Abstract
This paper summarizes the main properties of the microstructures formed during reverse (austenite → martensite) transitions in single crystals of the Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy, and discusses the relation between these properties and the mechanical stabilization effect. It is shown that all experimentally observed interfacial microstructures (X- and λ-interfaces and their non-classical equivalents) are not local minimizers of the quasi-static energy, and their formation is probably governed by requirements on mobility and dissipation. This conclusion is supported by finite elements models, and acoustic emission measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Among the copper-based shape memory alloys (SMAs), the Cu–Al–Ni system [1–4] has been by far the most studied one during the past four decades (see e.g. [5] for a review). There are several reasons why particularly this alloy has been so extensively studied both on the theoretical level and by experimental observations: both the cubic high-temperature phase (bcc austenite) and the tetragonal low-temperature phase (2H γ ′1 -martensite) of this alloy have simple crystal structures, the transformation strains are large (up to 8.5 %, [2]), the transitions are fully reversible and are not accompanied by any significant plastic flow, the twinning stress can be as low as 0.7 MPa [6], and the transition temperatures can be set close to the room temperature. In addition, the surface energy of the twinning planes in this alloy is relatively high [7], and so the martensitic laminates and other regular microstructures formed in single crystals of this alloy appear at the length-scales of several tens of micrometers or even larger, which enables easy observation of these microstructures by optical microscopy.
These properties predetermine the Cu–Al–Ni alloy to be used as an illustrative example of the SMAs [5, 8, 9]. In this sense, the optical micrographs of habit planes, macrotwins, or more complex microstructures in this alloy have been used several times to confirm the theoretical predictions of the mathematical theory of martensitic microstructures [10, 11], which explains the formation of the observed microstructures by means of energy minimization and kinematic compatibility.
One of the most interesting effects observed in the single crystals of the Cu–Al–Ni alloy is the mechanical stabilization of martensite [12–14], i.e., the strong dependence of the martensite → austenite transition temperature on the initial microstructure of martensite. This effect occurs whenever the initial microstructure cannot directly form any compatible interface with the austenite phase, and thus, the nucleation of austenite in the crystal requires local reorientation of martensite in order to form some microstructural object providing kinematic compatibility between the initial microstructure and the austenitic nucleus. This object is called the interfacial microstructure [15, 16], and propagates through the material with the growth of the austenitic nucleus until the transition is completed. The energy required for the formation of the interfacial microstructure increases the nucleation barrier for austenite, and so the transition is shifted to higher temperatures. In this paper, we will summarize the recent findings on the properties of such interfacial microstructures, with the focus laid on the relation between the kinematic compatibility and the mobility of these objects.
Theoretical Background for the Mechanical Stabilization Effect
The Cu–Al–Ni alloy belongs to the cubic-to-orthorhombic class [17], which implies that the martensitic phase can exist in six different structural variants and there can be three different twinning systems formed between these variants: Compound, Type 1, and Type 2. In the classical theory of martensitic microstructures [8, 10], the individual variants of martensite are described by different Bain matrices U 1…6. A given pair of variants (I,J) can then form a twin whenever the middle eigenvalue of the matrix C = U −1I U 2J U −1I is equal to one.
For the Cu–Al–Ni alloy, each pair of variants can form twins of one or two of the twinning system listed above, and, consequently, there can appear a broad variety of first order laminates (microstructures consisting of parallel, twin-connected plates of two variants of martensite with periodically altering thicknesses [8]) in the single crystals of this alloy. As the Compound twins can cross compatibly with the Type 1 and Type 2 twins, even a broader variety of more complex microstructures can appear by lamination of higher orders.
For compatible connection between a fine microstructure with an effective Bain matrix U μ and austenite (described by the Bain matrix equal to the identity matrix I), it is required that the middle eigenvalue of U μ is equal to one. It can be easily shown that this condition is satisfied neither for any of the single variants of 2H martensite, nor for any first order laminate of the Compound twins, while it can be satisfied by the first order laminates of the Type 1 and Type 2 twins with specific volume fractions of the individual components.
