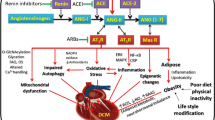
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) and heart failure (HF) are frequent comorbidities among elderly patients. HF, a leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide, is characterized by sympathetic nervous system hyperactivity. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) is rapidly growing and the risk of developing HF is higher among DM patients. DM is responsible for several macro- and micro-angiopathies that contribute to the development of coronary artery disease (CAD), peripheral artery disease, retinopathy, neuropathy and diabetic nephropathy (DN) as well. Independently of CAD, chronic kidney disease (CKD) and DM increase the risk of HF. Individuals with diabetic nephropathy are likely to present a distinct pathological condition, defined as diabetic cardiomyopathy, even in the absence of hypertension or CAD, whose pathogenesis is only partially known. However, several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the mechanism of diabetic cardiomyopathy: increased oxidative stress, altered substrate metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction, activation of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), insulin resistance, and autonomic dysfunction. In this review, we will focus on the involvement of sympathetic system hyperactivity in the diabetic nephropathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HF:
-
Heart failure
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- SNS:
-
Sympathetic nervous system
- CA:
-
Cathecolamines
- βARs:
-
β-adrenergic receptors
- DN:
-
Diabetic nephropathy
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- RAAS:
-
Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system
- NE:
-
Norepinephrine
- EN:
-
Epinephrine
- GRK2:
-
G-protein coupled receptor kinase 2.
References
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ (2016) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 133:e38–e360. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000350
Roger LV (2013) Epidemiology of heart failure. Circ Res 113:646–659
Katsanos S, Mavrogenis AF, Kafkas N, Sardu C, Kamperidis V, Katsanou P, Farmakis D, Parissis J (2017) Cardiac biomarkers predict 1-year mortality in elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery. Orthopedics 40:e417–e424
Velagaleti RS, Gona P, Larson MG, Wang TJ, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Selhub J, Jacques PF, Meigs JB, Tofler GH, Vasan RS (2010) Multimarker approach for the prediction of heart failure incidence in the community. Circulation 122:1700–1706. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.929661
Kalogeropoulos A, Georgiopoulou V, Psaty BM, Rodondi N, Smith AL, Harrison DG, Liu Y, Hoffmann U, Bauer DC, Newman AB, Kritchevsky SB, Harris TB, Butler J (2010) Health ABC Study Investigators. Health ABC Study Investigators. Inflammatory markers and incident heart failure risk in older adults: the health ABC (health, aging, and body composition) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2129–2137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.12.045
Rengo G, Lymperopoulos A, Leosco D, Koch WJ (2011) GRK2 as a novel gene therapy target in heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 50:785–792
Rengo G, Lymperopoulos A, Koch WJ (2009) Future g protein-coupled receptor target for treatment of heart failure. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 11:328–338
King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH (1998) Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 21:1414–1431
Fox CS, Golden SH, Anderson C, Bray GA, Burke LE, de Boer IH, Deedwania P, Eckel RH, Ershow AG, Fradkin J, Inzucchi SE, Kosiborod M, Nelson RG, Patel MJ, Pignone M, Quinn L, Schauer PR, Selvin E, Vafiadis DK (2015) Update on prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in light of recent evidence: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the American Diabetes Association. Circulation 132:691–718. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000230
Sobel BE, Schneider DJ (2005) Cardiovascular complications in diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:143–148
National Kidney Foundation (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39(Suppl 1):S1–S266
