Abstract
Estimates of the global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) range from 0.24 to 1%, but vary considerably around the globe. A variation in RA prevalence is also expected across Africa and the Middle East, due to ethnic, climate, and socioeconomic differences. To assess the prevalence of RA in Africa and the Middle East, we searched Medline (via PubMed) and databases of major rheumatology conferences. Seventeen journal articles and 0 abstracts met the inclusion criteria. Estimated prevalence ranged from 0.06 to 3.4%. Most studies reported values near or below 0.25%. Consistent with data from other regions, RA was more prevalent among urban than rural populations, and among women than men. The women:men prevalence ratio ranged from 1.3:1 to 12.5:1, which suggests notable differences from the global average of 2:1. Relative increases in prevalence were observed in North Africa and the Middle East (13% since 1990) and Western Sub-Saharan Africa (14%), whereas rates in Eastern, Central, and Southern Sub-Saharan Africa show decreases (4–12%). Low disease awareness, delays to visit rheumatologists, and socioeconomic factors appear to hinder early diagnosis and aggressive treatment. Few countries have developed RA-specific treatment guidelines, and many physicians and patients face limited access to even basic treatments. An improved understanding of the epidemiology and management of RA, and the related socioeconomic consequences is necessary, so that targeted attempts can be made to encourage early diagnosis and treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Why carry out this study? |
While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects 0.24–1% of the worldwide population, variations in prevalence can be expected across Africa and the Middle East (AfME) due to ethnic, climate, and socioeconomic differences. |
In this review, we discuss data on the prevalence of RA in the AfME region published in the last 10 years as well as potential barriers to effective treatment. |
What was learned from the study? |
Prevalence ranged from 0.06 to 3.4% across countries in the region, although most studies reported values of around 0.24%. |
Unmet needs included limited disease awareness, delays in diagnosis and start of treatment, lack of country-specific treatment guidelines, and difficulties accessing treatment. |
Increasing understanding of the epidemiology and management of RA is crucial to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, thereby improving outcomes for patients. |
Digital Features
This article is published with digital features, including a summary slide, to facilitate understanding of the article. To view digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.13168526.
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with joint erosion, functional loss, and reduced overall quality of life [1,2,3,4]. The global prevalence of RA has been estimated to range from 0.24 to 1%, although rates vary by region and country (Table 1; Fig. 1) [1, 5,6,7]. Factors such as age, ethnicity, smoking history, and urban living appear to affect the incidence of RA [2, 7]. When prevalence rates are estimated according to sex, women are consistently found to be at higher risk of RA than men (rates are generally ~ twofold higher among women), and the discrepancy appears to be related to hormonal factors [2, 7].
RA affects numerous aspects of daily life, by reducing mobility and affecting patients’ ability to work [8, 9]. In addition, patients with RA have reduced life expectancy compared with the general population [2]. More severe forms of the disease (e.g., poorer functional status, increased radiologic damage) are associated with higher mortality rates [2]. Although increased risk of mortality has been correlated with the presence of comorbidities and socioeconomic, educational, and marital status, disease treatment is also understood to play a role in patient outcome. In regions where access to treatment is limited due to socioeconomic circumstances, mortality rates are higher. Other factors such as the occurrence of severe infections and intermittent use of high-dose corticosteroids may also negatively affect mortality [10].
A wide diversity of ethnicities, weather climates, and socioeconomic conditions can be found across the countries of Africa and the Middle East. In addition, few studies have assessed the prevalence of RA in this region. The Global Burden of Disease systematic reviews conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2000, 2010, and 2017 have estimated incidence, prevalence, and disability associated with RA in global regions and individual countries [2, 5, 7, 11]. However, because of their design, these reviews provide only a high-level perspective of disease burden and do not describe the individual studies that comprise the results. Furthermore, disease prevalence can change over time, and these reviews include data from studies dating back as far as 1965 [2]. Given the social, economic, and cultural diversity of African and Middle Eastern countries, many studies conducted in this region may underestimate the prevalence of RA. A current and more detailed understanding of RA in these regions is therefore needed. This narrative review summarizes the available data on the prevalence of RA in Africa and the Middle East and discusses unmet needs for patients in this region.