As a consequence of this, a single crystal of Cu–Al–Ni austenite, when cooled down, transforms into a fine mixture of first order laminates of Type 1 or Type 2. Then, upon heating, the nucleation of austenite is easily possible due to local compatibility between this microstructure and the nuclei. However, if some mechanical stress is applied onto the martensitic microstructure and the microstructure gets reoriented into either a single variant of martensite, or any other microstructure without λ 2 = 1, the nucleation of austenite is suppressed, and the reverse transition is shifted to higher temperatures.
The mechanical stabilization appears then at two levels. Firstly, the nucleation barrier is increased by the energy necessary to create the compatible nucleus-to-martensite connection, i.e., to nucleate also the interfacial microstructure. Secondly, the growth of the austenitic nuclei is then accompanied by motion of the interfacial microstructure that dissipates additional energy and makes the reverse transition more energetically expensive.
The first effect, i.e., the increase of the nucleation barrier, plays an important role for the localization of the first austenitic nuclei. As shown and theoretically explained by Ball et al. [18], in a prismatic sample of the Cu–Al–Ni 2H martensite in a form of a single variant, the nucleation can occur only on one corner of the sample, where the necessary shear strains accompanying the formation of the interfacial miscrostructure are not blocked by geometrical constraints.
The second effect, i.e., the energy dissipation during the motion of the interfacial microstructure, gives then a possible explanation for the specific morphologies (X- or λ-interfaces, see the next section for more details) observed experimentally in the Cu–Al–Ni single crystals. As shown by Glatz et al. [19], once the nucleus is created these specific morphologies correspond to minimal dissipation paths for the transition from mechanically stabilized martensite to austenite.
Experimentally Observed Interfacial Microstructures
Types of the Observed Morphologies
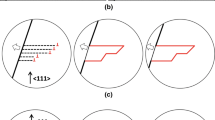
The first experimental observation of interfacial microstructures was reported by Basinski and Christian [20, 21] in single crystals of the In-Tl alloy. Two specific morphologies were observed in [20, 21], called X-interfaces and λ-interfaces. The difference between these two morphologies is outlined in Fig. 1a and b, where it is shown how the X-interfaces and λ-interfaces provide kinematically compatible connection between austenite and single variant of martensite. Both the X- and λ-morphologies consist of two twinned regions, each including one homogeneous 1st order laminate of twins, and in both cases these two regions meet along one line. In the X-interface, both these regions are connected to the single variant of martensite by a single twinning plane, i.e., the laminate inside each twinned region is parallel to the interface between this region and the single variant of martensite. In the λ-interface, on contrary, the laminate in at least one of the twinned regions is oriented generally with respect to this interface, and so the twinned region is connected to the single variant by a general twinned-to-detwinned planar interface (denoted as detwinning plane in Fig. 1b).
Morphologies of experimentally observed interfacial microstructures: a, b X- and λ- interface between austenite and single variant of martensite; c non-conventional modification of the X-interface between austenite and a 1st order laminate of Compound twins. The right column shows the sketches of the entire morphologies, the left column shows the corresponding optical micrographs. In c, the location and orientation of the micrograph with respect to the morphology is outlined by the shaded rectangle
In the Cu–Al–Ni, the first observation of interfacial microstructures was reported by Novák et al. [6]; the observed interface was a λ-interface with clearly visible habit and detwinning planes. However, no analysis of the compatibility and full morphology of the interface was provided. Seiner et al. [15, 22] observed first the formation of interfacial microstructures (both X- and λ-interfaces) in thermal gradients and by localized heating, and then also more complex microstructures consisting of so-called non-classical interfaces [23]. These microstructures form in the case when the mechanically stabilized martensite entering the transition is not a single variant, but a 1st order laminate of Compound twins that, itself, cannot form any compatible interface with austenite; as a result, the Compound laminate is penetrated by an X- or λ-interface such that a compatible connection appears between austenite and a crossing-twins microstructure (Fig. 1c). The existence of interfaces providing such a compatible connection was predicted theoretically by Ball and Carstensen [24] prior to the first experimental observations, who also suggested the term non-classical for them. The non-classical interfaces exhibit several unique features, for example they can be curved without losing the compatibility if the Compound laminate is heterogeneous.