National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (2000) US renal data system, USRDS 2000 annual data report. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda. http://www.usrds.org/atlas_2000.htm. Accessed 12 Sept 2003
Alonso A, Lopez FL, Matsushita K, Loehr LR, Agarwal SK, Chen LY, Soliman EZ, Astor BC, Coresh J (2011) Chronic kidney disease is associated with the incidence of atrial fibrillation: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Circulation 123:2946–2953. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.020982
Segall L, Nistor I, Covic A (2014) Heart failure in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic integrative review. Biomed Res Int 2014:937398. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/937398
Metivier F, Marchais SJ, Guerin AP, Pannier B, London GM (2000) Pathophysiology of anaemia: focus on the heart and blood vessels. Nephrol Dial Transpl 15 (Suppl 3):14–18
Bahrami H, Bluemke DA, Kronmal R, Bertoni AG, Lloyd-Jones DM, Shahar E, Szklo M, Lima JA (2008) Novel metabolic risk factors for incident heart failure and their relationship with obesity: the MESA (multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:1775–1783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2007.12.048
Arnlöv J, Evans JC, Meigs JB, Wang TJ, Fox CS, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, D’Agostino RB, Vasan RS (2005) Low-grade albuminuria and incidence of cardiovascular disease events in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic individuals: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 112:969–975. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.538132
Shlipak MG, Fried LF, Cushman M. Manolio TA, Peterson D, Stehman-Breen C, Bleyer A, Newman A, Siscovick D, Psaty B (2005) Cardiovascular mortality risk in chronic kidney disease: comparison of traditional and novel risk factors. JAMA 293:1737–1745. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.293.14.1737
Valmadrid CT, Klein R, Moss SE, Klein BE (2000) The risk of cardiovascular disease mortality associated with microalbuminuria and gross proteinuria in persons with older-onset diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 160:1093–1100
Ronco C, Haapio M, House AA, Anavekar N, Bellomo R (2008) Cardio-renal syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:1527–1539
Schefold JC, Filippatos G, Hasenfuss G, Anker SD, von Haehling S (2016) Heart failure and kidney dysfunction: epidemiology, mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Nephrol 12:610–623. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2016.113
Kasznicki J, Dzewowski J (2014) Heart failure in the diabetic population—pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Arch Med Sci 10:546–556. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2014.43748
Boudina S, Abel ED (2007) Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation 115:3213–3223
Petersson M, Friberg P, Lambert G, Rundqvist B (2005) Decreased renal sympathetic activity in response to cardiac unloading with nitroglycerin in patients with heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 7(6):1003–1010
Paollilo S, Rengo G, Pellegrino T, Formisano R, Pagano G, Gargiulo P, Savarese G, Carotenuto R, Petraglia L, Rapacciuolo A, Perrino C, Piscitelli S, Attena E, Del Guercio L, Leosco D, Trimarco B, Cuocolo A, Perrone-Filardi P (2013) Impact of diabetes on cardiac sympathetic innervation in patients with heart failure. Diabetes Care 36(8):2395–2401
Lymperopoulos A, Rengo G, Koch WJ (2012) GRK2 inhibition in heart failure: something old, something new. Curr Pharm Des 18:186–191
de Lucia C, Femminella GD, Gambino G, Pagano G, Allocca E, Rengo C, Silvestri C, Leosco D, Ferrara N, Rengo G (2014) Adrenal adrenoceptors in heart failure. Front Physiol 5:246. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00246
Ferrara N, Komici K, Corbi G, Pagano G, Furgi G, Rengo C, Femminella GD, Leosco D, Bonaduce D (2014) β-adrenergic receptor responsiveness in aging heart and clinical implications. Front Physiol 4:396
Zhu WZ, Zheng M, Koch WJ, Lefkowitz RJ, Kobilka BK, Xiao RP (2001) Dual modulation of cell survival and cell death by β2-adrenergic signalling in adult mouse cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1607–1612