Methods
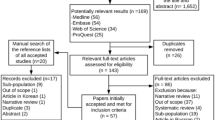
The NCBI PubMed database was searched for publications using the following search string: “(“rheumatoid arthritis” OR RA) AND (Africa OR “Middle East” OR AfME OR Arab) AND prevalence.” Results were limited to January 2009 through September 2019. This search was updated in April 2020 to identify any relevant publications between September 2019 and March 2020. Additional searches were conducted in September 2019 and April 2020 that replaced “(Africa OR (Middle East) OR AfME)” with individual countries in the region, including Afghanistan, Algeria, Bahrain, Democratic Republic of Congo, Djibouti, Dubai, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. In addition, the online databases of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), the Asia–Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology, and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) were searched for abstracts presented at annual congresses between 2014 and 2019.
Publications were included if they evaluated RA disease prevalence in the individual African or Middle Eastern countries listed above, or in African and Middle Eastern regions, using prospective or retrospective study designs or a systematic review or meta-analysis approach. Publications that solely evaluated RA incidence, or that were published prior to 2009, were excluded. Case reports and case series, editorials, and letters to the editor were also excluded from the results.
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Results
Search Results
The PubMed searches identified 460 potential hits of which 17 journal publications met the criteria. No conference abstracts were identified from searches of the congress databases. The results included a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies conducted in Africa between 1975 through 2014 [12] and 13 publications of data from individual countries (two of which were included in the 2014 meta-analysis) [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. An additional three publications reported RA-related data from 2010 [5], 2013 [11], and 2017 [7] from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Study.
Prevalence of RA in Africa and the Middle East
At a regional level, the estimated prevalence of RA ranged from 0.14% in Western Sub-Saharan Africa to 0.54% in urban areas across Africa (Table 1) [7, 12]. In individual countries, estimated RA prevalence ranged from 0.06% [11] to 3.4% [24]. The majority of studies were population-based. Despite the implementation of the updated ACR/EULAR classification criteria in 2010, [26] only one study used these to define RA [24]; most studies used ACR 1987 classification criteria to define RA. Notably, however, one Moroccan study included only patients whose sera had been tested by an autoimmunity laboratory, and results were not adjusted according to the general population [16]. When country-specific data from more than one study were available, these often varied widely. For example, prevalence of RA in Saudi Arabia was estimated to be 0.06% based on data from the GBD study [11], while a survey of university students on the occurrence of RA among their relatives reported a 20-fold higher prevalence of 0.3% [22]. Similar trends were seen for the United Arab Emirates, where estimated prevalence varied from 0.09% based on data from the GBD Study [11] to 3.4% based on a retrospective cohort study [24], and Morocco, where it ranged from 0.16% based on GBD data [11] to 2.8% based on retrospective data from an autoimmunity laboratory (described above) [16]. In all three cases, GBD prevalence estimates were at the lower end of the range [5, 7, 11]. A meta-analysis of African studies identified a prevalence of 2.54% in population-based studies conducted in urban South Africa [12]. However, the individual studies included in that analysis (all conducted prior to 1982) evaluated heterogeneous populations and reported prevalence rates of 0.91–5.71%, with higher rates associated with older study populations [12]. One study of women visiting primary health centers in Qatar identified a prevalence of 4.3%, but again, all patients were 40–60 years of age and the presence or absence of RA was self-reported rather than determined by an investigator [14]. Aside from these exceptions, the majority of studies reported prevalence rates below 1%.
Urban population-based studies that used the ACR 1987 classification criteria for RA identified prevalence estimates of 0.15% (Algeria) [21], 0.37% (Iran) [13], 0.56% (Turkey) [18], 0.6% (Democratic Republic of Congo) [20], and 0.9% (Dubai) [19]. Our review did not identify any population-based studies that specifically assessed rural populations, but a systematic review and meta-analysis included studies of rural and urban populations, reporting lower prevalence rates both in rural South Africa (rural, 0.07%; urban, 2.54%) and in rural areas across Africa as a whole (rural, 0.18%; urban, 0.54%) [12]. In addition, the meta-analysis by Usenbo et al. excluded one Nigerian study from the analysis because it reported a 0% prevalence among the rural population. That meta-analysis also found substantial heterogeneity among all studies included in the pooled analysis (Table 1) [12].