Transition Front Kinetics
In all reported observations of the formation and motion of the interfacial microstructures in Cu–Al–Ni, the austenite → martensite transition exhibited a two-stage behavior: after the nucleation in one of the corners of the sample, the growth of the nucleus induced the formation of the specific morphology (X- or λ-interface, either classical or non-classical). After this morphology had been formed, the interfacial microstructure propagated through the sample without any changes of its shape. The propagation speed in this stage was always of the order of 1 mm s−1 [22], which is probably a velocity determined by equilibrium between the latent heat production and heat conduction [the so-called Stefan’s problem [25, 26].
The shape-preserving propagation indicates that the X- or λ-morphologies are in some sense optimal for mobile interfacial microstructures, i.e., that they may exhibit either minimal dissipation (as discussed by Glatz et al. [19]), or minimal pinning on the defects or other local energetic minima (compare with the mobility of macro-twin interfaces discussed in [27]). This significance of the X- and λ-morphologies can be clearly illustrated by monitoring the acoustic emission activity (AE) during the transitions process.
Figure 2a shows a simple experimental arrangement for such measurement (see [28] for more details). The sample (a 11-mm-long prismatic bar, initially in a single variant of 2H martensite) was freely laid between a heated stage and a cooled stage to ensure the transition front propagation in the prescribed direction and contacted by glycerol droplets to two AE detectors. Such a liquid contacting enabled the detectors to record the AE activity during the whole transition process, regardless of the relatively pronounced changes of the shape of the sample due to the transition. The use of two independent detectors enabled approximate localization of the AE sources, which confirmed that the acoustic signals are indeed generated in the region surrounding the interfacial microstructure.
Measurement of the acoustic emission (AE) activity of the interfacial microstructure: a experimental set-up with the direction of transition front propagation controlled by a thermal gradient; b the AE record. In a, the mesoscale morphology of the λ-interface is outlined by solid lines (habit planes) and dashed lines (twinning and detwinning planes)
The results of the AE measurement are seen in Fig. 2b. As soon as the interfacial microstructure is fully formed, the AE rate per second abruptly decreases to nearly zero; another increase appears then in the final stage when the microstructure reaches the free end of the sample and gradually disappears.
The decrease of the AE rate proves that the propagation of the interfacial microstructure is related to much lower amount of abrupt, burst-like, or avalanche-like events than its formation or its disappearance. As discussed in [15], the mechanisms of motion of the X- and λ-microstructures are based on nucleation and growth of individual martensitic plates at the interfaces between the twinned regions and the mechanically stabilized single variant of martensite. According to the AE measurements this nucleation and growth occurs in a smooth, continuous manner, and is in this sense different from the reorientation processes accompanying the formation of the microstructure and its disappearance. In summary, the AE results are in agreement with the theoretical findings summarized in the next two subsections, where it is shown that the propagation of an interfacial microstructure cannot be understood as a sequence of energy-minimizing quasi-static states; such sequence would be expected to exhibit significant AE activity when overcoming the energy barriers between the individual minima.
Compatibility at the Mesoscale
Based on the observations of Basinski and Christian [20, 21], the compatibility of X-interfaces in In-Tl was analyzed by Ruddock [29], who showed that such morphology cannot be an energy minimizer, as elastic strains are necessary for it to achieve compatibility. This surprising finding was later confirmed for X- and λ-interfaces in Cu–Al–Ni by Seiner et al. [16], Glatz et al. [19, 30]; on the other hand, Stupkiewicz and Górzyńska-Lengiewicz [31] have shown that from all possible geometric arrangements of the X-interfaces, the experimentally observed ones are those with the lowest elastic energy, i.e., those most close to full kinematic compatibility without elastic strains.
All these calculations are valid at the mesoscale, i.e., at the scale where the laminates inside the twinned regions can be treated as infinitely fine and are described by homogenized (effective) Bain matrices U μ. If the twinned region provides compatible connection between austenite and a single variant of martensite (say the I-th variant described by the Bain matrix U I), it is required that the middle eigenvalues of the matrices U μ and C = U −1I U 2μ U −1I are both equal to one. These conditions must be satisfied for both two twinned regions forming the X- or λ-interfaces or for their non-classical equivalents, for which the Bain matrix of the single variant is replaced by the effective Bain matrix of the Compound laminate U Compound.
