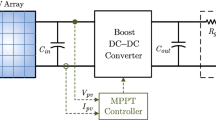
Abstract
Green energy endows the utmost environmental benefits, which include electric power produced from photovoltaic (PV) systems. The minimal conversion efficiency of PV systems (9–17%) decelerates the share in the energy market. One of the solutions to increase efficiency is efficient maximum power point tracking (MPPT) through precise controls. Within the available MPPT algorithms, the perturb and observe (P&O) is prominent due to its simplicity. However, its drawbacks slow down its usage. Most of the proposals involved in overcoming these drawbacks are hybrid nature, which increases the complexity. Alternately, this paper proposes shift and search (S&S) modified P&O algorithm, which not only retains the simplicity but also eliminates all the drawbacks of conventional algorithms with improved tracking efficiency. It is unique in its approach by having independent control over the steady state oscillations and the fast convergence, results in improved tracking efficiency. The performances of the proposed algorithm are validated in the simulation platform. Besides, the superiorities are verified by comparing with traditional and drift free P&O algorithms. The improved MPPT efficiency of the proposed technique aids in extracting the maximum power from solar energy.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Due to privacy and other restrictions, codes are not openly available.
Abbreviations
- PV:
-
Photovoltaic
- MPPT:
-
Maximum power point tracking
- P&O:
-
Perturb and observe
- S&S:
-
Shift and search
- IC:
-
Incremental conductance
- FOCV:
-
Fractional open circuit voltage
- FSCC:
-
Fractional short circuit current
- FL:
-
Fuzzy logic
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- CS:
-
Cuckoo search
- ABC:
-
Artificial bee colony
- ACO:
-
Ant colony optimization
- CFF:
-
Colony of flashing fireflies
- MPP:
-
Maximum power point
- Vt :
-
Voltage measured at time ‘t’
- Vt−1 :
-
Voltage measured at time ‘t − 1’
- M:
-
Minimum step voltage (V)
- X t :
-
Controlled variable at time ‘t’
- Xt−1 :
-
Controlled variable at time ‘t − 1’
- φv :
-
Step voltage (V)
- δp:
-
Change in power (W)
- δv:
-
Change in voltage (V)
- K:
-
Tuning constant
- S:
-
Second
- Wmax :
-
Maximum power (W)
- Wavg :
-
Average power (W)
- η:
-
Tracking efficiency (%)
- Vα :
-
Lower limit voltage (V)
- Vγ :
-
Upper limit voltage (V)
- Vβ :
-
Middle voltage (V)
References
Ebhota, W. S., & Chien, T. (2019). Fossil fuels environmental challenges and the role of solar photovoltaic technology advances in fast tracking hybrid renewable energy system. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00101-9.
Bhandari, B., Lee, K., Lee, G., Cho, Y., & Ahn, S. (2015). Optimization of hybrid renewable energy power systems : A review. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 2(1), 99–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-015-0013-z.
Dung, T., Minh, D., Nguyen, T., Binh, C., & Ahn, K. K. (2019). Development of a wave energy converter with mechanical power take-off via supplementary inertia control. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00098-1.
Moon, S. H., Gun, B., Ji, P., Kim, W., & Mok, J. (2019). Maximum power-point tracking control using perturb and observe algorithm for tidal current generation system. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00162-w.
Kim, K., Kim, H., Paek, I., Gil, H., & Jaehoon, K. (2019). Field validation of demanded power point tracking control algorithm for medium-capacity wind turbine. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00107-3.
Bhandari, B., Poudel, S. R., Lee, K. T., & Ahn, S. H. (2014). Mathematical modeling of hybrid renewable energy system: A review on small hydro-solar-wind power generation. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green , 1(2), 157–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-014-0021-4.
Venkateswari, R., & Sreejith, S. (2019). Factors influencing the efficiency of photovoltaic system. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 101, 376–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.11.012.
Khanlari, A., & Ozge, H. (2020). Experimental and numerical study of the effect of integrating plus-shaped perforated baffles to solar air collector in drying application us. Renewable Energy, 145, 1677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.07.076.
Doğuş, A., Sözen, A., Khanlari, A., Amini, A., & Şirin, C. (2020). Thermal performance analysis of a quadruple-pass solar air collector assisted pilot-scale greenhouse dryer. Solar Energy, 203, 304–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.04.030.
Tuncer, A. D., Khanlari, A., Sözen, A., Gürbüz, E. Y., Şirin, C., & Gungor, A. (2020). Energy–exergy and enviro-economic survey of solar air heaters with various air channel modifications. Renewable Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.06.087.
Badawy, M. O., Yilmaz, A. S., Sozer, Y., & Husain, I. (2014). Parallel power processing topology for solar PV applications. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 50(2), 1245–1255. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2013.2277546.
