Abstract
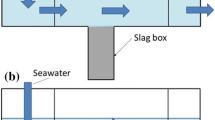
The mutual effect of steelmaking slag layer depth and diameter on alkali elution rate was investigated using two kinds of open channel vessels with straightened seawater. Seawater velocity, slag layer depth, and diameter were changed from 0.2 × 10−2 to 4.2 × 10−2 m/s, from 3.3 × 10−2 to 5.0 × 10−1 m, and from 0.10 × 10−2 to 2.18 × 10−2 m, respectively. The alkali elution rate increased with an increase in seawater velocity. The effective mass transfer coefficient, which was smaller than the true mass transfer coefficient, was calculated using the total slag surface area including the slag layer irrelevant to the alkali elution. It approached the true mass transfer coefficient when the slag diameter was larger and the slag layer was thinner. Moreover, the ratio of the effective mass transfer coefficient to the true one approached unity when the pH change in the slag layer was decreased. The slag layer height, H (m), involved in the alkali elution rate was calculated using H/d = 2.98 × 10−2 Re − 1.24 × 10−5 Re 2 when the total slag layer height, h s (m), was larger than H (m). Here, d is the slag diameter (m) and Re is the Reynolds number.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 December 2016
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Horii K, Tsutsumi N, Kitano Y, Kato T (2013) Processing and reusing technologies for steelmaking slag. Nippon Steel Tech Rep 104:123–129
The Japan Iron and Steel Federation (2008) Tenrokei Steelmaking Slag Kaiikiriyono Tebiki (Steelmaking Slag; a Guide for Usage in the Ocean Area). JISF, Tokyo
The Japan Iron and Steel Federation (2008) Tenrokei Steelmaking Slag Kaiikiriyono Tebiki, Bessatsu, Tenrokei Steelmaking Slag to Syunsetsudo tono Kongokairyokoho (Steelmaking Slag; a Guide for Usage in the Ocean Area, Supplementary volume, Mixing Method of Steelmaking Slag and dredged soil). JISF, Tokyo
Nakamura Y, Taniguchi A, Okada S, Tokuda M (1998) Positive growth of phytoplankton under conditions enriched with steel-making slag solution. ISIJ Int 38(4):390–398
Futatsuka T, Shitogiden K, Miki T, Nagasaka T, Hino M (2004) Dissolution behavior of nutrition elements from steelmaking slag into seawater. ISIJ Int 44(4):753–761
Tanaka M, Hirata J, Nakamoto D, Terada I, Ryumae I, Takahashi M, Oikawa T, Takahashi K, Aimoto M (2014) Dissolution behavior of silicic acid from steelmaking slag to seawater. Tetsu-to-Hagané 100(7):919–923
Liu D, Yamamoto M (2014) Influence of seawater temperature and organic matter on iron elution from a mixture of steelmaking slag and composts. Tetsu-to-Hagané 100(8):1043
Yamamoto M, Fukushima M, Liu D (2011) Effect of humic substances on iron elution in the method of restoration of seaweed beds with steelmaking slag. Tetsu-to-Hagané 97(3):159–164
Zhang X, Matsuura H, Tsukihashi F (2012) Dissolution mechanism of various elements into seawater for recycling of steelmaking slag. ISIJ Int 52(5):928–933
Zhang X, Matsuura H, Tsukihashi F (2014) Influence of gluconic acid on dissolution of Si, P and Fe from steelmaking slag with different composition into seawater. ISIJ Int 54(6):1443–1449
Zhang X, Matsuura H, Tsukihashi F (2015) Enhancement of the dissolution of nutrient elements from steelmaking slag into seawater by gluconic acid. J Sustain Metall 1(2):134–143
Zhang X, Matsuura H, Tsukihashi F (2016) Dissolution mechanism of steelmaking slag-dredged soil mixture into seawater. J Sustain Metall 2(2):123–132
Kato T, Kosugi C, Kiso E, Torii K (2015) Application of steelmaking slag to marine forest restoration. Nippon Steel Sumitomo Metal Techn Rep 109:79–84
Hayashi A, Watanabe T, Kaneko R, Takano A, Takahashi K, Miyata Y, Matsuo S, Yamamoto T, Inoue R, Ariyama T (2012) Decrease of sulfide in enclosed coastal sea by using steelmaking slag. Tetsuto-Hagané 98(5):207–214