However, these pairwise compatibility conditions onto the planar interfaces are not sufficient for the whole interfacial microstructure to attain full compatibility [8]. In addition, the two twinned regions must be able to form a compatible connection over a line, and, similarly, the single variant (or the compound laminate) must be able to connect compatibly to austenite over the same line, i.e., the habit planes and twinned-to-detwinned interfaces forming the microstructure must intersect in one line. In Fig. 3, it is visualized how this condition is satisfied for the X- and λ-morphologies in a simple prismatic bar; in particular, the orientations of the theoretical stress-free compatible interfaces (habit planes, twinning planes, and detwinning planes) are shown in this figure. It is clearly seen that these interfaces do not intersect in one line. While for the λ-morphology the difference is relatively small (~1.5°), for the X-morphology a more than 7° misfit is observed [31].
Misfits between stress-free orientations of the habit planes and twinning or detwinning planes calculated for experimentally observed arrangements of the X- and λ-interfaces. (Taken from Glatz [30] with courtesy of O. Glatz)
Lastly, besides the conditions for the symmetric Bain matrices, the compatibility of the interfacial microstructure gives also strict conditions onto the asymmetric parts of the deformation gradients, i.e., onto the mutual rotations between the individual components of the microstructure. In particular, the mutual rotation between the mechanically stabilized martensite and austenite by compatible connection over the first of the twinned region must be equal to the rotation required for compatible connection over the second twinned region. If this condition is not satisfied, the rotation must be compensated by elastic strains. (The typical rotation misfit for the interfacial microstructures in Cu–Al–Ni is ~0.2° [31].
Figure 4 shows the Tresca stress distribution in the X- and λ-morphologies calculated by finite elements method (FEM). The elastic stresses required to compensate the weak incompatibility due to the mismatch of the intersection lines and due to the small uncompensated rotation are obviously concentrated along the habit planes and other interfaces; the maximum values are relatively high (cf. similar calculations for microstructures in Cu–Zn–Al by Balandraud and Zanzotto [32]), higher than plateau-stress for the stress-induced transition in Cu–Al–Ni single crystals or twinning stresses [6], which means that these stresses may locally induce transition or reorientation, and, consequently, modify the morphology at the interfaces. However, such an effect cannot be analyzed at the mesoscale, where the twinned regions are treated as homogeneous. A finer experimental and theoretical analysis is required at the level of individual laminae, i.e., at the microscale.
Tresca stress distribution at surfaces of rectangular samples with X- and λ- interfaces. The arrows indicate the locations of the maxima. (Taken from Glatz [30] with courtesy of O. Glatz)
Compatibility at the Microscale
The mesoscale compatibility conditions require the laminates at the habit planes and detwinning planes to be infinitely fine, which typically leads to branching of the laminates in the vicinity of the interface in order to minimize the energy. This effect has been observed many times for many different alloys and takes partially place also in the interfacial microstructures discussed in this paper. However, a more detailed analysis reveals that the there are also other effects, not explainable by the energy minimization.
Most apparently, at the detwinning interfaces between a laminate and a single variant of martensite studied in detail in [33] the laminate exhibits only a negligible amount of branching. Instead, the interface consists of long, bending, and tapering needles, and the Bain matrix changes continuously from U μ to U I. The elastic strain analysis by FEM presented in [33] revealed, again, that the shape of the needles is not minimizing the energy. The difference between the energy-minimizing shape of the needles and the experimentally observed shape is sketched in Fig. 5; while the energy-minimizing morphology is approximately symmetric with respect to the twinning planes of the laminate, in the real (experimentally observed) morphology one of the faces of the needle follows one of the adjacent twinning planes and the thickness of the needle continuously increases until the final volume fraction is reached.
