Abstract
Background
Anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) represents a rare lethal human malignancy with poor prognosis. Multimodality treatment, including radiotherapy, is recommended to improve local control and survival. Valproic acid (VA) is a clinically available histone deacetylase inhibitor with a well-documented side effect profile. In this study, we aim to investigate the combined effect of VA with photon irradiation in vitro.
Methods
Anaplastic thyroid cancer cells (8505c) were used to investigate the radiosensitizing effect of VA.
Results
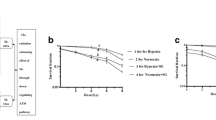
VA sensitized cells to photon irradiation. VA increased radiation-induced apoptosis and radiation-induced DNA damage measured by γH2AX foci induction. Furthermore, VA prolonged γH2AX foci disappearance over time in irradiated cells and decreased the radiation-induced levels of mRNA of key DNA damage repair proteins of the homologous recombination (HR) and the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) pathways.
Conclusions
VA at a clinically safe dose enhance the radiosensitivity of 8505c cells through an increase in radiation-induced apoptosis and a disruption in the molecular mechanism of HR and NHEJ DNA damage repair pathways.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds) (2014) Cronin K SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2011, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md, USA, 2013, based on November 2013 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2011/. Accessed 25 July 2022
Veness MJ, Porter GS, Morgan GJ (2004) Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: dismal outcome despite current treatment approach. ANZ J Surg 74(7):559–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-2197.2004.03062.x
Smallridge RC, Ain KB, Asaetal SL (2012) American Thyroid Association guidelines for management of patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer. Thyroid 22(11):1104–1139. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2012.0302
Busnardo B, Daniele O, Pelizzo MR, Mazzarotto R, Nacamulli D, Devido D, Mian C, Girelli ME (2000) A multimodality therapeutic approach in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: study on 39 patients. J Endocrinol Invest 23(11):755–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345066
Haigh PI, Ituarte PH, Wu HS, Treseler PA, Posner MD, Quivey JM, Duh QY, Clark OH (2001) Completely resected anaplastic thyroid carcinoma combined with adjuvant chemotherapy and irradiation is associated with prolonged survival. Cancer 91(12):2335–2342
Stavas MJ, Shinohara ET, Attia A, Ning MS, Friedman JM, Cmelak AJ (2014) Short course high dose radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. J Thyroid Res 2014:764281. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/764281
De Leo S, Trevisan M, Fugazzola L (2020) Recent advances in the management of anaplastic thyroid cancer. Thyroid Res 13(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13044-020-00091-w
Harari PM, Huang SM (2000) Modulation of molecular targets to enhance radiation. Clin Cancer Res 6(2):323–325
Lane AA, Chabner BA (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 27(32):5459–5468. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.22.1291
Marks PA, Xu WS (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: potential in cancer therapy. J Cell Biochem 107(4):600–608. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.22185
Ranganna K, Selvam C, Shivachar A, Yousefipour Z (2020) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as multitarget-directed epi-drugs in blocking PI3k oncogenic signaling: a polypharmacology approach. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):8198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218198
Munster PN, Marchion D, Thomas S, Egorin M, Minton S, Springett G, Lee JH, Simon G, Chiappori A, Sullivan D, Daud A (2009) Phase I trial of vorinostat and doxorubicin in solid tumours: histone deacetylase 2 expression as a predictive marker. Clin Trial Br J Cancer 101(7):1044–1050. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605293
Groselj B, Sharma NL, Hamdy FC, Kerr M, Kiltie AE (2013) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as radiosensitisers: effects on DNA damage signalling and repair. Br J Cancer 108:748–754. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.21
Moertl S, Payer S, Kell R, Winkler K, Anastasov N, Atkinson MJ (2019) Comparison of radiosensitization by HDAC Inhibitors CUDC-101 and SAHA in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 20(13):3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133259
van Breemen MS, Rijsman RM, Taphoorn MJ, Walchenbach R, Zwinkels H, Vecht CJ (2009) Efficacy of anti-epileptic drugs in patients with gliomas and seizures. J Neurol 256(9):1519–1526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5156-9
