Abstract
Background
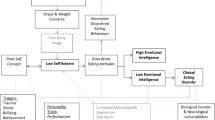
Prior research indicates that deficits in emotional abilities are key predictors of the onset and maintenance of eating disorders (ED). As a relatively new emotion-related construct, emotional intelligence (EI) comprises a set of basic emotional abilities. Preliminary research suggests that deficits in EI are linked with disordered eating and other impulsive behaviours. Also, previous research reveals that emotional and socio-cognitive abilities, as well as ED symptomatology, varies across lifespan development. However, while the findings suggest promising results for the development of potential effective treatments for emotional deficits and disordered eating, it is difficult to summarise the relationship between EI and ED due to the diversity of theoretical approaches and variety of EI and ED measures.
Objective
Our study, therefore, aimed to systematically review the current evidence on EI and ED in both the general and clinical populations and across different developmental stages.
Methods
The databases examined were Medline, PsycInfo and Scopus, and 15 eligible articles were identified. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were used.
Results
All the studies reviewed indicated negative associations between EI and the dimensions of ED. Additionally, several mechanisms involved, namely adaptability, stress tolerance and emotional regulation were highlighted.
Conclusion
The systematic review suggests promising but challenging preliminary evidence of the associations between EI and the dimensions of ED across diverse stages of development. In addition, future research, practical implications and limitations are discussed.
Level of evidence I
Systematic review.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Macht M (2008) How emotions affect eating: a five-way model. Appetite 50(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2007.07.002
Ekman P (1992) An argument for basic emotions. Cogn Emot 6:169–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699939208411068
Frijda N (1993) Moos, emotion episodes, and emotions. Handbook of emotions. Guilford Press, London, pp 381–403
Polivy J, Herman CP (1993) Etiology of binge eating: psychological mechanisms. Guilford Press, London
Agras W, Telch C (1998) The effects of caloric deprivation and negative affect on binge eating in obese binge-eating disordered women. Behav Ther 29:491–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-7894(98)80045-2
Mayer JD, Salovey P, Caruso D (2000) Models of emotional intelligence. In: Sternberg RJ (ed) Handbook of Intelligence. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 396–420. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511807947.019
Bar-On R (2000) Emotional and social intelligence: Insights from the emotional quotient inventory. In: Bar-On R, Parker JDA (eds) Handbook of Emotional Intelligence. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, pp 363–388
Boyatzis R, Goleman D, Rhee K (2000) Clustering competence in emotional intelligence: Insights from the emotional competence inventory (ECI). In: Bar-On R, Parker JDA (eds) Handbook of Emotional Intelligence. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, pp 343–362
Goleman D (1995) Inteligencia emocional. Kairós, Barcelona
Bar-On R (1997) The emotional quotient inventory (EQ-I): technical manual. Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
Mayer JD, Salovey P (1997) What is emotional intelligence? In: Salovey P, Sluyter D (eds) Emotional development and emotional intelligence: implications for educators. Basic Books, New York, pp 3–31
Salovey P (2007) Prologo. In: Mestre y JM, Fernández-Berrocal P (eds) Manual de Inteligencia Emocional. Pirámide, Madrid, pp 17–19
Peña-Sarrionandia A, Mikolajczak M, Gross JJ (2015) Integrating emotion regulation and emotional intelligence traditions: a meta-analysis. Front. Psychol 6:160. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00160
McRae K, Gross JJ (2020) Emotion regulation. Emotion 20(1):1
Bar-On, R (2006) The Bar-On model of emotional-social intelligence (ESI). Psicothema, 18, supl., 13-25
Cabello R, Sorrel MA, Fernández-Pinto I, Extremera N, Fernández-Berrocal P (2016) Age and gender differences in ability emotional intelligence in adults: a cross-sectional study. Dev Psychol 52(9):1486
Keefer KV, Holden RR, Parker JDA (2013) Longitudinal assessment of trait emotional intelligence: measurement invariance and construct continuity from late childhood to adolescence. Psychol Assess 25(4):1255–1272. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033903
Pons F, Harris P, de Rosnay M (2004) Emotion comprehension between 3 and 11 years: developmental periods and hierarchical organization. Eur J Develp Phychol 1:127–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405620344000022
Denham SA (2007) Dealing with feelings: how children negotiate the worlds of emotions and social relationships. Cognit Brain Behav 11(1):1–48
Saeki E, Watanabe Y, Kido M (2015) Developmental and gender trends in emotional literacy and interpersonal competence among Japanese children. Int J Emot Educ 7:15–35
Waxman SE (2009) A systematic review of impulsivity in eating disorders. Eur Eat Disord Rev 17:408–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.952
