Abstract
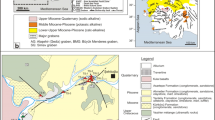
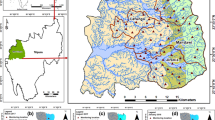
Stable isotopes of H and O are the integral parts of water molecule and serve as ideal tracers to understand the recharge processes in groundwater. Hence, a study has been conducted in hard rock aquifers of Madurai District of Tamilnadu to identify the recharge processes using stable isotopes. A total of 54 groundwater samples were collected representing the entire district from various lithounits during post monsoon. Samples were analysed for pH, EC, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, Cl− HCO3 −, SO4 2−, PO4 3−, H4SiO4, F−, δ18O and δD. Cl− and HCO3 − were the dominant ions in groundwater samples. Average values of Cl− and HCO3 − ranged from 247 and 244 mg/L in fissile hornblende biotite gneiss, 262 and 268 mg/L in Charnockite, 75 and 185 mg/L in quartzite, 323 and 305 mg/L in granite, 524 and 253 mg/L in floodplain alluvium rock types. Geochemical signatures of groundwater were used to identify the chemical processes that control hydrogeochemistry. Interpretation of δ18O and δD indicates recharge from the meteoric water in charnockite, quartzite, granite and some samples of fissile hornblende biotite gneiss. It is also inferred that recharge take place from evaporated water in floodplain alluvium and fissile hornblende biotite gneiss.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of Water and wastewater, 19th edn. APHA, Washington DC, USASS
Balamurugan C, Dheenadayalan MS (2013) Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Vaigai River basin at Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India. J of Chem, Biol and Phys Sci 2:1073–1078
Baskaran S, Ransley T, Brodie RS, Baker P (2009) Investigating groundwater–river interactions using environmental tracers, Aust J Earth Sci, 56: 13–19
Bhattacharya SK, Gupta SK, Krishnamurthy RV (1985) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic ratios in ground waters and river waters from India. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Earth Planet Sci) 94:283–294
CGWB (2010) Centre for groundwater board. A report on Madurai district
Chidambaram S (2000) Hydrogeochemical studies of groundwater in Periyar district, Tamilnadu, India. Unpublished Ph.D thesis, Department of Geology, Annamalai University
Chidambaram S, Bala Krishna Prasad M, Manivannan R, Karmegam U, Singaraja C, Anandhan P, Prasanna MV, Manikandan S (2012) Environmental hydrogeochemistry and genesis of fluoride in groundwaters of Dindigul District, Tamilnadu (India). Environ Earth Sci 68(2):333–342. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1741-9
Chidambaram S, John Peter A, Prasanna MV, Karmegam U, Balaji K, Ramesh R (2010) A study on the impact of land use pattern in the groundwater quality in and around Madurai Region. South India—Using GIS Techniques Online J Earth Sci 4:27–31
Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV, Ramanathan AL, Vasu K, Hameed S, Warrier UK, Manivannan R, Srinivasamoorthy K, Ramesh R (2009) Stable isotopic signatures in precipitation of 2006 southwest monsoon of Tamil Nadu. Curr Sci 96:9–10
Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV, Karmegam U, Singaraja C, Pethaperumal S, Manivannan R, Anandhan P, Tirumalesh (2011) Significance of pCO2 values in determining carbonate chemistry in groundwater of Pondicherry region, India. Front Earth Sci 5(2):197–206
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, New York
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meterotic waters. Am Assoc For The Adv Of Sci 133:1702–1703
Dalton MG, Upchurch SB (1978) Interpretation of hydrochemical facies by factor analysis. Groundw. 16(4):228–233
Datta PS, Tyagi SK, Chandrasekharan H (1991) Factors controlling stable isotope composition of rainfall in New Delhi. India, J of Hydrol 128:223–236
Deshpande RD, Gupta SK (2012) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in hydrological cycle: new data from IWIN National programme. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 78:321–331
Deshpande RD, Maurya AS, Angasaria RC, Dave M, Shukla AD, Bhandari N, Gupta SK (2013) Isotopic studies of megacryometeors in Western India. Curr Sci. 104(6):25
Dharmaraj J, Vadivel S, Ganeshkarthick E (2012) Physico-chemical analysis of ground water samples of selected districts of Tamilnadu and Kerala Int J of Sci & Technol Res 1(5):2277–8616
Fontes CH (1981) Environmental isotopes in groundwater hydrology, In: Handbook of Environmental Isotopes Geochemistry, P. Fritz and J.Ch. Fontes (eds.), Vol. 1,The Terrestrial Environment, A,1980; 75–140 Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co