Park, J., Lee, P., Jae, M., & Lee, P. (2019). Design and fabrication of long-term stable dye-sensitized solar cells : Effect of water contents in electrolytes on the performance the direct conversion of sunlight into electrical energy are. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00025-4.
Bhatnagar, P., & Nema, R. K. (2013). Maximum power point tracking control techniques: State-of-the-art in photovoltaic applications. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 23, 224–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.02.011.
Masoum, M. A. S., Dehbonei, H., & Fuchs, E. F. (2002). Theoretical and experimental analyses of photovoltaic systems with voltage- and current-based maximum power-point tracking. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 17(4), 514–522. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2002.805205.
Chiu, C. S. (2010). T–S fuzzy maximum power point tracking control of solar power generation systems. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 25(4), 1123–1132. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2010.2041551.
Liu, Y. H., Huang, S. C., Huang, J. W., & Liang, W. C. (2012). A particle swarm optimization-based maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 27(4), 1027–1035. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2012.2219533.
Elobaid, L. M., Abdelsalam, A. K., & Zakzouk, E. E. (2015). Artificial neural network-based photovoltaic maximum power point tracking techniques : a survey. IET Renewable Power Generation, 9, 1043–1063. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2014.0359.
Ahmed, J., & Salam, Z. (2014). A maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for PV system using Cuckoo search with partial shading capability. Applied Energy, 119, 118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.12.062.
Sundareswaran, K., Sankar, P., Nayak, P. S. R., Simon, S. P., & Palani, S. (2015). Enhanced energy output from a PV system under partial shaded conditions through artificial bee colony. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 6(1), 198–209. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2014.2363521.
Sundareswaran, K., Sankar, P., Simon, S. P., Nayak, S. R., & Palani, S. (2015). Development of an improved P&O algorithm assisted through a colony of foraging ants for MPPT in PV system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2015.2502428.
Sundareswaran, K., Peddapati, S., & Palani, S. (2014). MPPT of PV systems under partial shaded conditions through a colony of flashing fireflies. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 29(2), 463–472. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2015.2502428.
Ram, J. P., Babu, T. S., & Rajasekar, N. (2017). A comprehensive review on solar PV maximum power point tracking techniques. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 67, 826–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.076.
Elbaset, A. A., Ali, H., Sattar, M. A., & Khaled, M. (2015). Implementation of a modified perturb and observe maximum power point tracking algorithm for photovoltaic system using an embedded microcontroller. IET Renewable Power Generation. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2015.0309.
Sher, H. A., et al. (2015). A new sensorless hybrid MPPT algorithm based on fractional short-circuit current measurement. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2015.2438781.
Macaulay, J. (2018). A fuzzy logical-based variable step size P&O MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic system. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061340.
Pandey, A., Dasgupta, N., & Mukerjee, A. K. (2008). High-performance algorithms for drift avoidance and fast tracking in solar MPPT system. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 23(2), 681–689. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2007.914201.
Killi, M., & Samanta, S. (2015). Modified perturb and observe MPPT algorithm for drift avoidance in photovoltaic systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(9), 5549–5559. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2015.2407854.
Ahmed, J., & Salam, Z. (2016). A modified P&O maximum power point tracking method with reduced steady state oscillation and improved tracking efficiency. IEEE Transaction on Sustainable Energy, 3029, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2016.2568043.
Abdel-Salam, M., El-Mohandes, M. T., & El-Ghazaly, M. (2020). An efficient tracking of MPP in PV systems using a newly-formulated P&O-MPPT method under varying irradiation levels. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology, 15(1), 501–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-019-00283-x.
Kavya, M., & Jayalalitha, S. (2020). Developments in perturb and observe algorithm for maximum power point tracking in photo voltaic panel : A review. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-020-09461-x.
Pilakkat, D., & Kanthalakshmi, S. (2018). Drift free variable step size perturb and observe MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic systems under rapidly increasing insolation. Electronics, 22(1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.7251/ELS1822019P.
Kollimalla, S. K., & Mishra, M. K. (2014). A novel adaptive P&O MPPT algorithm considering sudden changes in the irradiance. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2014.2320930.
Bendib, B., Belmili, H., & Krim, F. (2015). A survey of the most used MPPT methods: Conventional and advanced algorithms applied for photovoltaic systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 45, 637–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.009.
Acknowledgements
The authors convey their honest thanks to the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India, for the INSPIRE fellowship awarded to the first author. (Fellowship No: DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2016/IF160835). Besides, the authors affirm their sincere gratitude to the management of SASTRA Deemed to be University for the assistance rendered during the research.
Funding
No funds, Grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavya, M., Jayalalitha, S. A Novel Shift and Search (S&S) Algorithm for Tracking Maximum Power in PV Systems: An Approach to Increase Efficiency. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 8, 1699–1710 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00297-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00297-1