Rengo G, Cannavo A, Liccardo D, Zincarelli C, de Lucia C, Pagano G, Komici K, Parisi V, Scala O, Agresta A, Rapacciuolo A, Perrone Filardi P, Ferrara N, Koch WJ, Trimarco B, Femminella GD, Leosco D et al (2013) Vascular endothelial growth factor blockade prevents the beneficial effects of β-blocker therapy on cardiac function, angiogenesis, and remodeling in heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 6:1259–1267. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000329
Rengo G, Perrone-Filardi P, Femminella GD, Liccardo D, Zincarelli C, de Lucia C, Pagano G, Marsico F, Lymperopoulos A, Leosco D (2012) Targeting the β-adrenergic receptor system through G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2: a new paradigm for therapy and prognostic evaluation in heart failure: from bench to bedside. Circ Heart Fail 5:385–391
Bathgate-Siryk A, Dabul S, Pandya K et al (2014) Negative impact of β-arrestin-1 on post-myocardial infarction heart failure via cardiac and adrenal-dependent neurohormonal mechanisms. Hypertension 63:404–412
Lymperopoulos A, Rengo G, Koch WJ (2013) Adrenergic nervous system in heart failure: pathophysiology and therapy. Circ Res 113:739–753. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300308
Iaccarino G, Barbato E, Cipolletta E, De Amicis V, Margulies KB, Leosco D, Trimarco B, Koch WJ (2005) Elevated myocardial and lymphocyte GRK2 expression and activity in human heart failure. Eur Heart J 17:1752–1758. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehi429
Lymperopoulos A, Rengo G, Funakoshi H, Eckhart AD, Koch WJ (2007) Adrenal GRK2 mediates sympathetic overdrive in heart failure. Nat Med 13:315–323. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1553
Rengo G, Pagano G, Filardi PP, Femminella GD, Parisi V, Cannavo A, Liccardo D, Komici K, Gambino G, D’Amico ML, de Lucia C, Paolillo S, Trimarco B, Vitale DF, Ferrara N, Koch WJ, Leosco D (2016) Prognostic value of lymphocyte G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 protein levels in patients with heart failure. Circ Res 118:1116–1124. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.308207
Salazar NC, Vallejos X, Siryk A, Rengo G, Cannavo A, Liccardo D, De Lucia C, Gao E, Leosco D, Koch WJ, Lymperopoulos A (2013) GRK2 blockade with βARKct is essential for cardiac β2-adrenergic receptor signaling towards increased contractility. Cell Commun Signal 11:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-11-64
Rengo G, Lymperopoulos A, Zincarelli C, Femminella G, Liccardo D, Pagano G, de Lucia C, Cannavo A, Gargiulo P, Ferrara N, Perrone Filardi P, Koch W, Leosco D (2009) Myocardial adeno-associated virus serotype 6-βARKct gene therapy improves cardiac function and normalizes the neurohormonal axis in chronic heart failure. Circulation 119:89–98
Lim KHA (2014) Diabetic nephropathy—complications and treatment. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 7:361–381
Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T (2005) Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 28:164–176
American Diabetes Association (2016) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. In: 2016 standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 39:S13–S22
Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:977–986
Shurraw S, Hemmelgarn B, Lin M et al (2011) Association between glycemic control and adverse outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Arch Intern Med 171:1920–1927
Oh SW, Kim YC, Koo HS et al (2011) Glycated haemoglobin and the incidence of end-stage renal disease in diabetics. Nephrol Dial Transpl 26:2238–2244
Levin BE, Sullivan AC (1987) Glucose-induced norepinephrine levels and obesity resistance. Am J Physiol 253:R475–R481
Anderson EA, Hoffman RP, Balon TW, Sinkey CA, Mark AL (1991) Hyperinsulinemia produces both sympathetic neural activation and vasodilation in normal humans. J Clin Invest 87:2246–2252
Jyotsna VP, Sahoo A, Sreenivas V, Deepak KK (2009) Prevalence and pattern of cardiac autonomic dysfunction in newly detected type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 83:83–88
Morisco C, Lembo G, Trimarco B (2006) Insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk: new insights from molecular and cellular biology. Trends Cardiovasc Med 16:183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2006.03.008