Hartmann A, Zeeck A, Barrett MS (2010) Interpersonal problems in eating disorders. Int J Eat Disord 43:619–627. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20747
Hsu L (1990) Experiential aspects of bulimia nervosa—implications for cognitive behavioral-therapy. Behav Modificat 14(1):50–65. https://doi.org/10.1177/01454455900141004
Perry JA, Silvera DH, Neilands TB, Rosenvinge JH, Hanssen T (2008) A study of the relationship between parental bonding, self-concept and eating disturbances in Norwegian and American college populations. Eat Behav 9(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2007.01.007
Ridout N, Wallis DJ, Autwal Y, Sellis J (2012) The influence of emotional intensity on facial emotion recognition in disordered eating. Appetite 59(1):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2012.04.013
Stein KF, Corte C (2007) Identity impairment and the eating disorders: content and organization of the self-concept in women with anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Eur Eat Disord Rev 15(1):58–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.726
Connors M, Johnson C (1987) Epidemiology of bulimia and bulimic behaviors. Addict Behav 12(2):165–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(87)90023-2
Fox JR, Powe MJ (2009) Eating disorders and multi-level models of emotion: an integrated model. Clin Psychol Psychother 16:240–267. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.626
Goldner E, Srikameswaran S, Schroede M, Livesley W, Birmingham C (1999) Dimensional assessment of personality pathology in patients with eating disorders. Psychiatry Res 85(2):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-1781(98)00145-0
Stice E, Shaw H (2004) Eating disorder prevention programs: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull 130:206–227. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.130.2.206
Ross M, Wade T (2004) Shape and weight concern and self-esteem as mediators of externalized self-perception, dietary restraint and uncontrolled eating. Eur Eat Disord Rev 12(2):129–136. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.531
Neumark-Sztainer DR, Wall MM, Haines JI, Story MT, Sherwood NE, Van den Berg PA (2007) Shared risk and protective factors for overweight and disordered eating in adolescents. Am J Prev Med 33(5):359–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2007.07.031
Muris P, Meesters C, Blom W, Mayer B (2005) Biological, psychological, and sociocultural correlates of body change strategies and eating problems in adolescent boys and girls. Eat Behav 6(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2004.03.002
Bravender T, Bryant-Waugh R, Herzog D, Katzman D, Kreipe RD, Lask B et al (2007) Classification of child and adolescent eating disturbances. Workgroup for Classification of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents (WCEDCA). Int J Eat Disord 40:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20458
Christian C, Perko VL, Vanzhula IA, Tregarthen JP, Forbush KT, Levinson CA (2020) Eating disorder core symptoms and symptom pathways across developmental stages: a network analysis. J Abnorm Psychol 129(2):177–190. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000477
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009(339):b2535. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2535
Garner DM, Garfinkel PE (1979) The eating attitudes test: an index of the symptoms of anorexia nervosa. Psychol Med 9(2):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291700030762
Garner DM, Olmsted MP, Bohr Y, Garfinkel PE (1982) The Eating Attitudes Test: psychometric features and clinical correlates. Psychol Med 12:871–878. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291700049163
Thelen MH, Farmer J, Wonderlic S, Smith M (1991) A revision of the bulimia test: the BULIT-R. Psychol Assess 3(1):119–124. https://doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.3.1.119
Thelen MH, Mintz LB, Vander Wal JS (1996) The bulimia test-revised: validation with DSM-IV criteria for bulimia nervosa. Psychol Assess 8:219–221. https://doi.org/10.1037//1040-3590.3.1.119
Praeger S (2005) Emotional eating, Part I [Hebrew] Tel Aviv. United Books, Israel
Fairburn CG, Beglin SJ (1994) Assessment of eating disorder psychopathology: interview or self-report questionnaire? Int J Eating Disord 16(4):363–370
Berg KC, Peterson CB, Frazier P, Crow SJ (2012) Psychometric evaluation of the eating disorder examination and eating disorder examination-questionnaire: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Eat Disord 45(3):428–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20931
Stice E, Telch CF, Rizvi SL (2000) Development and validation of the Eating Disorder Diagnostic Scale: a brief self-report measure of anorexia, bulimia, and binge-eating disorder. Psychol Assess 12(2):123–131. https://doi.org/10.1037//1040-3590.12.2.123
Garner DM (1991) Eating disorder inventory-2 manual. Psychological Assessment Recourses Inc, Odessa
Tapper K, Pothos EM (2010) Development and validation of a Food Preoccupation Questionnaire. Eat Behav 11(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2009.09.003
Millon T (2004) MACI. Inventario Clínico para Adolescentes de Millon. Manual. TEA, Madrid
Millon T (1993) Manual of millon adolescent clinical inventory. NCS, Minneapolis
Garner DM (2004) Eating disorder inventory 3 (EDI-3). Professional manual. Odessa. Psychological Assessment Resources, Fl