Zhu MM, Li HL, Shi LH, Chen XP, Luo J, Zhang ZL (2017) The pharmacogenomics of valproic acid. J Hum Genet 62(12):1009–1014. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2017.91
Gottlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, Kramer OH, Schimpf A, Giavara S, Sleeman JP, Lo Coco F, Nervi C, Pelicci PG, Heinzel T (2001) Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J 20(24):6969–6978. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.24.6969
Blaheta RA, Michaelis M, Driever PH, Cinatl JJ (2005) Evolving anticancer drug valproic acid: insights into the mechanism and clinical studies. Med Res Rev 25:383–397. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.20027
Cinatl JJ, Cinatl J, Scholz M, Driever PH, Henrich D, Kabickova H, Vogel JU, Doerr HW, Kornhuber B (1996) Antitumor activity of sodium valproate in cultures of human neuroblastomacells. Anticancer Drugs 7:766–773. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001813-199609000-00008
Driever PH, Knüpfer MM, Cinatl J, Wolff JEA (1999) Valproic acid for the treatment of pediatric malignant glioma. Klin Padiatr 211:323–328. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1043809
Michaelis M, Doerr HW, Cinatl J (2007) Valproic acid as anti-cancer drug. Current Pharmaceut Des 13:3378–3393
Catalano MG, Fortunati N, Pugliese M, Costantino L, Poli R, Bosco O, Boccuzzi G (2005) Valproic acid induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in poorly differentiated thyroid cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(3):1383–1389. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-1355
Fortunati N, Catalano MG, Arena K, Brignardello E, Piovesan A, Boccuzzi G (2004) Valproic acid induces the expression of the Na+/I- symporter and iodine uptake in poorly differentiated thyroid cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(2):1006–1009. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-031407
Karagiannis TC, El-Osta A (2006) Modulation of cellular radiation responses by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oncogene 25(28):3885–3893. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209417
Makita N, Ninomiya I, Tsukada T, Okamoto K, Harada S, Nakanuma S, Sakai S, Makino I, Kinoshita J, Hayashi H, Katsunobu O, Hisatoshi N, Tomoharu M, Hidehiro T, Hiroyuki T, Sachio F, Tetsuo O (2015) Inhibitory effects of valproic acid in DNA double-strand break repair after irradiation in esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 34(3):1185–1192. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4089
Luo Y, Wang H, Zhao XP, Dong X, Zhang FM, Guo G, Guo WXW, Powell SN, Feng ZH (2016) Valproic acid causes radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells via disrupting the DNA repair pathway. Toxicol Res (Cam) 5(3):859–870. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5tx00476d
Van Oorschot B, Granata G, Franco S, Cate R, Rodermond HM, Todaro M, Medema JP, Franken NAP (2016) Targeting DNA double strand break repair with hyperthermia and DNA-PKCS inhibition to enhance the effect of radiation treatment. Oncotarget 7:65504–65513. https://doi.org/10.1863/oncotarget.11798
Chinnaiyan P, Cerna D, Burgan WE, Beam K, Williams ES, Camphausen K, Tofilon PJ (2008) Postradiation sensitization of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid. Clin Cancer Res 14:5410–5415. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0643
Perona M, Thomasz L, Rossich L, Rodriguez C, Pisarev MA, Rosemblit C, Cremaschi GA, Dagrosa MA, Juvenal GJ (2018) Radiosensitivity enhancement of human thyroid carcinoma cells by the inhibitors of histone deacetylase sodium butyrate and valproic acid. Mol Cell Endocrinol 478:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2018.08.007
Barker CA, Bishop AJ, Chang M, Beal K, Chan TA (2013) Valproic acid use during radiation therapy for glioblastoma associated with improved survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86(3):504–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.02.012
Krauze AV, Myrehaug SD, Chang MG, Holdford DJ, Smith S, Shih J, Tofilon PJ, Fine HA, Camphausen K (2015) A phase 2 study of concurrent radiation therapy, Temozolomide, and the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid for patients with glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 92(5):986–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.04.038
Tennvall J, Lundell G, Wahlberg P, Bergenfelz A, Grimelius L, Akerman M, Hjelm Skog AL, Wallin G (2002) Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: three protocols combining doxorubicin, hyperfractionated radiotherapy and surgery. Br J Cancer 86(12):1848–1853. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6600361
