Abstract
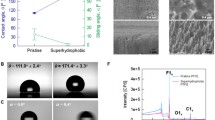
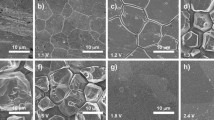
We present a novel method of realizing instant hydrophobic and long-lasting superhydrophilic states on stainless steel (SS) surfaces by micropatterning and thermally-induced surface layers (TISL). Heat treatment of SS surfaces in the air for 6 h yields hydrophobic TISLs at 140 °C and hydrophilic TISLs at 300 °C. The result of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reveals the correlation of chromium depletion with the hydrophilic TISLs, as well as surface oxidation with the hydrophobic TISLs. We fabricated superhydrophilic SS surfaces holding the wettability over 40 days, and hydrophobic SS surfaces realized in an hour-scale period via the fabrication process comprised of laser beam machining, electrochemical etching, and heat treatment in serial.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen, L., Tian, Y., & Jiang, L. (2015). Bioinspired super-wettability from fundamental research to practical applications. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 54(11), 3387–3399.
Yao, X., Song, Y., & Jiang, L. (2011). Applications of bio-inspired special wettable surfaces. Advanced Materials, 23(6), 719–734.
Barthwal, S., & Lim, S.-H. (2020). Robust and chemically stable superhydrophobic aluminum-alloy surface with enhanced corrosion-resistanceproperties. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 7(2), 481–492.
Liu, K., & Jiang, L. (2011). Metallic surfaces with special wettability. Nanoscale, 3(3), 825–838.
Lo, K. H., Shek, C. H., & Lai, J. (2009). Recent developments in stainless steels. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 65(4–6), 39–104.
Ryan, M. P., Williams, D. E., Chater, R. J., Hutton, B. M., & McPhail, D. S. (2002). Why stainless steel corrodes. Nature, 415(6873), 770.
Jafari, A., Meshkani, S., & Ghoranneviss, M. (2016). The study of surface properties of tokamak first wall using TiN coated on stainless steel. Journal of Fusion Energy, 35(2), 235–239.
Staib, P., Dylla, H., & Rossnagel, S. M. (1980). The surface chemistry of stainless steel and evaporated titanium layers in tokamaks. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 93, 315–321.
Davies, D., Adcock, P., Turpin, M., & Rowen, S. (2000). Stainless steel as a bipolar plate material for solid polymer fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 86(1–2), 237–242.
Asri, N. F., Husaini, T., Sulong, A. B., Majlan, E. H., & Daud, W. R. W. (2017). Coating of stainless steel and titanium bipolar plates for anticorrosion in PEMFC: A review. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(14), 9135–9148.
Li, L., Zhang, G., & Su, Z. (2016). One-step assembly of phytic acid metal complexes for superhydrophilic coatings. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 55(31), 9093–9096.
Wang, H., Zou, M., & Wei, R. (2009). Superhydrophilic textured-surfaces on stainless steel substrates. Thin Solid Films, 518(5), 1571–1574.
Xue, Z., Wang, S., Lin, L., Chen, L., Liu, M., Feng, L., et al. (2011). A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Advanced Materials, 23(37), 4270–4273.
Yang, J., Zhang, Z., Xu, X., Zhu, X., Men, X., & Zhou, X. (2012). Superhydrophilic–superoleophobic coatings. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(7), 2834–2837.
Bagherifard, S., Hickey, D. J., de Luca, A. C., Malheiro, V. N., Markaki, A. E., Guagliano, M., et al. (2015). The influence of nanostructured features on bacterial adhesion and bone cell functions on severely shot peened 316L stainless steel. Biomaterials, 73, 185–197.
Ceylan, H., Tekinay, A. B., & Guler, M. O. (2011). Selective adhesion and growth of vascular endothelial cells on bioactive peptide nanofiber functionalized stainless steel surface. Biomaterials, 32(34), 8797–8805.
Müller, R., Abke, J., Schnell, E., Macionczyk, F., Gbureck, U., Mehrl, R., et al. (2005). Surface engineering of stainless steel materials by covalent collagen immobilization to improve implant biocompatibility. Biomaterials, 26(34), 6962–6972.
Li, L., Breedveld, V., & Hess, D. W. (2012). Creation of superhydrophobic stainless steel surfaces by acid treatments and hydrophobic film deposition. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4(9), 4549–4556.
Liu, Y., Bai, Y., Jin, J., Tian, L., Han, Z., & Ren, L. (2015). Facile fabrication of biomimetic superhydrophobic surface with anti-frosting on stainless steel substrate. Applied Surface Science, 355, 1238–1244.
Wu, B., Zhou, M., Li, J., Ye, X., Li, G., & Cai, L. (2009). Superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated by microstructuring of stainless steel using a femtosecond laser. Applied Surface Science, 256(1), 61–66.
Chen, L. J., Chen, M., Di Zhou, H., & Chen, J. M. (2008). Preparation of super-hydrophobic surface on stainless steel. Applied Surface Science, 255(5), 3459–3462.
Liang, J., Li, D., Wang, D., Liu, K., & Chen, L. (2014). Preparation of stable superhydrophobic film on stainless steel substrate by a combined approach using electrodeposition and fluorinated modification. Applied Surface Science, 293, 265–270.
Beckford, S., & Zou, M. (2011). Micro/nano engineering on stainless steel substrates to produce superhydrophobic surfaces. Thin Solid Films, 520(5), 1520–1524.