Hayashi A, Asaoka S, Watanabe T, Kaneko R, Takano A, Takahashi K, Miyata Y, Matsuo S, Kim K, Inoue R, Ariyama T (2012) Mechanism of suppression of sulfide ion seawater using steelmaking slag. Tetsu-to-Hagané 98(11):618–625
Miyata Y, Hayashi A, Kuwayama M, Yamamoto T, Urabe N (2014) Reduction test of hydrogen sulfide in the silty sediment of the Fukuyama inner harbor using steelmaking slag. Tetsu-to-Hagané 100(3):421–428
Miyata Y, Hayashi A, Kuwayama M, Yamamoto T, Tanishiki K, Urabe N (2014) A field experiment of sulfide reduction in silty sediment using steelmaking slag. Tetsu-to-Hagané 100(11):1426–1432
Kiso E, Tsujii M, Ito K, Nakagawa M, Gomyo M, Nagatome K (2008) Method of dredged soil improvement by mixing with converter steel-making slag. J Civil Eng Ocean 24(7):327–332
Takeda M, Gomyo M, Nagatome T, Tsujii M, Kiso E, Nakagawa M (2008) Field experiments on dreged soil improvement by continuously mixing with converter steelmaking slag. J Civil Eng Ocean 24(7):351–356
Miki T, Shitogiden K, Samada Y, Hino M (2004) Elution mechanism of fluorine from steelmaking slag into seawater. ISIJ Int 44(5):935–939
Mizukami H, Ishikawa M, Hirata T, Kamiyama T, Ichikawa K (2004) Dissolution mechanism of fluorine in aqueous solution from fluorine containing synthetic slag. ISIJ Int 44(3):623–629
Miki T, Futatsuka T, Shitogiden K, Nagasaka T, Hino M (2004) Dissolution behavior of environmentally regulated elements from steelmaking slag into seawater. ISIJ Int 44(4):762–769
Kanayama S, Souma A, Tanaka Y, Tsujii M, Kiso E, Nakagawa M (2008) Prediction of influence on pH by utilization of mixture of dredged soil and converter steel-making slag for coastal environment improvement works. J Civil Eng Ocean 24(7):333–338
Kanayama S, Sakanakura H, Mizutani S, Kato Y, Takahashi K, Kiso E, Hirai N, Miyazaki T (2013) Study on the elution of alkalinity from steel-making slag piled in seawater. J Civil Eng B3(Ocean) 70(2):I_1152–I_1157
Miyazaki T, Sakanakura H, Mizutani S, Takahashi K, Kiso E, Hirai N, Takeda M, Kurahara Y (2013) Experimental study on alkali diffusion behavior from steel slag products in steady seawater flow. J Civil Eng B3(Ocean) 69(2):I_1142–I_1147
Tamaki H, Uddin MA, Kato Y, Takahashi K (2013) Alkali elution behavior of steelmaking slag into seawater by batch test. Tetsu-to-Hagané 99(11):676–682
Takeuchi G, Uddin MA, Kato Y, Takahashi K (2015) Alkali elution behavior of steelmaking slag into seawater by continuous stirred tank reactor. ISIJ Int 55(10):2252–2257
Chow VT (1959) Open-channel hydraulics. International student edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Miki T, Shitogiden K, Samada Y, Nagasaka T, Hino M (2003) Consideration of dissolution behavior of elements in steelmaking slag based on their stability diagram in seawater. Tetsu-to-Hagane 89(4):388
Chemical Society of Japan (1975) Handbook of chemistry, basic edition reviews, 2nd edn. Maruzen, Tokyo
Hoffert M, Wey YC, Callegari AJ, Broecker WS (1979) Atmospheric response to deep-sea injections of fossil-fuel carbon dioxide. Clim Change 2(1):53–68
Sohma S, Kakio T, Sekiguchi Y (2005) Introduction of the global ocean ecosystem model “DONGURI” and its implementation to investigate the biochemical effects on global warming. In: Proceedings 7th international conference on greenhouse gas control technologies, IEA (International Energy Agency), Paris, pp 2389–2393
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out under collaboration with Nippon Slag Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was D. Panias.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-016-0113-1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeuchi, G., Tamaki, H., Uddin, M.A. et al. Mutual Effect of Steelmaking Slag Layer Depth and Diameter on Alkali Elution Rate in Open Channel Vessels with Straightened Seawater Flow. J. Sustain. Metall. 3, 459–468 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-016-0107-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-016-0107-z