Chateauvieux S, Morceau F, Dicato M, Diederich M (2010) Molecular and therapeutic potential and toxicity of valproic acid. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:479364. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/479364
Noguchi H, Yamashita H, Murakami T, Hirai K, Noguchi Y, Maruta J, Yokoi T, Noguchi S (2009) Successful treatment of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma with a combination of oral valproic acid, chemotherapy, radiation and surgery. Endocr J 56:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.k08e-016
Catalano MG, Pugliese M, Gallo M, Brignardello E, Milla P, Orlandi F, Limone PP, Arvat E, Boccuzzi G, Piovesan A (2016) Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with paclitaxel for anaplastic thyroid cancer: results of a multicenter randomized controlled phase II/III trial. Int J Endocrinol 2016:2930414. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2930414
Nilubol N, Merkel R, Yang L, Patel D, Reynolds JC, Sadowski SM, Neychev V, Kebebew E (2016) A phase II trial of valproic acid in patients with advanced, radioiodine-resistant thyroid cancers of follicular cell origin. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 86(1):128–133. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13154
Duenas-Gonzalez A, Candelaria M, Perez-Plascencia C, Perez-Cardenas E, de la Cruz-Hernandez E, Herrera LA (2008) Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: preclinical, clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev 34:206–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.11.003
Brown JM, Attardi LD (2005) The role of apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev Cancer 5:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1560
Karagiannis TC, Harikrishnan KN, El-Osta A (2005) The histone deacetylase inhibitor, trichostatin a, enhances radiation sensitivity and accumulation of gammaH2A.X. Cancer Biol Ther 4:787–793. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.4.7.1922
Shirbhate E, Patel P, Patel VK, Veerasamy R, Sharma PC, Rajak H (2020) The combination of histone deacetylase inhibitors and radiotherapy: a promising novel approach for cancer treatment. Future Oncol 16(30):2457–2469. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2020-0385
Kawano T, Akiyama M, Agawa-Ohta M, Mikami-Terao Y, Iwase S, Yanagisawa T, Ida H, Agata N, Yamada H (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors valproic acid and depsipeptide sensitize retinoblastoma cells to radiotherapy by increasing H2AX phosphorylation and p53 acetylation-phosphorylation. Int J Oncol 37(4):787–795. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo_00000728
Chiou HY, Lai WK, Huang LC, Huang SM, Chueh SH, Ma HI, Hueng DY (2015) Valproic acid promotes radiosensitization in meningioma stem-like cells. Oncotarget 6:9959–9969. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3692
Jackson SP (2002) Sensing and repairing DNA double-strand breaks. Carcinogenesis 23(5):687–696. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/23.5.687
Olive PL, Banáth JP (2004) Phosphorylation of histone H2AX as a measure of radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:331–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.028
Redon CE, Nakamura AJ, Zhang YW, Ji JJ, Bonner WM, Kinders RJ, Parchment RE, Doroshow JH, Pommier Y (2010) Histone gammaH2AX and poly(ADP-ribose) as clinical pharmacodynamic biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res 16(18):4532–4542. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0523
Rothkamm K, Löbrich M (2003) Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(9):5057–5062. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0830918100
Ward IM, Minn K, Jorda KG, Chen J (2003) Accumulation of checkpoint protein 53BP1 at DNA breaks involves its binding to phosphorylated histone H2AX. J Biol Chem 278:19579–19582. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C300117200
Funding
Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica, Gobierno de Argentina, Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica, PICT0041, Guillermo Juvenal,Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas, PIP0082, Guillermo Juvenal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
In this article no studies involving human participants or animals were performed.
Informed consent
Formal consent is not required for this type of study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Perona, M., Ibañez, I.L., Thomasz, L. et al. Valproic acid radiosensitizes anaplastic thyroid cells through a decrease of the DNA damage repair capacity. J Endocrinol Invest 46, 2353–2365 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02092-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02092-6