Abstract
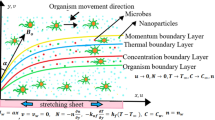
In this investigation, we intend to present the magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) heat and mass transfer of nanofluids along a stretching cylinder in the presence of non-uniform heat source/sink and chemical reaction under the prescribed surface heat flux boundary conditions on the cylinder surface. The governing partial differential equations are approximated by a system of non-linear locally similarity ordinary differential equations which are solved numerically using fifth-order Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg (RKF45) integration scheme shooting method. Present results are compared with the previously published results in some limiting cases and the results are found to be in an excellent agreement. Three different kinds of nanoparticles, namely copper (Cu), alumina (\({\hbox {Al}}_2{\hbox {O}}_3\)) and titanium dioxide (\({\hbox {TiO}}_2\)) with water as base fluid are considered here. The numerical results for the dimensionless velocity, temperature and nanoparticle volume fraction as well as on local skin-friction coefficient, local Nusselt number and Sherwood number have been constructed and illustrated graphically to reveal some interesting physical phenomena. The results of the present paper show that the flow velocity and temperature on the stretching cylinder and also skin-friction coefficient are strongly influenced by the curvature parameter.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(A^*\) :
-
Space dependent heat source/sink parameter
- \(B^*\) :
-
Temperature dependent heat source/sink parameter
- \(C_f\) :
-
Skin-friction coefficient
- \(C_p\) :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
- \(D_m\) :
-
Specific diffusitivity
- M :
-
Magnetic field parameter
- \(Nu_x\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- \(q'''\) :
-
Non-uniform heat source/sink
- \(Re_x\) :
-
Local Reynolds number
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number
- T :
-
Temperature of the fluid
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
Free stream temperature
- \(T_w\) :
-
Temperature at the wall
- u :
-
Velocity component in x-direction
- \(u_w\) :
-
Stretching/shrinking sheet velocity
- U :
-
Free stream velocity of the nanofluid
- v :
-
Velocity component in y-direction
- x, y :
-
Direction along and perpendicular to the plate, respectively
- \(\alpha _{nf}\) :
-
Effective thermal diffusivity of the nanofluid
- \(\alpha _f\) :
-
Fluid thermal diffusivity
- \(\phi \) :
-
Solid volume fraction of the nanoparticles
- \(\eta \) :
-
Similarity variable
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Carveture parameter
- \(\varGamma \) :
-
Chemical reaction parameter
- \(\mu _{nf}\) :
-
Effective dynamic viscosity of the nanofluid
- \(\mu _f\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the fluid
- \(\nu _f\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the fluid
- \(\rho _{nf}\) :
-
Effective density of the nanofluid
- \(\theta \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature of the fluid
- \(\theta _w\) :
-
Wall temperature excess ratio parameter
- \({\psi }\) :
-
Stream function
- \(\kappa _{nf}\) :
-
Effective thermal conductivity of the nanofluid
- \(\kappa _f\) :
-
Thermal conductivity of the fluid
- \('\) :
-
Differentiation with respect to y
- nf :
-
Nanofluid
- f :
-
Fluid
- s :
-
Solid
References
Choi, S.U.S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, In: The Proceedings the ASME International Mechanical Enjeneering Congress and Exposition, San Fransisco, USA, ASME Fluids Eng Div, 231/MD 66, 99–105 (1995)
Das, S.K., Choi, S.U.S., Yu, W., Pradeep, T.: Nanofluids: Science and Technology. Wiley, New Jersey (2007)
Kaka, S., Pramuanjaroenkij, A.: Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 3187–3196 (2009)
Das, S.K., Putra, N., Thiesen, P., Roetzel, W.: Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 125(4), 567–574 (2003)