Sheehan DV, Sheehan KH, Shytle RD, Janavs J, Bannon Y, Rogers JE et al (2010) Reliability and validity of the mini international neuropsychiatric interview for children and adolescents (MINI-KID). J Clin Psychiatry 71(3):313–326. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.09m05305whi
Wardle J, Guthrie CA, Sanderson S, Rapoport L (2001) Development of the children’s eating behaviour questionnaire. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 42(7):963–970. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00792
Bar-on R (1997) The emotional quotient inventory (EQ-i): a test of emotional intelligence. Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
Bar-on R (2002) Bar-on EQ-i: S technical manual. Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
Bar-on R, Parker JDA (2000) Bar-On Emotional Quotient Inventory (youth version): technical manual. Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
Salovey P, Mayer JD, Goldman SL, Turvey C, Palfai TP (1995) Emotional attention, clarity, and repair: exploring emotional intelligence using the Trait Meta-Mood Scale. In: Pennebaker JW (ed) Emotion. Disclosure and health. American Psychological Association, Washington, pp 125–151
Wong CS, Law KS (2002) The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitudes. Leadersh Q 13(3):243–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1048-9843(02)00099-1
Li T, Saklofske DH, Bowden SC, Yan G, Fung TS (2012) The measurement invariance of the wong and law emotional intelligence scale (WLEIS) across three Chinese university student groups from Canada and China. J Psychoeduc Assess 30(4):439–452. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734282912449449
Schutte NS, Malouff JM, Hal LE, Haggerty DJ, Cooper JT, Golden CJ et al (1998) Development and validation of a measure of emotional intelligence. Pers Individ Differ 25(2):167–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(98)00001-4
Zysberg L, Levy A, Zisberg A (2011) Emotional intelligence in applicant selection for care-related academic programs. J Psychoeduc Assess 29(1):27–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734282910365059
Tett RP, Fox KE, Wang A (2005) Development and validation of a self-report measure of emotional intelligence as a multidimensional trait domain. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 31(7):859–888. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167204272860
Salovey P, Mayer J (1990) Emotional intelligence. Imagin Cogn Pers 9(3):185–211. https://doi.org/10.2190/DUGG-P24E-52WK-6CDG
Mayer JD, Caruso DR, Salovey P (1999) Emotional intelligence meets traditional standards for an intelligence. Intelligence 27:267–298
Mayer JD, Salovey P, Caruso DR (2002) Mayer-salovey-caruso emotional intelligence Test (MSCEIT): user’s manual. Multi-Health Systems Inc, Toronto. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-2896(99)00016-1
Mayer JD, Salovey P, Caruso DR (2004) Emotional intelligence: theory, findings, and implications. Psychol Inquiry. 15(3):197–215. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327965pli1503_02
Petrides KV, Sangareau Y, Farnham A, Frederickson N (2006) Trait emotional intelligence and children’s peer relations at school. Soc Dev 15(3):537–547. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.2006.00355.x
Lundqvist D, Flykt A, Öhman A (1998) The Karolinska Directed Emotional Faces-KDEF. CD ROM from Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Psychology section. Karolinska Institute, Solna
Goeleven E, De Raedt R, Leyman L, Verschuere B (2008) The Karolinska directed emotional faces: a validation study. Cognit Emot 22(6):1094–1118. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699930701626582
Costarelli V, Demerzi M, Stamou D (2009) Disordered eating attitudes in relation to body image and emotional intelligence in young women. J Hum Nutr Diet 22(3):239–245. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-277X.2009.00949.x
Zysberg L, Rubanov A (2010) Emotional intelligence and emotional eating patterns: a new insight into the antecedents of eating disorders? J Nutr Educ Behav 42(5):345–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneb.2009.08.009
Foye U, Hazlett DE, Irving P (2019) Exploring the role of emotional intelligence on disorder eating. Eat Weight Disord 24(2):299–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0629-4
Lane AM, Meyer BB, Devonport TJ, Davies KA, Thelwell R, Gil GS et al (2009) Validity of the emotional intelligence scale for use in sport. J Sport Sci Med 8:289–295
Zysberg L, Tell E (2013) Emotional intelligence, perceived control, and eating disorders. SAGE Open 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244013500285
Zysberg L (2013) Emotional intelligence, personality, and gender as factors in disordered eating patterns. J Health Psychol 19(8):1035–1042. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105313483157
Gardner KJ, Quinton S, Qualter P (2014) The role of trait and ability emotional intelligence in bulimic symptoms. Eat Behav 15(2):237–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2014.02.002
Hambrook D, Brown G, Tchanturia K (2012) Emotional intelligence in anorexia nervosa: is anxiety a missing piece of the puzzle? Psychiatry Res 200:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2012.05.017
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112:155–159
