Abstract
Steelmaking slag is considered as a promising phosphorus resource as it contains the phosphorus in a condensed phase of Ca2SiO4–Ca3P2O8 solid solution (C2S–C3P)ss. In the present study, the carbothermic reduction of (C2S–40 mol% C3P)ss at 1573 K was carried out to understand the phosphorus removal mechanism by varying reduction temperature, external gas flow rate, amount of graphite, and concentration of Ca3P2O8 in (C2S–C3P)ss. The carbothermic reduction proceeded as a zero-order reaction when the temperature was 1573 K, despite the P2O5 concentration decrease with the reduction time. At temperatures less than 1473 K, the reduction did not occur. Based on the XRD analysis of the reduced (C2S–C3P)ss samples, it was found that carbothermic reduction of the C2S–C3P solid solution proceeded by the decomposition of the C2S–C3P solid solution into CaO and C2S with the removal of phosphorus, but not by a uniform decrease of the phosphorous throughout the C2S–C3P solid solution. The overall reduction degrees were found to be independent of the reduction rate (zero-order reaction) and the P2O5 concentration in the (C2S–C3P)ss. From these independencies, the rate-controlling step of the carbothermic reduction of (C2S–C3P)ss was concluded to be the Boudouard reaction.
Graphical Abstract












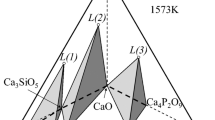
Reproduced from [26], under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elser J, Bennett E (2011) A broken biogeochemical cycle. Nature 478:29–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/478029a
Matsubae K, Webeck E, Nansai K et al (2015) Hidden phosphorus flows related with non-agriculture industrial activities: a focus on steelmaking and metal surface treatment. Resour Conserv Recycl 105:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.10.002
Matsubae-Yokoyama K, Kubo H, Nakajima K, Nagasaka T (2009) A material flow analysis of phosphorus in Japan. J Ind Ecol 13:687–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2009.00162.x
Matsubae K, Kajiyama J, Hiraki T, Nagasaka T (2011) Virtual phosphorus ore requirement of Japanese economy. Chemosphere 84:767–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.077
Matsubae K, Yamasue E, Inazumi T et al (2016) Innovations in steelmaking technology and hidden phosphorus flows. Sci Total Environ 542:1162–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.107
Wilfert P, Kumar PS, Korving L et al (2015) The relevance of phosphorus and iron chemistry to the recovery of phosphorus from wastewater: a review. Environ Sci Technol 49:9400–9414. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00150
Havukainen J, Nguyen MT, Hermann L et al (2016) Potential of phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge and manure ash by thermochemical treatment. Waste Manage 49:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.01.020
Kelessidis A, Stasinakis AS (2012) Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries. Waste Manage 32:1186–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.012
Fisher LV, Barron AR (2019) The recycling and reuse of steelmaking slags: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:244–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.010
Koizumi S, Miki T, Nagasaka T (2016) Enrichment of phosphorus oxide in steelmaking slag by utilizing capillary action. J Sustain Metall 2:38–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-015-0035-3
Kubo H, Matsubae-Yokoyama K, Nagasaka T (2010) Magnetic separation of phosphorus enriched phase from multiphase dephosphorization slag. ISIJ Int 50:59–64. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.50.59
Li C, Gao J, Wang Z et al (2017) Separation of Fe-bearing and P-bearing phase from the steelmaking slag by super gravity. ISIJ Int 57:767–769. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-694
Lin L, Bao Y, Wang M et al (2014) Separation and recovery of phosphorus from P-bearing steelmaking slag. J Iron Steel Res Int 21:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60077-7
Matsubae-Yokoyama K, Kubo H, Nagasaka T (2010) Recycling effects of residual slag after magnetic separation for phosphorus recovery from hot metal dephosphorization slag. ISIJ Int 50:65–70. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.50.65
Ohtake H, Tsuneda S (2019) Phosphorus recovery and recycling. Springer, Singapore
Yokoyama K, Kubo H, Mori K et al (2007) Separation and recovery of phosphorus from steelmaking slags with the aid of a strong magnetic field. ISIJ Int 47:1541–1548. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.47.1541
Shimio S, Sano N, Matsushita Y (1977) Removal of phosphorus in BOF slags. Tetsu-to-Hagane 63:1520–1528. https://doi.org/10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.63.9_1520
Ryu J-Y, Fruehan RJ, Morales AT (1999) Kinetics of phosphorus vaporization from slag.pdf. ISS Trans. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.33.479
Matsui A, Nakase K, Kikuchi N et al (2011) Phosphorus separation from steelmaking slag by high temperature reduction with mechanical stirring. Tetsu-to-Hagane 97:416–422. https://doi.org/10.2355/tetsutohagane.97.416
Yu H, Miki T, Sasaki Y, Nagasaka T (2020) Crystallography of the high-temperature Ca2SiO4-Ca3P2O8 solid solutions. Metall Mater Trans B. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01945-2
Zhong M, Matsuura H, Tsukihashi F (2015) Activity of P2O5 in solid solution between Di-calcium silicate and Tri-calcium phosphate at 1 823 and 1873 K. ISIJ Int 55:2283–2288. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-019
Hasegawa M, Kashiwaya Y, Iwase M (2012) Thermodynamic properties of solid solutions between Di-calcium silicate and Tri-calcium phosphate. High Temp Mater Process 31:421–430. https://doi.org/10.1515/htmp-2012-0077
Lahijiani R, Zainal ZA, Mohammadi M, Mohamed AR (2014) Conversion of greenhouse gas CO2 to the fuel gas CO via the Boudouard reaction: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 41:615–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.201408.034
Kornath A, Kaufmann A, Torheyden M (2002) Raman spectroscopic studies on matrix-isolated phosphorus molecules P4 and P2. J Chem Phys 116:3323–3326. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1436112
Fix W, Heymann H, Heinke R (1969) Sobsolidus relations in the system of 2CaO·SiO2-3CaO·P2O5. J Am Ceram Soc 52:346–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1969.tb11948.x
Jain A, Ong SP, Hautier G et al (2013) The materials project: a materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation. APL Mater 1:011002. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4812323
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Il Sohn.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Lu, X., Miki, T. et al. Phosphorous Recovery from Ca2SiO4–Ca3P2O8 Solid Solution By Carbothermic Reduction. J. Sustain. Metall. 7, 459–469 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00350-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00350-6