Mangmool S, Denkaew T, Parichatikanond W, Kurose H (2017) β-adrenergic receptor and insulin resistance in the heart. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 25:44–56. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2016.128
Marsh SA, Powell PC, Agarwal A, Dell’Italia LJ, Chatham JC (2007) Cardiovascular dysfunction in Zucker obese and Zucker diabetic fatty rats: role of hydronephrosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H292–H298
Marsh SA, Dell’italia LJ, Chatham JC (2009) Interaction of diet and diabetes on cardiovascular function in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296:H282–H292
Thackeray JT, Radziuk J, Harper ME et al (2011) Sympathetic nervous dysregulation in the absence of systolic left ventricular dysfunction in a rat model of insulin resistance with hyperglycemia. Cardiovasc Diabetol 10:75
Sellers DJ, Chess-Williams R (2001) The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on cardiac beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in the rat. J Auton Pharmacol 21:15–21
Rengo G, Pagano G, Paolillo S et al (2015) Impact of diabetes mellitus on lymphocyte GRK2 protein levels in patients with heart failure. Eur J Clin Invest 45:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.12395
Uriel N, Gonzalez-Costello J, Mignatti A, Morrison KA1, Nahumi N, Colombo PC, Jorde UP (2013) Adrenergic activation, fuel substrate availability, and insulin resistance in patients with congestive heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 1:331–337
Ciccarelli M, Chuprun JK, Rengo G, Gao E, Wei Z, Peroutka RJ, Gold JI, Gumpert A, Chen M, Otis NJ, Dorn GW II, Trimarco B, Iaccarino G, Koch WJ (2011) G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 activity impairs cardiac glucose uptake and promotes insulin resistance after myocardial ischemia. Circulation 123:1953–1962
Santulli G, Pagano G, Sardu C, Xie W, Reiken S, D’Ascia SL, Cannone M, Marziliano N, Trimarco B, Guise TA, Lacampagne A, Marks AR (2015) Calcium release channel RyR2 regulates insulin release and glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest 125:1968–1978. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI79273
Wang Q, Liu Y, Fu Q, Xu B, Zhang Y, Kim S, Tan R, Barbagallo F, West T, Anderson E, Wei W, Abel ED, Xiang YK (2017) Inhibiting insulin-mediated β2-adrenergic receptor activation prevents diabetes-associated cardiac dysfunction. Circulation 135:73–88. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022281
Pfeifer MA, Weinberg CR, Cook DL, Renan A, Halter JB, Ensinck JW, Porte D Jr (1984) Autonomic neural dysfunction in recently diagnosed diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 7:447–453
Taskiran M, Rasmussen V, Rasmussen B, Fritz-Hansen T, Larsson HB, Jensen GB, Hilsted J (2004) Left ventricular dysfunction in normotensive Type 1 diabetic patients: the impact of autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Med 21:524–530
Pop-Busui R, Kirkwood I, Schmid H, Marinescu V, Schroeder J, Larkin D, Yamada E, Raffel DM, Stevens M (2004) Sympathetic dysfunction in type 1 diabetes: association with impaired myocardial blood flow reserve and diastolic dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:2368–2374
Guarino D, Nannipieri M, Iervasi G, Taddei S, Bruno RM (2017) The role of the autonomic nervous system in the pathophysiology of obesity. Front Physiol 8:665. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00665
Sardu C, Santamaria M, Funaro S, Sacra C, Barbieri M, Paolisso P, Marfella R, Paolisso G, Rizzo MR (2017) Cardiac electrophysiological alterations and clinical response in cardiac resynchronization therapy with a defibrillator treated patients affected by metabolic syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e6558. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000006558
Sardu C, Carreras G, Katsanos S, Kamperidis V, Pace MC, Passavanti MB, Fava I, Paolisso P, Pieretti G, Nicoletti GF, Santulli G, Paolisso G, Marfella R (2014) Metabolic syndrome is associated with a poor outcome in patients affected by outflow tract premature ventricular contractions treated by catheter ablation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 14:176. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2261-14-176
Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, Parfrey P, Pfeffer M, Raij L, Spinosa DJ, Wilson PW, American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention, American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention (2003) Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 108:2154–2169