Kim, D., Kim, J. G., & Chu, C. N. (2016). Aging effect on the wettability of stainless steel. Materials Letters, 170, 18–20.
Bae, W. G., Song, K. Y., Rahmawan, Y., Chu, C. N., Kim, D., Chung, D. K., et al. (2012). One-step process for superhydrophobic metallic surfaces by wire electrical discharge machining. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4(7), 3685–3691.
Bae, W.-G., Kim, D., Song, K. Y., Jeong, H. E., & Chu, C. N. (2015). Engineering stainless steel surface via wire electrical discharge machining for controlling the wettability. Surface and Coatings Technology, 275, 316–323.
Cardoso, J., Aguilar-Morales, A., Alamri, S., Huerta-Murillo, D., Cordovilla, F., Lasagni, A., et al. (2018). Superhydrophobicity on hierarchical periodic surface structures fabricated via direct laser writing and direct laser interference patterning on an aluminium alloy. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 111, 193–200.
Kwon, M. H., Shin, H. S., & Chu, C. N. (2014). Fabrication of a super-hydrophobic surface on metal using laser ablation and electrodeposition. Applied Surface Science, 288, 222–228.
Ta, D. V., Dunn, A., Wasley, T. J., Kay, R. W., Stringer, J., Smith, P. J., et al. (2015). Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications. Applied Surface Science, 357, 248–254.
Kietzig, A.-M., Hatzikiriakos, S. G., & Englezos, P. (2009). Patterned superhydrophobic metallic surfaces. Langmuir, 25(8), 4821–4827.
Allahyari, E., Nivas, J. J., Oscurato, S. L., Salvatore, M., Ausanio, G., Vecchione, A., et al. (2018). Laser surface texturing of copper and variation of the wetting response with the laser pulse fluence. Applied Surface Science., 470, 817–824.
Geng, W., Hu, A., & Li, M. (2012). Super-hydrophilicity to super-hydrophobicity transition of a surface with Ni micro–nano cones array. Applied Surface Science, 263, 821–824.
Wang, G., & Zhang, T.-Y. (2012). Oxygen adsorption induced superhydrophilic-to-superhydrophobic transition on hierarchical nanostructured CuO surface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 377(1), 438–441.
Long, J., Zhong, M., Zhang, H., & Fan, P. (2015). Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of picosecond laser microstructured aluminum in ambient air. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 441, 1–9.
Chun, D.-M., Ngo, C.-V., & Lee, K.-M. (2016). Fast fabrication of superhydrophobic metallic surface using nanosecond laser texturing and low-temperature annealing. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 65(1), 519–522.
Zhang, Y., Zou, G., Liu, L., Zhao, Y., Liang, Q., Wu, A., et al. (2016). Time-dependent wettability of nano-patterned surfaces fabricated by femtosecond laser with high efficiency. Applied Surface Science, 389, 554–559.
Ngo, C.-V., & Chun, D.-M. (2017). Fast wettability transition from hydrophilic to superhydrophobic laser-textured stainless steel surfaces under low-temperature annealing. Applied Surface Science, 409, 232–240.
Trdan, U., Hočevar, M., & Gregorčič, P. (2017). Transition from superhydrophilic to superhydrophobic state of laser textured stainless steel surface and its effect on corrosion resistance. Corrosion Science, 123, 21–26.
Masseria, V. (1981). Metals handbook: Heat treatment. Cleveland: American Society for Metals.
Lee, S. W., Shin, H. S., & Chu, C. N. (2013). Fabrication of micro-pin array with high aspect ratio on stainless steel using nanosecond laser beam machining. Applied Surface Science, 264, 653–663.
Shin, H., Park, M., & Chu, C. (2010). Electrochemical etching using laser masking for multilayered structures on stainless steel. CIRP Annals, 59(1), 585–588.
Quéré, D. (2008). Wetting and roughness. Annual Review of Materials Research, 38, 71–99.
Feng, L., Zhang, Y., Xi, J., Zhu, Y., Wang, N., Xia, F., et al. (2008). Petal effect: A superhydrophobic state with high adhesive force. Langmuir, 24(8), 4114–4119.
Hakiki, N., Montemor, M., Ferreira, M., & da Cunha Belo, M. (2000). Semiconducting properties of thermally grown oxide films on AISI 304 stainless steel. Corrosion Science, 42(4), 687–702.
Cornell, R. M., & Schwertmann, U. (2003). The iron oxides: Structure, properties, reactions, occurrences and uses. Hoboken: Wiley.
Khanna, A. S. (2002). Introduction to high temperature oxidation and corrosion. Cleveland: ASM International.
Demidov, A., & Markelov, I. (2010). Thermodynamics of formation of iron oxides and their hydrogen reduction. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 83(2), 232–236.
Mittal, A., Albertsson, G. J., Gupta, G. S., Seetharaman, S., & Subramanian, S. (2014). Some thermodynamic aspects of the oxides of chromium. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 45(2), 338–344.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Research Lab Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the MSIT (2018R1A4A1059976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This study is dedicated to the late Professor Chong Nam Chu who deceased 28 April 2019.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Kim, JG., Kim, T. et al. Long-Lasting Superhydrophilic and Instant Hydrophobic Micropatterned Stainless Steel Surface by Thermally-Induced Surface Layers. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 8, 435–444 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00207-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00207-5