This observed asymmetrization of the morphology may follow either from the shear stresses acting onto the twinned-to-detwinned interfaces due to the weak incompatibility at the mesoscale, or from some requirements on higher mobility of this microstructure—the analysis of the dissipation at such curved interfaces has not been done yet. Nevertheless, similar deviations from theoretically predicted micromorphologies can be observed also at other interfaces comprised by the interfacial microstructures. Figure 6 shows examples of detailed micrographs of the morphologies at the habit planes ((a) classical habit plane, (b) non-classical habit plane) taken from the experimentally observed X-interfaces. Instead of branching, a needle-like structure is observed again, which has been never reported in the literature for Cu–Al–Ni for forward (austenite → martensite) transitions of for reverse transitions without mechanical stabilization. However, such needle-like structure was observed only at some parts of the habit planes and only at sample faces with specific crystallographic orientations, so the understanding to the mechanisms of their formation would require further analysis. On the other hand, this microstructure resembles the zig-zag habit plane morphology observed in Ti–Mn alloy [34] and analyzed theoretically by Stupkiewicz et al. [35].
Conclusions
The main aim of this paper was to show that the thermally driven transitions from mechanically stabilized martensite to austenite proceed via formation of specific mobile microstructures, called interfacial microstructures. These microstructures exhibit several weak deviation from the expected energy-minimizing morphologies, both at the mesoscale and at the microscale. These deviations, together with the low acoustic emission activity of these microstructures during their steady-state motion, indicate that the morphology of the interfacial microstructures is probably not governed only by the energy minimization, but also by requirements on mobility.
As mentioned in the Introduction, Cu–Al–Ni is a prototypical SMA, often used to illustrate specific behaviors of this class of materials. In a similar sense, the findings related to the mechanical stabilization effect and to the interfacial microstructures summarized in this paper can be generalized for other SMAs and also for the effective behavior of SMA polycrystals (see e.g., [36, 37] for such approach adopted for polycrystalline NiTi).
References
Otsuka K, Shimizu K (1970) Memory effect and thermoelastic martensite transformation in CuAlNi alloy. Scr Metall 4(6):469–472
Otsuka K, Wayman CM, Nakai K, Sakamoto H, Shimizu K (1976) Superelasticity effects and stress-induced martensitic transformations in CuAlNi alloys. Acta Metall 24(3):207–226
Otsuka K, Sakamoto H, Shimizu K (1979) Successive stress-induced martensitic transformations and associated transformation pseudoelasticity in Cu-Al-Ni alloys. Acta Metall 27(4):585–601
Abeyaratne R, Chu C, James RD (1996) Kinetics of materials with wiggly energies: theory and application to the evolution of twinning microstructures in a Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloy. Philos Mag A 73(2):457–497
Hane KF (1998) Microstructures in thermoelastic martensites. PhD thesis, University of Minnesota
Novák V, Šittner P, Ignacová S, Černoch T (2006) Transformation behavior of prism shaped shape memory alloy single crystals. Mater Sci Eng, A 438–440:755–762
Shilo D, Mendelovich A, Novák V (2007) Investigation of twin boundary thickness and energy in CuAlNi shape memory alloy. Appl Phys Lett 90(19):193113
Bhattacharya K (2003) Microstructure of martensite. Oxford University Press, New York
Chu CH (1998) Hysteresis and microstructures: a study of biaxial loading on compound twins of copper-aluminium-nickel single crystals. PhD thesis, University of Minnesota
Ball JM, James RD (1987) Fine phase mixtures as minimizers of energy. Arch Rat Mech Anal 100(1):13–52
Ball JM (2004) Mathematical models of martensitic microstructure. Mater Sci Eng, A 378:61–69
L’vov VA, Picornell C, Pons J, Cesari E (2005) Statistical description of mechanical stabilization of Cu-Al-Ni martensite. Mater Trans 46(5):983–989