Ishii M, Ikeda T, Takagi M, Kimura K, Atarashi K, Uehara Y, Matsuoka H, Murao S (1983) Elevated plasma catecholamines in hypertensives with primary glomerular diseases. Hypertension 5:545–551
Converse RL Jr, Jacobsen TN, Toto RD, Jost CM, Cosentino F, Fouad-Tarazi F, Victor RG et al (1992) Sympathetic overactivity in patients with chronic renal failure. N Engl J Med 327:1912–1918
Hausberg M, Kosch M, Harmelink P, Barenbrock M, Hohage H, Kisters K, Dietl KH, Rahn KH (2002) Sympathetic nerve activity in end-stage renal disease. Circulation 106:1974–1979
Campese VM, Kogosov E, Koss M (1995) Renal afferent denervation prevents the progression of renal disease in the renal ablation model of chronic renal failure in the rat. Am J Kidney Dis 26:861–865
Costa F, Diedrich A, Johnson B, Sulur P, Farley G, Biaggioni I (2001) Adenosine, a metabolic trigger of the exercise pressor reflex in humans. Hypertension 37:917–922
Ding Y, Kim S, Lee SY, Koo JK, Wang Z, Choi ME (2014) Autophagy regulates TGF-β expression and suppresses kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2835–2846. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2013101068
Di Lullo L, Rivera R, Barbera V, Bellasi A, Cozzolino M, Russo D, De Pascalis A, Banerjee D, Floccari F, Ronco C (2016) Sudden cardiac death and chronic kidney disease: from pathophysiology to treatment strategies. Int J Cardiol 217:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.04.170 (review)
Oikawa K, Ishihara R, Maeda T, Yamaguchi K, Koike A, Kawaguchi H, Tabata Y, Murotani N, Itoh H (2009) Prognostic value of heart rate variability in patients with renal failure on hemodialysis. Int J Cardiol 131:370–377
Kamal FA, Travers JG, Schafer AE, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Blaxall BC (2017) G protein-coupled receptor-G-protein βγ-subunit signaling mediates renal dysfunction and fibrosis in heart failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 28:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2015080852
Chan CT, Shen XS, Picton P, Floras J (2008) Nocturnal home hemodialysis improves baroreflex effectiveness index of end-stage renal disease patients. J Hypertens 26:1795–1800
Underwood CF, Hildreth CM, Wyse BF, Boyd R, Goodchild AK, Phillips JK (2017) Uraemia: an unrecognized driver of central neurohumoral dysfunction in chronic kidney disease? Acta Physiol (Oxf) 219:305–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12727
Liu ZZ, Bullen A, Li Y, Singh P (2017) Renal oxygenation in the pathophysiology of chronic kidney disease. Front Physiol 8:385. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00385
Cheong HI, Asosingh K, Stephens OR, Queisser KA, Xu W, Willard B, Hu B, Dermawan JK, Stark GR, Naga Prasad SV, Erzurum SC (2016) Hypoxia sensing through β-adrenergic receptors. JCI Insight 1:e90240. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90240
Weinrauch LA, D’Elia JA, Gleason RE, Keough J, Mann D, Kennedy FP (1995) Autonomic function in type I diabetes mellitus complicated by nephropathy. A cross-sectional analysis in the presymptomatic phase. Am J Hypertens 8:782–789
Hansen HP, Rossing P, Tarnow L, Nielsen FS, Jensen BR, Parving HH (1996) Circadian rhythm of arterial blood pressure and albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 50:579–585
Monteagudo PT, Nóbrega JC, Cezarini PR, Ferreira SR, Kohlmann O Jr, Ribeiro AB, Zanella MT (1996) Altered blood pressure profile, autonomic neuropathy and nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Eur J Endocrinol 135:683–688
Nielsen FS, Hansen HP, Jacobsen P, Rossing P, Smidt UM, Christensen NJ, Pevet P, Vivien-Roels B, Parving HH (1999) Increased sympathetic activity during sleep and nocturnal hypertension in type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Diabet Med 16:555–562
Weinrauch LA, Kennedy FP, Gleason RE, Keough J, D’Elia JA (1998) Relationship between autonomic function and progression of renal disease in diabetic proteinuria: clinical correlations and implications for blood pressure control. Am J Hypertens 11(Pt 1):302–308
Giordano M, Manzella D, Paolisso G, Caliendo A, Varricchio M, Giordano C (2001) Differences in heart rate variability parameters during the post-dialytic period in type II diabetic and non-diabetic ESRD patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl 16:566–573