Markey MA, Vander Wal JS (2007) The role of emotional intelligence and negative affect in bulimic symptomatology. Compr Psychiat 48(5):458–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2007.05.006
Filaire E, Larue J, Rouvieux M (2010) Eating behaviours in relation to emotional intelligence. Int J Sports Med 32(4):309–315. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1269913
Pettit ML, Jacobs SC, Page KS, Porras CV (2009) An assessment of perceived emotional intelligence and eating attitudes among college students. Am J Health Educ 41(1):46–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/19325037.2010.10599126
Li Y (2018) Social anxiety and eating disorder risk among Chinese adolescents: the role of emotional intelligence. Sch Ment Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-018-9257-4
Zavala MA, López I (2012) Adolescentes en situación de riesgo psicosocial ¿Qué papel juega la inteligencia emocional? Behav Psychol 20(1):59–75
Peres V, Corcos M, Robin M, PhamScottez A (2018) Emotional intelligence, empathy and alexithymia in anorexia nervosa during adolescence. Eat Weight Disord. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0482-5
Cuesta C, González I, García LM (2017) The role of trait emotional intelligence in body dissatisfaction and eating disorder symptoms in preadolescents and adolescents. Pers Individ Differ 126:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.12.021
Koch A, Pollatos O (2015) Reduced facial emotion recognition in overweight and obese children. J Psychosomat Res 79(6):635–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2015.06.005
Wisniewski L, Kelly E (2003) The application of dialectical behavior therapy to the treatment of eating disorders. Cogn Behav Pract 10:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1077-7229(03)80021-4
Arlt J, Yiu A, Eneva K, Dryman MT, Heimberg RG, Chen EY (2016) Contributions of cognitive inflexibility to eating disorder and social anxiety symptoms. Eat Behav 21:30–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2015.12.008
Ciarma JL, Mathew JM (2017) Social anxiety and disordered eating: the influence of stress reactivity and self-esteem. Eat Behav 26:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2017.03.011
Diehl NS, Johnson CE, Rogers RL, Petrie TA (1998) Social physique anxiety and disordered eating: what’s the connection? Addict Behav 23(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4603(97)00003-8
Hinrichsen H, Wright F, Waller G, Meyer C (2003) Social anxiety and coping strategies in the eating disorders. Eat Behav 4(2):117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1471-0153(03)00016-3
Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL (2012) Social anxiety and eating disorder comorbidity: the role of negative social evaluation fears. Eat Behav 13(1):27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2011.11.006
Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL (2016) Clarifying the prospective relationships between social anxiety and eating disorder symptoms and underlying vulnerabilities. Appetite 107:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.07.024
Linardon J, Braithwaite R, Cousins R, Brennan L (2017) Appearance-based rejection sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between symptoms of social anxiety and disordered eating cognitions and behaviors. Eat Behav 27:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2017.10.003
Wonderlich-Tierney AL, Vander Wal JS (2010) The effects of social support and coping on the relationship between social anxiety and eating disorders. Eat Behav 11(2):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2009.10.002
Bydlowski S, Corcos M, Jeammet P, Paternity S, Berthoz S, Laurier C et al (2005) Emotion-processing deficits in eating disorders. Int J Eat Disord 37(4):321–329. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20132
Kessler H, Schwarze M, Filipic S, Traue HC, Wietersheim J (2006) Alexithymia and facial emotion recognition with eating disorders. Int J Eating Disord 39(3):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20228
Henderson NJ, Huon GF (2002) Negative affect and binge eating in overweight women. Br J Health Psychol 7:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1348/135910702169376
Johnson SJ, Batey M, Holdsworth L (2009) Personality and health: the mediating role of trait emotional intelligence and work locus of control. Pers Individ Differ 47:470–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2009.04.025
Salovey P, Hsee CK, Mayer JD (1993) Emotional intelligence and the self-regulation of affect. In: Wegner D, Pennebaker JW (eds) Handbook of mental control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood cliffs NJ, pp 258–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have No conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies performed by any of the authors involving human participants or animals.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The article is part of the Topical Collection on Personality and Eating and Weight Disorders.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romero-Mesa, J., Peláez-Fernández, M.A. & Extremera, N. Emotional intelligence and eating disorders: a systematic review. Eat Weight Disord 26, 1287–1301 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-020-00968-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-020-00968-7