Abstract
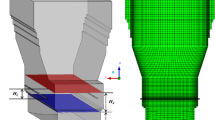
Appropriate primary air injection mode (PAIM) is the key to ensure high smelting efficiency of oxygen-rich side-blown bath smelting furnace (OSBF). In this study, the influence of PAIM on the gas–liquid multiphase flow in the OSBF was investigated by numerical simulation. The PAIM including number of nozzles, nozzle insertion length, nozzle tilt angle, and nozzle diameter was optimized by orthogonal test design. The results indicate that the order of the influence of PAIM on the OSBF process is nozzle insertion length, nozzle diameter, nozzle tilt angle, and nozzle number. The optimum conditions of PAIM were determined as number of nozzles: 8, nozzle insertion length: 0.12 m, nozzle tilt angle: 0°, and nozzle diameter: 0.03 m, and the smelting efficiency was improved by 45% compared to the practical conditions. Furthermore, it was verified that the optimum conditions of PAIM effectively improved the smelting efficiency of the OSBF by physical model experiments.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [Desheng Chen], upon reasonable request.
References
Li DB, Chen XG, Wang ZS (2019) Modern side-blown smelting technology for nonferrous metals. Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing
Romenets VA, Valavin VS, Pokhvisnev YV, Makeev SA, Gimmelfarb AI (2010) Use of the innovative Romelt technology to process iron-bearing wastes from mines and metallurgical plants. Metallurgist 54:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-010-9292-3
Chen L, Hao ZD, Yang TZ, Xiao H, Liu WF, Zhang DC, Bin S, Bin WD (2015) An efficient technology for smelting low grade bismuth-lead concentrate: oxygen-rich side blow process. JOM 67(9):1997–2004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1491-8
Meijer K, Zeilstra C, Teerhuis C, Ouwehand M, Stel J (2013) Developments in alternative ironmaking. Trans Indian Inst Met 66:475–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-013-0309-z
Yi SH, Choi ME, Kim DH, Ko CK, Park WI, Kim SY (2019) FINEX® as an environmentally sustainable ironmaking process. Ironmak Steelmak 46:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2019.1641682
Grechko AV (2000) Prospects for the use of bubbling processes in pyrometallurgy. Metallurgist 44:151–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02466165
Hirata T, Ishikawa M, Anezaki S (1992) Stirring effect in bath-smelting furnace with combined blowing of top and side blown oxygen and bottom blown nitrogen. ISIJ Int 32(2):182–189. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.32.182
Jiang X, Cui ZX, Chen M, Zhao BJ (2019) Mixing behaviors in the horizontal bath smelting furnaces. Metall Mater Trans B 50:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1433-2
Liu YT, Yang TZ, Chen Z, Zhu ZY, Zhang L, Huang Q (2020) Experiment and numerical simulation of two-phase flow in oxygen enriched side-blown furnace. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 30:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65196-4
Conejo AN, Mishra R, Mazumdar D (2019) Effects of nozzle radial position, separation angle, and gas flow partitioning on the mixing, eye area, and wall shear stress in ladles fitted with dual plugs. Metall Mater Trans B 50:1490–1502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01546-8
Wang H, Brito-Parada PR (2021) Shape deformation and oscillation of particle-laden bubbles after pinch-off from a nozzle. Chem Eng J 412:127499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127499
Li LM, Li XJ, Zhu ZC, Li BK (2020) Numerical modeling of multiphase flow in gas stirred ladles: from a multiscale point of view. Powder Technol 373:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.06.028
Wang B, Shen SY, Ruan YW, Cheng SY, Peng WJ, Zhang JY (2020) Simulation of gas-liquid two-phase flow in metallurgical process. Acta Metall Sin 56:619–632. https://doi.org/10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00385
Mantripragada VT, Sarkar S (2018) Wall stresses in dual bottom purged steel making ladles. Chem Eng Res Des 139:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.09.036
Mantripragada VT, Sarkar S (2020) Slag eye formation in single and dual bottom purged industrial steelmaking ladles. Can Met Q 59:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/00084433.2020.1715697
Mantripragada VT, Sarkar S (2022) Multi-objective optimization of bottom purged steelmaking ladles. Trans Indian Inst Met 75(9):2289–2298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02602-9