Meinhold JA, Maslowska-Wessel E, Bender R, Sawicki PT (2001) Low prevalence of cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetic patients without nephropathy. Diabet Med 18:607–613
Luippold G, Beilharz M, Mühlbauer B (2004) Chronic renal denervation prevents glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetic rats. Nephrol Dial Transpl 19:342–347
Yao Y, Davis G, Harrison JC, Walker RJ, Sammut IA (2016) Renal functional responses in diabetic nephropathy following chronic bilateral renal denervation. Auton Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2016.09.019
Strojek K, Grzeszczak W, Górska J, Leschinger MI, Ritz E (2001) Lowering of microalbuminuria in diabetic patients by a sympathicoplegic agent: novel approach to prevent progression of diabetic nephropathy? J Am Soc Nephrol 12:602–605
Yasuda G, Hasegawa K, Kuji T, Ogawa N, Shimura G, Umemura S, Tochikubo O (2005) Effects of doxazosin on ambulatory blood pressure and sympathetic nervous activity in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. Diabet Med 22:1394–1400
Aritomi S, Niinuma K, Ogawa T, Konda T, Nitta K (2013) Additive effects of cilnidipine and angiotensin II receptor blocker in preventing the progression of diabetic nephropathy in diabetic spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Nephrol 17:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0677-4
Yasuda G, Saka S, Ando D, Hirawa N (2015) Effects of doxazosin as the third agent on morning hypertension and position-related blood pressure changes in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Hypertens 37:75–81. https://doi.org/10.3109/10641963.2014.913599
Ohno S, Yokoi H, Mori K, Kasahara M, Kuwahara K, Fujikura J, Naito M, Kuwabara T, Imamaki H, Ishii A, Saleem MA, Numata T, Mori Y, Nakao K, Yanagita M, Mukoyama M (2016) Ablation of the N-type calcium channel ameliorates diabetic nephropathy with improved glycemic control and reduced blood pressure. Sci Rep 6:27192. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27192
Kiuchi MG, Chen S, Graciano ML, de Queiroz Carreira MA, Kiuchi T, Andrea BR et al (2015) Acute effect of renal sympathetic denervation on blood pressure in refractory hypertensive patients with chronic kidney disease. Int J Cardiol 190:29–31
Ott C, Mahfoud F, Schmid A, Toennes SW, Ewen S, Ditting T et al (2015) Renal denervation preserves renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease and resistant hypertension. J Hypertens 33:1261–1266
Hering D, Marusic P, Duval J, Sata Y, Head GA, Denton KM, Burrows S, Walton AS, Esler MD, Schlaich MP (2017) Effect of renal denervation on kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Int J Cardiol 232:93–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.01.047
Yao Y, Davis G, Harrison JC, Walker RJ, Sammut I (2017) Renal functional responses in diabetic nephropathy following chronic bilateral renal denervation. Auton Neurosci 204:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2016.09.019
Brunström M, Eliasson M, Nilsson PM, Carlberg B (2017) Blood pressure treatment levels and choice of antihypertensive agent in people with diabetes mellitus: an overview of systematic reviews. J Hypertens 35:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000001183
Hart PD, Bakris GL (2007) Should beta-blockers be used to control hypertension in people with chronic kidney disease? Semin Nephrol 27:555–564
Funding
G. Rengo was supported by the Ministry of Health (Italy) Grant Number GR-2011-02346878 and by San Paolo Bank of Naples and University of Naples Federico II—STAR Program 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GR and KK contributed to the review conception and design. KK, GM F, CdL, AC and LB conducted the literature searches and reviewed the identified articles. AC and GC provided critical analysis. DL and NF revised the manuscript for intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komici, K., Femminella, G.D., de Lucia, C. et al. Predisposing factors to heart failure in diabetic nephropathy: a look at the sympathetic nervous system hyperactivity. Aging Clin Exp Res 31, 321–330 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-018-0973-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-018-0973-2