Abstract
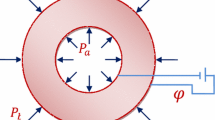
Modeling of elastic waves in an infinite fluid-loaded and immersed homogeneous, transversely isotropic piezoelectric circular fiber is studied using linear elasticity theory. The equations of motion of the fiber are formulated using the constitutive equations of a transversely isotropic piezoelectric material. The equations of motion of the internal and external fluids are formulated using the constitutive equations of an inviscid fluid. Displacement potentials are used to solve the equations of motion of the fiber and the fluids. The frequency equation of the coupled system consisting of the fiber and the internal and external fluid is developed under the assumption of no-slip boundary condition at the fluid–solid interface. The computed non-dimensional frequencies, non-dimensional wave number, phase velocity, attenuation and electro mechanical coupling are plotted in the form of dispersion curves for the lead zirconate titanate (PZT-4) ceramics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meeker, T.R., Meitzler, A.H.: Guided wave propagation in elonged cylinders and plates. In: Mason, W.P. (ed.) Physical Acoustics, vol. 1. Academic, New York (1964)
Morse, R.W.: Compressional waves along an anisotropic circular cylinder having hexagonal symmetry. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 26, 1018–1021 (1954)
Mirsky, I.: Wave propagation in transversely isotropic circular cylinders, part I: theory, part II: numerical results. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 37, 1016–1026 (1965)
Saadatfar, M.: Effect of multiphysics conditions on the behavior of an exponentially graded smart cylindrical shell with imperfect bonding. Meccanica 50(8), 2135–2152 (2015)
Saadatfar, M., Aghaie-Khafri, M.: On the behavior of a rotating functionally graded hybrid cylindrical shell with imperfect bonding subjected to hygrothermal condition. J. Therm. Stresses. 38(8), 854–881 (2015)
Tiersten, H.F.: Linear Piezoelectric Plate Vibrations. Plenum, New York (1969)
Parton, V.Z., Kudryavtsev, B.A.: Electromagnetoelasticity. Gordon and Breach, New York (1988)
Shul’ga, N.A.: Propagation of harmonic waves in anisotropic piezoelectric cylinders. Homogeneous piezoceramic wave guides. Int. Appl. Mech. 38(8), 933–953 (2002)
Saadatfar, M., Aghaie-Khafri, M.: Electromagnetothermoelastic behavior of a rotating imperfect hybrid functionally graded hollow cylinder. Smart Struct. Syst. 15(6), 1411–1437 (2015)
Saadatfar, M., Aghaie-Khafri, M.: Thermoelastic analysis of a rotating functionally graded cylindrical shell with functionally graded sensor and actuator layers on an elastic foundation placed in a constant magnetic field. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 27(4), 512–527 (2016)
Paul, H.S., Venkatesan, M.: Wave propagation in a piezoelectric ceramic cylinder of arbitrary cross section. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 82(6), 2010–2013 (1987)
Paul, H.S., Venkatesan, M.: Wave propagation in a piezoelectric ceramic cylinder of arbitrary cross section with a circular cylindrical cavity. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 85(1), 163–170 (1989)
Nagaya, K.: Dispersion of elastic waves in bars with polygonal cross-section. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70, 763–770 (1981)
Rajapakse, R.K.N.D., Zhou, Y.: Stress analysis of piezoceramic cylinders. Smart Mater. Struct. 6, 169–177 (1997)
Wang, Q.: Axi-symmetric wave propagation in cylinder coated with a piezoelectric layer. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 3023–3037 (2002)
Ebenezer, D.D., Ramesh, R.: Analysis of axially polarized piezoelectric cylinders with arbitrary boundary conditions on the flat surfaces. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 113(4), 1900–1908 (2003)
Berg, M., Hagedorn, P., Gutschmidt, S.: On the dynamics of piezoelectric cylindrical shell. J. Sound Vib. 274, 91–109 (2004)
Botta, F., Cerri, G.: Wave propagation in Reissner–Mindlin piezoelectric coupled cylinder with non-constant electric field through the thickness. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 6201–6219 (2007)
Kim, J.O., Lee, J.G.: Dynamic characteristics of piezoelectric cylindrical transducers with radial polarization. J. Sound Vib. 300, 241–249 (2007)
Graff, K.F.: Wave Motion in Elastic Solids. Dover, New York (1991)
Achenbach, J.D.: Wave Motion in Elastic Solids. Dover, New York (1973)
Yas, M.H., Aragh, B.S.: Free vibration analysis of continuous grading fiber reinforced plates on elastic foundation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 48(12), 1881–1895 (2010)
Reyes, V.G., Cantwell, W.J.: The mechanical properties of fiber-metal laminates based on glass fiber reinforced polypropylene. Composite. Sci. Tech. 60(7), 1085–1094 (2000)
Sinha, K., Plona, J., Kostek, S., Chang, S.: Axisymmetric wave propagation in a fluid-loaded cylindrical shells, I: theory; II: theory versus experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 92, 1132–1155 (1992)
Berliner, J., Solecki, R.: Wave propagation in a fluid-loaded, transversely isotropic cylinders, part I analytical formulation; part II numerical results. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 99, 1841–1853 (1996)
Dayal, V.: Longitudinal waves in homogeneous anisotropic cylindrical bars immersed in fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93, 1249–1255 (1993)
Nagy, B.: Longitudinal guided wave propagation in a transversely isotropic rod immersed in fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 98(1), 454–457 (1995)
Shanker, B., Nath, C.N., Shah, S.A., Reddy, P.M.: Vibrations in a fluid-loaded poroelastic hollow cylinder surrounded by a fluid in plane-strain form. I. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. 18(1), 189–216 (2013)
Ahmed, F.: Guided waves in a transversely isotropic cylinder immersed in fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. 109(3), 886–890 (2001)
Ponnusamy, P., Selvamani, R.: Wave propagation in magneto thermo elastic cylindrical panel. Euro. J. Mech. A Solids 39, 76–85 (2013)
Ponnusamy, P., Selvamani, R.: Wave propagation in a transversely isotropic magneto-electro-elastic solid bar immersed in an inviscid fluid. J. Egypt. Math. Soc. 24, 92–99 (2016)
Paul, H.S., Raju, D.P.: Asymptotic analysis of the modes of wave propagation in a piezoelectric solid cylinder. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 71(2), 255–263 (1982)
Berlincourt, D.A., Curran, D.R., Jaffe, H.: Piezoelectric and Piezomagnetic Materials and their Function in Transducers. Academic Press, New York (1964)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvamani, R. Modeling of Elastic Waves in a Fluid Loaded and Immersed Piezoelectric Hollow Fiber. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 3, 3263–3277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-016-0292-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-016-0292-2