Whereas previous studies have reported that women are approximately twice as likely as men to experience RA [2], global regional data from the GBD study suggest that the ratio is closer to 3:1 in Africa and the Middle East [5]. Five country-level studies reported prevalence according to sex. In those, prevalence rates were consistently higher among women than men, but women:men ratios varied from 1.3:1 (Iran) [15] to 9:1 (Turkey) [18], 11:1 (Dubai) [19], 11:1 (Saudi Arabia) [22], and 12.5:1 (Algeria) [21]. A separate study of patient characteristics in Egypt reported a ratio of 3:1 [27], which also supports the understanding that patient populations vary considerably across the regions of Africa and the Middle East. At a regional level, across sub-Saharan Africa and in North Africa and the Middle East, the women:men ratios of RA prevalence were approximately 3:1 [5].
While the prevalence of RA is increasing in some regions, it is decreasing in others. Globally, a relative increase of 7.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 5.3–9.4%) was observed between 1990 and 2017 [7]. The rates have increased in North Africa and the Middle East (13.3% [95% CI, 10.6–16.1%]) and Western sub-Saharan Africa (13.9% [95% CI, 10.8–17.1%]) [7], but appear to have decreased in eastern (– 4.8% [95% CI, – 7.9 to – 1.8%]), central (– 4% [95% CI, – 8.3–0.3%]), and southern sub-Saharan Africa (– 11.7% [95% CI, – 15.1 to – 8.3%]).
Discussion
Prevalence of RA in Africa and the Middle East
The prevalence of RA varies across individual countries and regions of Africa and the Middle East but, overall, it appears to be in the lower range of global estimates (< 0.25% for most countries, although estimates up to 3.4% were observed) [1, 5, 7]. The range in reported prevalence rates reflects diverse study designs and subject populations. Higher estimates were reported for studies of older populations, patients who self-reported the presence of RA, clinic- or hospital-based (as opposed to population-based) studies, and studies of urban populations. The lower estimates reported in publications using data from the GBD Study [5, 7, 11] may reflect fundamental differences in methodology compared with other, more local studies. While recent GBD studies have concentrated on describing burden of disease in terms of years lived with disability and disability-adjusted life years, estimating prevalence remains an important goal of the study [11, 28, 29]. Data sources used in the GBD Study include disease registries, population surveys, epidemiological studies, and health facility data [30]; however, available data sources will vary between countries and regions. This could explain the low prevalence found for this region, where robust data sources for some countries are limited. On the other hand, many of the publications reporting county-level prevalence of RA are based on self-reported data from small regions [14, 15, 17, 21, 22, 24], which may also result in skewed estimates. This uncertainty may be reflected in secular trends, too. Certain areas of Africa and the Middle East are experiencing an apparent increase in prevalence of RA, but decreasing rates were noted in others, primarily in Sub-Saharan Africa (Table 1). However, the limited number of robust epidemiological studies covering entire countries or even wider regions likely hinder development of accurate estimates.
The diversity of populations and settings across Africa and the Middle East adds a challenge in obtaining reliable prevalence estimates of RA, and the presence of certain risk factors that influence RA prevalence may vary considerably from one local population to another. However, consistent with global estimates of urban and rural prevalence, RA is reported to occur at lower rates among rural populations of Africa and the Middle East than in urban settings.
The findings of this review support the general understanding that RA is more likely to occur in women than men [5]. However, the women:men ratios of diagnosis vary considerably across countries. In addition to biological reasons for why RA is more common among women than men, study design and conduct and inclusion criteria might also contribute to some findings of unusually high ratios of women to men with RA. For example, if house-to-house surveys were conducted in the middle of the working day, women might comprise the primary respondents in some countries. Alternatively, men in some regions might be less likely to report joint pain to a study surveyor due to sociocultural factors. Cultural factors, economic limitations, and work requirements may also affect the number of men who seek care at primary health centers, thus affecting their inclusion in studies.