Wang, C.Y.: Fluid flow due to a stretching cylinder. Phys. Fluids 31, 466–468 (1988)
Bachok, N., Ishak, A.: Mixed convection boundary layer flow over a permeable vertical cylinder with prescribed surface heat flux. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 34, 46–54 (2009)
Ishak, A., Nazar, R., Pop, I.: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow and heat transfer due to a stretching cylinder. Energy Convers, Manage. 49, 3265–3269 (2008)
Elbashbeshy, E.M.A., Emam, T.G., EIAzab, M.S., Abdelgaber, K.M.: Laminar boundary layer flow along a stretching horizontal cylinder embedded in a porous medium in the presence of a heat source or sink with suction/injection. Int. J. Energy Technol. 4(28), 1–6 (2012)
Lin, H.T., Shih, Y.P.: Buoyancy effects on the laminar boundary layer heat transfer along vertically moving cylinders. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 4, 47–51 (1981)
Mukhopadhay, S.: Chemically reactive solute transfer in MHD boundary layer flow along a stretching cylinder with partial slip. Int. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 9, 62–79 (2013)
Ashorynejad, H.R., Sheikhholeslami, M., Pop, I., Ganji, D.D.: Nanofluid flow and heat transfer due to a stretching cylinder in the presence of magnetic field. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 427–436 (2013)
Aydin, O., Kaya, A.: MHD mixed convection of a viscous dissipating fluid about a vertical slender cylinder. Desal. Water Treat. 51, 3576–3583 (2013)
Dessie, H., Kishan, N.: Unsteady MHD flow of heat and mass transfer of nanofluids over stretching sheet with a non-uniform heat source/sink considering viscous dissipation and chemical reaction. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 14, 1–12 (2015)
Sheikholeslami, M.: Effect of uniform suction on nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a cylinder, J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng., 1–11 (2014)
El-Aziz, M.A.: Effect of time-dependent chemical reaction on stagnation point flow and heat transfer over a stretching sheet in a nanofluid. Physica Scripta 89(8), 085205 (2014)
Das, S., Jana, R.N., Makinde, O.D.: MHD boundary layer slip flow and heat transfer of nanofluid past a vertical stretching sheet with non-uniform heat generation/absorption. Int. J. Nanosci. 13(03), 1450019 (2014). (12 pages)
Manjunatha, P.T., Gireesha, B.J., Prasannakumara, B.C.: Effect of radiation on flow and heat transfer of MHD dusty fluid over a stretching cylinder embedded in a porous medium in presence of heat source, Int. J. of Appl. Comput. Math. 1–18 (2015)
Malik, M.Y., Hussain, A., Salahuddin, T., Awais, M., Bilal, S.: Numerical solution of sisko fluid Over a stretching cylinder and heat transfer with variable thermal conductivity, J. Mech.: 1–9 (2016)
Malik, M.Y., Bibi, M., Khan, F., Salahuddin, T.: Numerical solution of Williamson fluid flow past a stretching cylinder and heat transfer with variable thermal conductivity and heat generation/absorption. AIP Adv. 6(3), 035101 (2016)
Majeed, A., Javed, T., Ghaffari, A., Rashidi, M.M.: Analysis of heat transfer due to stretching cylinder with partial slip and prescribed heat flux: A Chebyshev Spectral Newton Iterative Scheme. Alexandria Eng. J. 54(4), 1029–1036 (2015)
Majeed, A., Javed, T., Mustafa, I., Ghaffari, A.: Heat transfer over a stretching cylinder due to variable prandtl number influenced by internal heat generation/absorption: a numerical study. REVISTA MEXICANA DE FISICA 62(4), 317–324 (2016)
Majeed, A., Javed, T., Ghaffari, A., Pop, I.: Numerical study of unsteady mixed convection stagnation point flow over a stretching cylinder with sinusoidal surface temperature”. REVISTA MEXICANA DE FISICA 62(4), 290–298 (2016)
Javed, T., Ghaffari, A., Ahmad, H.: Numerical study of unsteady MHD oblique stagnation point flow with heat transfer over an oscillating flat plate. Canadian J. of Physics 93(10), 1138–1143 (2015)