Gat JR (1981) Stable isotope hydrology: deuterium and oxygen-18 in the water cycle In: J.R. Gat and R. Gonfiantini, (Eds.), IAEA Technical Reports Series, No. 210. Vienna: IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency)
GSI (Geological Survey of India). (1995). Geological and mineral map of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Geological survey of India. Source: http://www.portal.gsi.gov.in/gsiImages/information/misc_pub_30_tamilnadu_2006_wm.pdf
Gupta SK (1983) An isotopic investigation of a near-surface groundwater system. Hydrol Sci J 28(2):261–272
Harvey CF (2005) Groundwater arsenic contamination on the Ganges Delta: biogeochemistry, hydrology, human perturbations, and human suffering on a large scale. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 337(1–2):285–296
Hendry MJ, Schwartz FW (1988) An alternative view on the origin of chemical and isotopic patterns in groundwater from the milk River aquifer. Canada Water Resour Res 24:1747–1763
Herczeg A, Lamontagne S, Pritchard J, Leaney F, Dighton J (1992) Groundwater-surface water interactions: testing conceptual models with environmental tracres. 8th Murray Darling Basin groundwater workshop, Victor Harbor, South Australia. p. 6B.3
IMD (2014) Indian meteorological department. Source: http://www.imd.gov.in/section/hydro/dynamic/rfmaps/WeeklyProgress.htm
Jaiswal RK, Lohani AK, Tiwari HL (2015) Statistical analysis for change detection and trend assessment in climatological parameters. Environ Process 2(4):729–749. doi:10.1007/s40710-015-0105-3
Kondoh A, Shimada J (1997) The origin of precipitation in Eastern Asia by deuterium excess. J Japan Soc Hydrol & Water Resour 10(6):627–629
Krabbenhoft DP, Bowser CJ, Anderson MP, Valley JW (1990) Estimating groundwater exchange with lakes: the stable isotope mass balance method. Water Resour Res 26:2445–2453
Krishnamurthy RV, Bhattacharya SK (1991) Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotope ratios in shallow groundwaters from India and a study of the role of evapotranspiration in the Indian monsoon. The Geochem Soc, Spec Publ 3:187–193
Machavaram MV, Krishnamurthy (1995) Earth surface evaporation process: a case study from the Great Lakes region of the United States based on deuterium excess in precipitation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:4279–4283
Mazor E (1991) Chemical and isotopic groundwater hydrology. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Mukherjee TK, Chandrasekharan H (1993) Environmental stable isotopes on rainfall over Delhi and Bombay- some observations. J Nucl Agric Biol 22:34–41
Navaraj PS, Krishnammal S (2012) Investigation of water quality and its quotient factor in Thiruppalai Village, Madurai, India. IOSR J of Pharm and Biol Sci 2(6):40–46
Padmanaban R, Dharmendira Kumar M, Sakthivel PB, Elangovan NS (2013) A case study on chemical properties of ground water in Madurai District, Tamil Nadu, India. Int J of Eng And Adv Technol 2(4):2249–8958
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928
Prasanna MV, Chidambaram S, Srinivasamoorthy K, John Peter A, Anandhan P (2007) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in Gadilam River basin, through statistical analysis. Int Q J of Environ and Soc Sci 2(1):21–26
Prasanna MV, Chidambaram S, Shahul Hameed A, Srinivasamoorthy K (2010) Study of evaluation of groundwater in gadilam basin using hydrogeochemical and isotope data. Environ Monit Assess 168:63–90
Ranjana UK, Piyadasa, Champa Naverathna M (2011) River sand mining in Southern Sri- Lanka and its effect on environment. 11th International River symposium on “A Future of Extremes” Brisbane, Australia, 2008
Raymahashay BC (1986) Geochemistry of bicarbonate in river water. J of Geol Soc of India. 27:114–118
Rozanski K, Araguas-Araguas L, Gonfiantini R (1993) Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation. In: Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records, American Geophysical Union Monograph, vol 78, pp. 1–36
Sivasankar V, Omine K, Msagati TAM, Senthil kumar M, Chandramohan A (2013) Evaluation of groundwater quality in Madurai City, South India for drinking, irrigation and construction purposes. Arabian J Geosci 7:3093–3107. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-0994-2
Sukhija BS, Reddy DV, Nagabhushanam P (1998) Isotopic fingerprints of paleoclimates during the last 30,000 years in deep confined groundwaters of Southern India. Quat Res 50:252–260