Migration between different parts of the region are common and are a major contributor to its high heterogeneity. Similar to European and East Asian patients with RA, certain HLA–DRB1 alleles are associated with an increased risk of developing RA in Middle Eastern patients; however, two loci (5p13 and 17p13) have been identified as additional risk factors in this population [31].
Incidence rates are a complementary component to prevalence rates and can help to clarify the epidemiology and unmet needs related to RA. However, incidence rates can be difficult to evaluate in the absence of centralized hospital or healthcare systems or patient registries. In fact, studies on incidence rates of RA in Africa and the Middle East are scarce. In some countries, such as Egypt, the healthcare system consists primarily of private practitioners rather than hospital-based systems. In such cases, individual providers may sense competition from their colleagues and be reluctant to register patients in registries. The lack of rheumatologists in many countries in this region [32], particularly in rural areas, makes it difficult to accurately estimate the incidence and prevalence of rheumatologic diseases, and may skew results towards higher prevalence in urban areas. In addition, some patients may visit healthcare professionals other than rheumatologists (e.g., general practitioners, orthopedic specialists). In Cameroon, this shortage of rheumatologists led to the centralization of diagnostic and therapeutic resources, which permits collection of data from a wide spectrum of patients but also increases pressure on tertiary centers to prescribe or monitor drugs in cases when primary and secondary care centers are unable to do so [33, 34]. Multiple attempts have been made to establish RA patient registries in Saudi Arabia, the most recent being the Rheumatoid Arthritis Saudi Database (RASD), from which data are beginning to emerge [35, 36]. Where available, registries such as the Kuwait Registry for Rheumatic Diseases [KRRD] and the Dubai Private Database, facilitate our understanding of patient characteristics, such as the mean age at diagnosis (49 years), prevalence of family history of rheumatic autoimmune disease (13%), the women:men ratio (3:1) [37], and main reasons for discontinuation of biologics (loss of efficacy and patient choice) [38].
Region-Specific Unmet Needs
Following on from the discussion of the highly variable prevalence data available for this region, the authors sought to explore some of the unmet needs in the management of RA.
RA-related loss of function can severely affect patients’ ability to work and to participate in social life. Employment rates decline most rapidly within 3 years of disease onset, with some patients experiencing reduced work ability within the first year of diagnosis, and up to 30% affected within 10 years of diagnosis [8, 36]. The effects of disease on work function are seen both in reduced working hours (absenteeism, retirement) and reduced productivity while at work (presenteeism, activity impairment) [36]. Reduced work ability, particularly in conjunction with increased healthcare costs associated with greater disease severity, can negatively influence economic status of families (and, ultimately, local economies) and patients’ sense that they are contributing to their family and community [8, 36]. Therefore, a treat-to-work rather than a treat-to-target approach has been suggested, with the aim to aid patients’ continued ability to work and participate in daily life [8].
In addition to adjusting medication and other treatment approaches to improve the ability to work, it appears that the patients who have some control over their work schedule may have higher levels of presenteeism [36]. However, work environment, functional requirements, and cultural expectations in the working environment may all influence the level of impairment an individual experiences related to work. With an understanding of how such factors can vary among communities and countries, researchers in the Middle East have recommended that studies assessing quality of life and patient-reported outcomes be designed specifically for the populations that they are intended to assess [36].
Early diagnosis and treatment of RA has been clearly shown to improve outcomes for patients, and delays as short as 3 months can adversely affect long-term outcomes in RA [39]. For patients who do initiate treatment soon after diagnosis, international and regional RA management guidelines recommend a treatment goal of disease remission [39,40,41]. Those with a longer duration of un- or undertreated disease may only be able to achieve minimal disease activity.