Picornell C, Pons J, Cesari E (2006) Mechanical stabilisation and anomalous behaviour of the stress-strain loops in Cu-Al-Ni single crystals. Scr Mater 54(3):459–463
Liu Y (1999) Mechanical stabilisation of martensite due to cold deformation. Mater Sci Eng, A 273–275:668–672
Seiner H, Sedlák P, Landa M (2008) Shape recovery mechanism observed in single crystals of Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloy. Phase Trans 81(6):537–551
Seiner H, Glatz O, Landa M (2009) Interfacial microstructures in martensitic transitions: from optical observations to mathematical modeling. Int J Multiscale Comp Eng 7(5):445–456
Hane KF, Shield TW (2000) Microstructure in a cubic to orthorhombic transition. J Elast 59(1–3):267–318
Ball JM, Koumatos K, Seiner H (2013) Nucleation of austenite in mechanically stabilized martensite by localized heating. J Alloys Compd 577(Suppl 1):S37–S42
Glatz O, Seiner H, Landa M (2010) Rate-dependent model of mobility of interfacial microstructures in shape memory alloys. In: Gumbsch P, van der Giessen E (eds), Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Multiscale Materials Modelling MMM2010, Oct 48, 2010 (Freiburg), Fraunhofer Verlag, p 58–61
Basinski ZS, Christian JW (1954a) Experiments on the martensitic transformation in single crystals of indium-thallium alloys. Acta Metall 2:148–166
Basinski ZS, Christian JW (1954b) Crystallography of deformation by twin boundary movements in Indium-thallium alloys. Acta Metall 2:102–116
Seiner H, Landa M, Sedlák P (2007) Propagation of an austenite-martensite interface in a thermal gradient. Proc Eston Acad Sci 56(2):218–225
Seiner H, Landa M (2009) Non-classical austenite-martensite interfaces observed in single crystals of Cu-Al-Ni. Phase Trans Phase Transit 82(11):793–807
Ball JM, Carstensen C (1998) Nonclassical austenite-martensite interfaces. J de Phys IV 7(5):C5-35–C5-40
Gupta SG (2003) The classical Stefan problem: basic concepts, modelling and analysis. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hill JM (1987) One-dimensional Stefan problems: an introduction. Longman Scientific and Technical, Harlow
Seiner H, Straka L, Heczko O (2014) A microstructural model of motion of macro-twin interfaces in Ni-Mn-Ga 10 M martensite. J Mech Phys Solids 64(1):198–211
Seiner H (2008) Dynamic and transient phenomena in single crystals of shape memory alloys. PhD thesis, Prague: Czech Technical University
Ruddock G (1994) A Microstructure of martensite which is not a minimiser of energy: the X-interface. Arch Rat Mech Anal 127:1–39
Glatz O (2010) Mathematical modelling of mobility of martensitic microstructures. MSc thesis, Prague: Czech Technical University
Stupkiewicz S, Górzyńska-Lengiewicz A (2012) Almost compatible X-microstructures in CuAlNi shape memory alloy. Contin Mech Thermodyn 24(2):149–164
Balandraud X, Zanzotto G (2007) Stressed microstructures in thermally induced M9R-M18R martensites. J Mech Phys Solids 55(1):194–224
Seiner H, Glatz O, Landa M (2011) A finite element analysis of the morphology of the twinned-to-detwinned interface observed in microstructure of the Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloy. Int J Solids Struct 48(13):2005–2014
Knowles KM, Smith DA (1981) The nature of the parent-martensite interface in titanium-manganese. Acta Metall 29(8):1445–1466
Stupkiewicz S, Maciejewski G, Petryk H (2007) Low-energy morphology of the interface layer between austenite and twinned martensite. Acta Mater 55:6292–6306
Sedlák P, Frost M, Benešová B, Ben Zineb T, Šittner P (2012) Thermomechanical model for NiTi-based shape memory alloys including R-phase and material anisotropy under multi-axial loadings. Int J Plast 39:132–151
Frost M, Benešová B, Sedlák P (2015) A microscopically motivated constitutive model for shape memory alloys: formulation, analysis and computations. Math. Mech. Solids (in press). doi:10.1177/1081286514522474
Acknowledgments
This work has been financially supported by the Czech Science Foundation (Project No. 14-15264S).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seiner, H. Mobile Interfacial Microstructures in Single Crystals of Cu–Al–Ni Shape Memory Alloy. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 1, 268–274 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-015-0009-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-015-0009-0