Mustafa, I., Javed, T., Ghaffari, A.: Heat transfer in MHD stagnation point flow of a ferrofluid over a stretchable rotating disk. J. of Molecular Liquids 219, 526–532 (2016)
Mahmood, A., Chen, B., Ghaffari, A.: Hydromagnetic Hiemenz flow of micropolar fluid over a nonlinearly stretching/shrinking sheet: Dual solutions by using Chebyshev Spectral Newton Iterative Scheme. J. of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 416, 329–334 (2016)
Pal, D., Mandal, G., Vajravelu, K.: Stagnation-point flow and heat transfer of radiative nanofluids over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a porous medium with a non-uniform heat source/sink. Journal of Nanofluids 5(3), 375–383 (2016)
Pal, D., Mandal, G., Vajravelu, K.: Soret and Dufour effects on MHD convectiveradiative heat and mass transfer of nanofluids over a vertical non-linear stretching/shrinking sheet. Applied Mathematics and Computation 287, 184–200 (2016)
Najib, N., Bachok, N., Arifin, N.M., Ishak, A.: Stagnation point flow and mass transfer with chemical reaction past a stretching/shrinking cylinder. Scientific reports (2014). doi:10.1038/srep04178
Khalili, S., Khalili, A., Kafashian, S., Abbassi, A.: Mixed convection on a permeable stretching cylinder with prescribed surface heat flux in porous medium with heat generation or absorption, Journal of Porous Media, 16(11) (2013)
Gireesha, B.J., Rudraswamy, N.G.: Chemical reaction on MHD flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid near the stagnation point over a permeable stretching surface with non-uniform heat source/sink. Int. J. of Engineering Science and Technology 6(5), 13–25 (2014)
Rudraswamy, N.G., Gireesha, B.J.: Influence of chemical reaction and thermal radiation on MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over an exponentially stretching sheet. J. of Applied Mathematics and Physics 2(2), 42204 (2014). (9 pages)
Bandari, S., Gorfie, E.H.: Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with thermal radiation, viscous dissipation, chemical reaction and ohmic effects. Journal of Nanofluids 3(3), 227–237 (2014)
Qasim, M., Khan, Z.H., Khan, W.A., Shah, I.A.: Mhd boundary layer slip flow and heat transfer of ferrofluid along a stretching cylinder with prescribed heat flux. PloS one 9(1), e83930 (2014)
Pal, D., Mondal, H.: Effect of variable viscosity on MHD non-Darcy mixed convection heat transfer over a stretching sheet embedded in a porous medium with non-uniform heat source/sink. Comm. Nonlinear Sci. Num. Sim. 15, 1533–1564 (2010)
Pal, D., Mandal, G.: Effectiveness of convection-radiation interaction on stagnation-point flow of nanofluids past a stretching/shrinking sheet with viscous dissipation. Physica Scripta 89(12), 125202 (2014)
Oztop, H.F., Abu-Nada, E.: Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 29, 1326–1336 (2008)
Bachok, N., Ishak, A.: Flow and heat transfer over a stretching cylinder with prescribed heat flux. Malysian J. Mathematical Sciences 4, 159–169 (2010)
Yih, K.A.: Free convection effect on MHD coupled heat and mass transfer of a moving permeable vertical surface. Int. Commum. Heat and Mass Transf. 29, 95–104 (1999)
Ali, F.M., Nazar, R., Arifin, N.M., Pop, I.: Effect of Hall current on MHD mixed convection boundary layer flow over a stretched vertical flat plate. Meccanica 46, 1103–1112 (2011)
Aurangzaib, A.R.M., Kasim, N.F., Mohammad, S.: Shafie, Effects of thermal atratification on MHD free convetion with heat and mass transfer over an unsteady stretching surface, Hall current and chemical reaction, Int. J. Adv Eng Sci Appl Math 09/2012; 4(3). doi:10.1007/s12572-012-0066-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, D., Mandal, G. Magnetohydrodynamic Heat Transfer of Nanofluids Past a Stretching Cylinder with Non-Uniform Heat Source/Sink and Chemical Reaction. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 3, 2889–2908 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-016-0241-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-016-0241-0