Even though the importance of optimal treatment has been demonstrated, in Africa and the Middle East diagnoses are often delayed for months or even years after symptom onset [39, 42,43,44]. One study from Saudi Arabia showed that patients may not receive a diagnosis of RA for up to 30 months after the onset of symptoms [43]. Other studies have identified delays from symptom onset to diagnosis of 20 weeks in Morocco, 54 months in Senegal, and 63 months in Nigeria [34, 39]. Raising public awareness of RA and treatment options is also an important tool for reducing time to diagnosis [39]. Public education programs can lead to earlier diagnosis and initiation of therapy, as observed in patients in the United Arab Emirates [45]. Increased public awareness may also lead to patients with symptoms of RA visiting rheumatology clinics rather than other specialties, thereby receiving adequate and timely treatment.
Delayed diagnoses can be attributed to a variety of reasons. In general, primary healthcare providers are the first point of contact for patients with symptoms of RA. However, many generalists and non-rheumatologist specialists lack the musculoskeletal (MSK) examination skills to identify and diagnose musculoskeletal conditions such as RA, including conducting differential diagnoses [39, 46,47,48,49], which can lead to MSK conditions being undiagnosed or untreated [50]. MSK examination skills are often insufficiently taught during medical training and many generalists report low confidence in their ability to diagnose MSK conditions such as RA [51]. In addition, a lack of consistent, easily applicable diagnostic and referral criteria can also contribute to delays in diagnosis. The New Early Arthritis Referral Criteria are currently being validated in a real-world setting in order to address this issue [52, 53]. The shortage of rheumatologists in the region further contributes to diagnostic and treatment delay, as wait times for an initial visit sometimes exceed 3 months [33, 54, 55].
Factors that may cause patients to delay seeking diagnosis and treatment for RA symptoms are more likely to vary by region, and may include healthcare costs, underestimation of the effects of symptoms on daily function [56], perspectives on allopathic versus traditional medicine, and work schedules. Furthermore, patients may not understand the chronic, progressive nature of RA and, if they are under financial constraints, may be more likely to stop treatment after their symptoms improve [39]. Delayed diagnoses are also more likely among patients who visit multiple doctors prior to receiving a diagnosis, whose symptoms do not involve hand or wrist pain, and rural populations [43], the latter of which could perhaps be related to the lower prevalence rates observed in rural populations.
Once a diagnosis is made, effective treatment should be rapidly initiated to slow disease progression. The EULAR recommendations suggest that patients who do not respond to the first disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) should be switched to a second DMARD or given a biologic [19, 41]. However, management practices for RA, healthcare infrastructure, regulatory approval processes and the level of financial burden on patients vary considerably across countries in Africa and the Middle East [34, 39]. A study in Kuwait reported lower disease activity and a positive impact on overall physical function in patients with easy access to biologic DMRDs compared with those without easy access [57]. Similar results were observed in a study in the United Arab Emirates where only 43% of patients received DMARDs [55], underlining the importance of easy access to highly effective treatments. Access and usage of DMARDs varies widely between different countries in the region with only some countries facilitating access through subventions [58].
Few countries in Africa and the Middle East have established national treatment guidelines that take into account the specific contexts for that country. At the time of writing, most recent country-specific guidelines were published in Kuwait [59] while a number of other countries follow established international guidelines, e.g., those published by ACR or EULAR [60, 61]. However, even in countries that have established recommendations, failure to update the guidelines (and healthcare policies based on them) to account for new therapies and clinical data can lead to delays in effective treatment [39, 54]. Barriers to the successful implementation of treatment guidelines include delays in referral to rheumatologists, suboptimal use of synthetic DMARDs, and poor access to biologics [41]. This may reflect the differences in resources and health systems found across this highly diverse region. The development and implementation of updated, region-specific guidelines will therefore improve outcomes for patients [40].
Once guidelines are in place, however, they must be implemented, and a survey of rheumatologists in the Middle East and Africa suggested that although EULAR recommendations are applicable to their practice, barriers in some regions, related to treatment access and disease monitoring, might challenge their practical implementation in some regions [19, 34]. Furthermore, many generalists are unaware of treatment recommendations and therefore do not implement the guidelines, and in some areas access may be limited to methotrexate or other, less common DMARDs [34, 39]. RA is often undertreated in certain regions of Africa and the Middle East, which can lead to increased disease burden for patients, more rapid disease progression, reduced health-related quality of life, increased morbidity and mortality, and higher direct and indirect disease-related costs in the long term [39]. The development of regional guidelines for RA management can help to overcome the barriers of disease awareness and treatment implementation, which may support better patient outcomes [34].