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Singaraja C, Thilagavathi R, Prasanna MV, Jainab I (2013) A study on the significance of lithology in groundwater quality of Madurai district, Tamil Nadu (India) Environment. Dev and Sustain 15:1365–1387. doi:10.1007/s10668-013-9439-z
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Thilagavathi R, Prasanna MV, Singaraja C, Nepolian M, Sundarrajan M (2014a) Identification of the geochemical processes in groundwater by factor analysis in hard rock aquifers of Madurai district, South India. Arabian J Geosci 7:3767–3777. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1065-4
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Tirumalesh K, Prasanna MV, Thilagavathi R, Nepolian M (2014b) Occurrence of the radionuclides in groundwater of crystalline hard rock regions of Central Tamil Nadu, India. J of Radio-Analytical and Nucl Chem 302:1349–1355
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Thilagavathi R, Prasanna MV, Nepolian M, Tirumalesh K, Jacob N (2014c) Spatio-temporal identification of regions with anomalous values of 222Rn in groundwater of Madurai district, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Process 1:353–367
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Thilagavathi R (2014d) Evaluation of drinking water quality index (DWQI) and its seasonal variations in hard rock aquifers of Madurai district, Tamilnadu. Int J of Adv Geosci 2(2):48–52
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Thilagavathi R, Adithya VS, Nepolian M, Singaraja C (2014e) A study on the seasonal variations of groundwater quality in hard rocks aquifer of Madurai district. Tamilnadu Enviro Geo Chimica Acta 1(4):243–248
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Thilagavathi R, Prasanna MV, Singaraja C, Adithya VS, Nepolian M (2015a) A multivariate statistical approach to identify the spatio-temporal variation of geochemical process in a hard rock aquifer. Environ Monit & Assess, 187 (552): 1–19
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Rao MS, Thilagavathi R, Prasanna MV, Manikandan S (2015b) Assessment of fluoride contaminations in groundwater of hard rock aquifers in Madurai district, Tamil Nadu (India), Appl Water Sci, 5: 1–13. doi. 10.1007/s13201-015-0312-0
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Keesari T, Prasanna MV, Thilagavathi R, Adithya VS, Singaraja C (2015c) Lithological and hydrochemical controls on distribution and speciation of uranium in groundwaters of hard-rock granitic aquifers of Madurai District, Tamil Nadu (India). Environ Geochem Health 37:1–13. doi:10.1007/s10653-015-9735-7
Trusdell A H, Jones B F (1973) WATEQ: A computer program for calculating chemical equilibria of natural waters. J of Res US Geol Surv, 2(2): 233–248
Tirumalesh K, Shivanna K, Jalihal AA (2007) Isotope hydrochemical approach to understand fluoride release into groundwaters of Ilkal area, Bagalkot District, Karnataka, India. Hydrogeol J 15:589–598
Turner JV, Townlcy LR, Rosen MR, Sklash MK (1992) Coupling the spatial distribution of solute concentration and stable isotope enrichments to hydrological processes in hypersaline palcochannel aquifers. In: 7th international symposium on Water-Rock interaction (Park City, Utah, USA, July 1992), 217–222
Viswanath CV, Dileep Kumar PG, Ammad KK, Usha Kumari ER (2015) Groundwater quality and multivariate statistical methods, Environ Process, 2(2): 347–360
Wu J, Liu W, Zeng W, Ma L, Bai R (2014) Water quantity and quality of six lakes in the arid Xinjiang region, NW China, Environ Process, 1(2): 115–125
Yousif M, Oguchi T, Anazawa K (2015) Framework for investigation of karst aquifer in an arid zone, using isotopes, remote sensing and GIS applications: the Northwestern Coast of Egypt, Environ Processes, 2(1): 37–60
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their thanks to University Grants Commission (UGC), India, for providing the necessary financial support to carry out this study with vide reference to UGC letter No. F: 39-143/2010 (SR) dated 27.12.2010. The authors are also grateful to the editor and anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions, which led to significant improvements to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thivya, C., Chidambaram, S., Rao, M.S. et al. Identification of Recharge Processes in Groundwater in Hard Rock Aquifers of Madurai District Using Stable Isotopes. Environ. Process. 3, 463–477 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0137-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0137-3