease rates in small areas: a new mixed model for spatial dependence. In: Statistical Models in Epidemiology, the Environment, and Clinical Trials, pp. 179–191. Springer (2000)
Rue, H., Held, L.: Gaussian Markov Random Fields: Theory and Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Ugarte, M.D., Adin, A., Goicoa, T., Militino, A.F.: On fitting spatio-temporal disease mapping models using approximate bayesian inference. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 23(6), 507–530 (2014)
Bernardinelli, L., Clayton, D., Montomoli, C.: Bayesian estimates of disease maps: how important are priors? Stat. Med. 14(21–22), 2411–2431 (1995)
Spiegelhalter, D.J., Best, N.G., Carlin, B.P., Van Der Linde, A.: Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J. Royal Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 64(4), 583–639 (2002)
Richardson, S., Thomson, A., Best, N., Elliott, P.: Interpreting posterior relative risk estimates in disease-mapping studies. Environ. Health Perspect. 112(9), 1016 (2004)
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Vector Borne Disease Sector, Ministry of Health Malaysia, for the dengue disease data provided in this study. Acknowledgement to Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia for Fundamental Research Grant Scheme with Project Code: FRGS/1/2018/STG06/USM/02/12. We also thank the reviewers and editors of Bulletin of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society for their valuable comments with preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Anton Abdulbasah Kamil.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd Naeeim, N.S., Abdul Rahman, N. & Md. Ghani, N.A. Spatio-Temporal Modelling of Dengue Fever Patterns in Peninsular Malaysia from 2015–2017. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 45 (Suppl 1), 345–364 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40840-022-01313-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40840-022-01313-0
Keywords
- Disease mapping
- Relative risk estimation
- Dengue disease
- Integrated nested Laplace approximation method
- Spatio-temporal model