Conclusions
Prevalence estimates for RA are approximately 0.25% globally, but estimates within countries in Africa and the Middle East vary considerably, from 0% in Nigeria to 2.8% in Morocco. This variation is partly related to differences in study design, but also to differences among populations and risk factors between (and even within) individual countries. However, general trends are consistent with the global data, wherein women and urban populations are at higher risk of the disease than are men and rural populations. One common factor across Africa and the Middle East is that populations are generally underdiagnosed and undertreated. This is in part related to low disease awareness and a lack of appropriate MSK examination skills on the part of healthcare providers, who may also attribute a lower importance to early diagnosis and treatment relative to the importance of other chronic diseases with which they are more familiar. Furthermore, in many areas, patients may encounter long wait times to see rheumatologists, and healthcare policies may delay effective treatment. Access to treatment can be limited in many areas. Financial cost is also a consideration for patients of low socioeconomic status. Many may discontinue treatment if they are not educated on the importance of continual treatment, and if doctor visits or medication costs accumulate.
Solutions to these unmet needs include increased focus on MSK examination skills, validation of diagnosis criteria, increased physician and patient awareness of the progressive nature of RA, and of the optimal treatment approaches as well as country-specific treatment guidelines. Robust population-based studies covering whole countries rather than single regions are needed to accurately determine prevalence of RA across countries in Africa and the Middle East.
References
Reginster JY. The prevalence and burden of arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002;41(Supp 1):3–6.
Symmons D, Mathers C, Pfleger B. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis in the year 2000 global burden of disease. World Health Organ. 2015;18(4):1–30.
Goma SAR, Abdelbary NM. Impact of rheumatoid arthritis on the quality of life and its relation to disease activity. Egypt Rheumatol Rehabil. 2019;46:304–12.
Gamal RM, El Fetoh SA, Janbib NA. Quality of life assessment in Egyptian rheumatoid arthritis patients: relation to clinical features and disease activity. Egypt Rheumatol. 2016;38:65–70.
Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:1316–22.
Gibofsky A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Manag Care. 2012;18:S295-302.
Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Hoy D, et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1463–71.
Almoallim H, Kamil A. Rheumatoid arthritis: should we shift the focus from “Treat to Target” to “Treat to Work?” Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:285–7.
Janoudi N, Almoallim H, Husien W, Noorwali A, Ibrahim A. Work ability and work disability evaluation in Saudi patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Special emphasis on work ability among housewives. Saudi Med J. 2013;34:1167–72.
Darmawan J, Muirden KD, Valkenburg HA, Wigley RD. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis in Indonesia. Br J Rheumatol. 1993;32:537–40.
Moradi-Lakeh M, Forouzanfar MH, Vollset SE, et al. Burden of musculoskeletal disorders in the Eastern Mediterranean region, 1990–2013: findings from the global burden of disease study 2013. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1365–73.
Usenbo A, Kramer V, Young T, Musekiwa A. Prevalence of arthritis in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0133858.
Davatchi F, Sandoughi M, Moghimi N, et al. Epidemiology of rheumatic diseases in Iran from analysis of four COPCORD studies. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19:1056–62.
Gerber LM, Chiu YL, Verjee M, Ghomrawi H. Health-related quality of life in midlife women in Qatar: relation to arthritis and symptoms of joint pain. Menopause. 2016;23:324–9.
Kolahi S, Khabbazi A, Malek Mahdavi A, et al. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders in Azar cohort population in Northwest of Iran. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37:495–502.
Missoum H, Alami M, Bachir F, et al. Prevalence of autoimmune diseases and clinical significance of autoantibody profile: data from National Institute of Hygiene in Rabat. Morocco Hum Immunol. 2019;80:523–32.
Moghimi N, Davatchi F, Rahimi E, et al. WHO-ILAR COPCORD study (stage 1, urban study) in Sanandaj. Iran Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34:535–43.
Tuncer T, Gilgil E, Kacar C, et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis in Turkey: a nationwide study. Arch Rheumatol. 2018;33:128–36.