Xiao YD, Lu TT, Zhou YG, Su QQ, Mu LZ, Wei T, Zhao HL, Liu FQ (2021) Computational fluid dynamics study on enhanced circulation flow in a side-blown copper smelting furnace. JOM 73(9):2724–2732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04800-0
Zou Q, Hu JH, Yang SL, Wang H, Deng G (2023) Investigation of the splashing characteristics of lead slag in side-blown bath melting process. Energies 16:1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16021007
Lu TT, Mu LZ, Xiao YD, Zhao HL, Liu FQ (2022) CFD study on bottom-blown copper smelting furnace with unsymmetric gas injection. J Sustain Metall. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-022-00565-1
Dai WX, Cheng GG, Li SJ, Huang Y, Zhang GL, Qiu YL, Zhu WF (2019) Numerical simulation of multiphase flow and mixing behavior in an industrial Single Snorkel Refining Furnace (SSRF): the effect of gas injection position and snorkel diameter. ISIJ Int 59(7):1214–1223. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2018-826
Zhang YM, Yi LY, Wang LN, Chen DS, Wang WJ, Liu YH, Zhao HX, Qi T (2017) A novel process for the recovery of iron, titanium, and vanadium from vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite: sodium modification–direct reduction coupled process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 24(5):504–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1431-4
Chen DS, Zhao LS, LiuYH QT, Wang JC, Wang LN (2013) A novel process for recovery of iron, titanium, and vanadium from titanomagnetite concentrates: NaOH molten salt roasting and water leaching processes. J Hazard Mater 244:588–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.10.052
Chen LM, Zhen YL, Zhang GH, Chen DS, Wang LN, Zhao HX, Liu YH, Meng FC, Wang M, Qi T (2022) Mechanism of sodium carbonate-assisted carbothermic reduction of titanomagnetite concentrate. Metall Mater Trans B 53(4):2272–2292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02528-z
Son G, Hur N (2002) A coupled level set and volume-of-fluid method for the buoyancy-driven motion of fluid particles. Numer Heat Transf B 42:523–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407790260444804
Brackbill JU, Kothe DB, Zemach C (1992) A continuum method for modeling surface-tension. J Comput Phys 100:335–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(92)90240-Y
Shih TH, Zhu J, Lumley JL (1995) A new Reynolds stress algebraic equation model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 125:287–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7825(95)00796-4
Ansys, Inc. (2018) ANSYS Fluent theory guide 19.0
Chen LM, Zhen YL, Zhang GH, Wang LN, Chen DS, Zhao HX, Liu YH, Meng FC, Peng YH, Qi T (2023) Role of Na2O and TiO2 on viscosity and structure of Sodium-Titanium-bearing slag. J Non-Cryst Solids 602:122080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2022.122080
Liu CJ, Zhang R, Meng YF, Wang Z, Jiao SY, Jia JX, Min Y (2021) Mirco-level insight into the surface tension-structure relationship of molten CaO–MgO–SiO2–FexO–P2O5 Slags. ISIJ Int 61(11):2765–2772. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2021-236
Obiso D, Kriebitzsch S, Reuter M, Meyer B (2019) The importance of viscous and interfacial forces in the hydrodynamics of the top-submerged-lance furnace. Metall Mater Trans B 50:2403–2420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01630-z
Zhang JF (2007) On the efficiency of experimental design and its some related problems. J Appl Stat Manage 26(5):792–801. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-6735.2001.04.009
Zhang LQ, Luo P (2012) Practical optimization method. China Science Publishing & Media Ltd., Beijing
Zhang ZY, Yan HJ, Liu FK, Wang JM (2013) Optimization analysis of lance structure parameters in oxygen enriched bottom-blown furnace. Chin J Nonferrous Met 23:1471–1478. https://doi.org/10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2013.05.041
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDC04010100), Special Project for Transformation of Major Technological Achievements in Hebei Province (No. 19044012Z), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC1900500), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21908231), Province Key R&D Program of Hebei (No. 20374105D), and President Fund of China Institute of Standardization (No. 542022Y-9371).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Yongxiang Yang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, Z., Chen, D., Sun, L. et al. Numerical Simulation and Optimization Analysis of Primary Air Injection Mode in Oxygen-Rich Side-Blown Bath Smelting Furnace. J. Sustain. Metall. 9, 871–883 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-023-00699-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-023-00699-w