Al Saleh J, Sayed ME, Monsef N, Darwish E. The prevalence and the determinants of musculoskeletal diseases in Emiratis attending primary health care clinics in Dubai. Oman Med J. 2016;31:117–23.
Malemba JJ, Mbuyi-Muamba JM, Mukaya J, Bossuyt X, Verschueren P, Westhovens R. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo–a population-based study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:1644–7.
Slimani S, Ladjouze-Rezig A. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in an urban population of Algeria: a prospective study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53:571–3.
Albishri JB, Alsabban M, Altwairqi AA. Prevalence of RA and SLE in Saudi Arabia. Scholars J Appl Med Sci. 2015;3:2096–9.
Chaaya M, Slim ZN, Habib RR, et al. High burden of rheumatic diseases in Lebanon: a COPCORD study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012;15:136–43.
Namas R, Joshi A, Ali Z, Al Saleh J, Abuzakouk M. Demographic and clinical patterns of rheumatoid arthritis in an Emirati cohort from United Arab Emirates. Int J Rheumatol. 2019;2019:3057578.
Sandoughi M, Zakeri Z, Tehrani Banihashemi A, et al. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders in southeastern Iran: a WHO-ILAR COPCORD study (stage 1, urban study). Int J Rheum Dis. 2013;16:509–17.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–81.
Elsaman AM, Radwan AR, Dahab A, Sherif AM, Al-Fadl A. Epidemiology and comorbidity of rheumatoid arthritis in upper, Egypt a hospital-based study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:AB0291.
GBD 2013 DALYs and HALE Collaborators, Murray CJ, Barber RM, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 306 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 188 countries, 1990–2013: quantifying the epidemiological transition. Lancet. 2015;386:2145–91.
Protocol for the global burden of diseases. injuries, and risk factors study (GBD). Instit Health Metrics Eval. 2018;96(4):380–7.
Murray CL, Mathers CD, Stein C. The Global Burden of Disease 2000 project: aims, methods and data sources. WHO global programme on evidence for health policy discussion paper. J Dental Res. 2001;1:4–36.
Saxena R, Plenge RM, Bjonnes AC, et al. A multinational Arab genome-wide association study identifies new genetic associations for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69:976–85.
Al Maini M, Adelowo F, Al Saleh J, et al. The global challenges and opportunities in the practice of rheumatology: white paper by the world forum on rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34:819–29.
Singwe-Ngandeu M, Meli J, Ntsiba H, et al. Rheumatic diseases in patients attending a clinic at a referral hospital in Yaounde. Cameroon East Afr Med J. 2007;84:404–9.
El Zorkany B, Alwahshi HA, Hammoudeh M, et al. Suboptimal management of rheumatoid arthritis in the Middle East and Africa: could the EULAR recommendations be the start of a solution? Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:151–9.
Almoallim HM, Alharbi LA. Rheumatoid arthritis in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2014;35:1442–54.
Almoallim H, Janoudi N, Alokaily F, et al. Achieving comprehensive remission or low disease activity in rheumatoid patients and its impact on workability - Saudi Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry. Open Access Rheumatol. 2019;11:89–95.
Al-Herz A, Al-Awadhi A, Saleh K, et al. A comparison of rheumatoid arthritis patients in Kuwait with other populations: results from the KRRD Registry. Br J Med Res. 2016;14:1–11.
Badsha H, Harifi G, Kirubakaran R, Khan B. AB0367 Reasons for discontinuation of biological drug and targeted synthetic drugs among patients with inflammatory arthritis in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1642–3.
Halabi H, Alarfaj A, Alawneh K, et al. Challenges and opportunities in the early diagnosis and optimal management of rheumatoid arthritis in Africa and the Middle East. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18:268–75.
Arayssi T, Harfouche M, Darzi A, et al. Recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis in the Eastern Mediterranean region: an adolopment of the 2015 American College of rheumatology guidelines. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:2947–59.
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Bijlsma J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:960–77.
Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, Stamm TA, Uffmann M, Smolen JS. Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43:906–14.
Hussain W, Noorwali A, Janoudi N, et al. From symptoms to diagnosis: an observational study of the journey of rheumatoid arthritis patients in Saudi Arabia. Oman Med J. 2016;31:29–34.
Barhamain AS, Magliah RF, Shaheen MH, et al. The journey of rheumatoid arthritis patients: a review of reported lag times from the onset of symptoms. Open Access Rheumatol. 2017;9:139–50.
Zafar S, Badsha H, Mofti A, et al. Efforts to increase public awareness may result in more timely diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2012;18:279–82.
Coady DA, Walker DJ, Kay LJ. Teaching medical students musculoskeletal examination skills: identifying barriers to learning and ways of overcoming them. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33:47–51.
Oswald AE, Bell MJ, Snell L, Wiseman J. The current state of musculoskeletal clinical skills teaching for preclerkship medical students. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:2419–26.
Stansfield RB, Diponio L, Craig C, et al. Assessing musculoskeletal examination skills and diagnostic reasoning of 4th year medical students using a novel objective structured clinical exam. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:268.
Al Marzooqi AM, Al Saleh J. What is the fastest route for patients with inflammatory arthritis to early arthritis clinic. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:1237.
Almoallim HG. Musculoskeletal examination skills: are we still interested? Internat J Clin Med. 2012;3:335–40.
Zaini R, Almoallim H, Hafiz W, et al. Musculoskeletal teaching and training in Saudi internal medicine residency programmes. Creative Edu. 2016;7:824–30.
Magliah R, Hafiz W, Alahmadi ZA, et al. Early diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis by primary care physicians following training by a rheumatologist. Open Access Rheumatol. 2019;11:315–21.
Almoallim H, Janoudi N, Attar SM, et al. Determining early referral criteria for patients with suspected inflammatory arthritis presenting to primary care physicians: a cross-sectional study. Open Access Rheumatol. 2017;9:81–90.
Watad A, Al-Saleh J, Lidar M, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y. Rheumatology in the Middle East in 2017: clinical challenges and research. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19:149.
Badsha H, Kong KO, Tak PP. Rheumatoid arthritis in the United Arab Emirates. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27:739–42.
Bahlas S, Fathaldin O, Janoudi N, Almoallim H, Ibrahim A, Algohary S. Do rheumatoid arthritis patients rate their health status different than their caregivers? Antiinflamm Anti Agents Med Chem. 2015;14:199–203.
Al-Herz A, Saleh K, Al-Awadhi A, et al. Easy accessibility of biologics and its impact on disease activity and quality of life in Kuwaiti patients with rheumatoid arthritis [abstract]. Arth Rheumatol. 2018;70:8.
Dargham SR, Zahirovic S, Hammoudeh M, et al. Epidemiology and treatment patterns of rheumatoid arthritis in a large cohort of Arab patients. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0208240.
Alhajeri H, Abutiban F, Al-Adsani W, et al. Kuwait association of rheumatology 2018 treatment recommendations for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39:1483–97.
Emadi SA, Hammoudeh M, Mounir M, Mueller RB, Wells AF, Sarakbi HA. An assessment of the current treatment landscape for rheumatology patients in Qatar: recognising unmet needs and moving towards solutions. J Int Med Res. 2017;45:733–43.
Al Saleh J, Ragab G, Nash P, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis in the middle East and Africa: are we any closer to optimising its management? Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34:1–8.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The literature review to support this manuscript and the Rapid Service Fee was sponsored by Pfizer, New York, New York, USA.
Medical Writing Assistance
Medical writing support was provided by Andrea Schauenburg, PhD, of Engage Scientific Solutions and was sponsored by Pfizer.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Disclosures
Hani Almoallim, Jamal Al Saleh, Humeira Badsha, Ayman El Garf, and Jeanine A Menassa have nothing to disclose. Haytham Mohamed Ahmed and Sara Habjoka are employees and shareholders of Pfizer.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article, as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Almoallim, H., Al Saleh, J., Badsha, H. et al. A Review of the Prevalence and Unmet Needs in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Africa and the Middle East. Rheumatol Ther 8, 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40744-020-00252-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40744-020-00252-1