Abstract
Background
Eating disorders (EDs) are associated with a reduced ability to regulate emotion and impulses during the life span. Working memory and executive functions (EFs) are cognitive regulatory systems supported by networks involving the pre-frontal cortex. Studies in EDs found impaired functioning in these domains, showing an association between EDs and the reduced ability to control emotions and impulses.
Objective
To investigate EF in adolescents and young women with eating disorders (ED) using a quasi-experimental design, focusing on cognitive efficiency, emotional regulation (ER) and behavioural outcomes also taking into account pharmacological treatment and duration of illness.
Methods
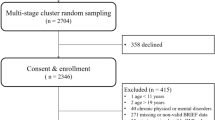
A sample of 151 females belonging to two groups took part in this study. Twenty-six girls and young women (Mage 22;8 years) with ED and 125 typically developed girls and young women (Mage 17;4 years) completed a battery of cognitive tasks (Go–no-go, Stop-signal task, Symmetry span, Reading Span) and the Youth Self-Report and the Difficulties in Emotional Regulation Scale Performance. A series of ANOVA with the Brown–Forsythe test was used to compare the groups.
Results
Participants with ED and controls did not show significant differences in EF tasks, whereas differences between younger and older participants with ED emerged. Moreover, ER difficulties seem to be associated with mainly internalizing problems in EDs. Further analysis on the full ED sample did not reveal any significant differences associated with the disorder persistence. Considering pharmacological treatment effects over cognitive, emotional and behavioural measures emerged.
Conclusions
The present study documented no specific differences in EF between control and participants with EDs, whereas important differences emerged in ER and behavioural outcomes perception in the clinical sample, together with a partial influence of pharmacological treatment.
Level of evidence
No level of evidence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischer S, Munsch S (2012) Self-regulation in eating disorders and obesity—implications for treatment. Verhaltenstherapie 22:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1159/000341540
van Elburg A, Treasure J (2013) Advances in the neurobiology of eating disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 26:556–561. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0b013e328365a2e7
van Zutphen L, Maier S, Siep N, Jacob GA, Tüscher O, Tebartz van Elst L, Zeeck A, Arntz A, O’Connor M-F, Stamm H, Hudek M, Joos A (2018) Intimate stimuli result in fronto-parietal activation changes in anorexia nervosa. Eat Weight Disord 24:1155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-017-0474-x
Donofry SD, Roecklein KA, Wildes JE, Miller MA, Erickson KI (2016) Alterations in emotion generation and regulation neurocircuitry in depression and eating disorders: a comparative review of structural and functional neuroimaging studies. Neurosci BiobehavRev 68:911–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.07.011
Nyman-Carlsson E, Birgegård A, Engström I, Gustafsson SA, Nevonen L (2019) Predictors of outcome among young adult patients with anorexia nervosa in a randomised controlled trial. Eur Eat Disorders Rev 27(1):76–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2630
Giedd JN, Blumenthal J, Jeffries NO, Castellanos FX, Liu H, Zijdenbos A, Paus T, Evans AC, Rapoport L (1999) Brain development during childhood and adolescence: a longitudinal MRI study. Nat Neurosci 2:861–863. https://doi.org/10.1038/13158
Miyake A, Friedman NP, Emerson MJ, Witzki AH, Howerter A, Wager TD (2000) The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: a latent variable analysis. Cogn Psychol 41:49–100. https://doi.org/10.1006/cogp.1999.0734
Malagoli C, Usai MC (2018) The effects of gender and age on inhibition and working memory organization in 14- to 19-year-old adolescents and young adults. Cog Dev 45:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogdev.2017.10.005
Huizinga M, Dolan CV, Van der Molen MW (2006) Age-related change in executive function. Developmental trends and latent variable analysis. Neuropsychologia 44:2017–2036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.01.010
Finn AS, Kraft MA, West MR, Leonard JA, Bish CE, Martin RE (2014) Cognitive skills, student achievement tests, and schools. Psychol Sci 25:736–744. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613516008
Romer D, Betancourt L, Giannetta JM, Brodsky NL, Farah M, Hurt H (2009) Executive cognitive functions and impulsivity as correlates of risk taking and problem behavior in pre-adolescents. Neuropsychologia 47:2916–2926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.06.019
Vitaro F, Ferland F, Jacques C, Ladouceur R (1998) Gambling, substance use, and impulsivity during adolescence. Psychol Addict Behav 12:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.12.3.185
Fikke LT, Melinder A, Landro NI (2011) Executive functions are impaired in adolescents engaging in non suicidal self injury. Psychol Med 41:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291710001030
Wu M, Hartmann M, Skunde M, Herzog W, Friederich HC (2013) Inhibitory control in bulimic-type eating disorders. A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083412
Darcy AM, Fitzpatrick KK, Manasse SM, Datta N, Klabunde M, Colborn D, Aspen V, Stiles-Shields C, Labuschagne Z, Le Grange D, Lock J (2015) Central coherence in adolescents with bulimia nervosa spectrum eating disorders. Int J Eat Disord 48:487–493. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22340
Lopez C, Tchanturia K, Stahl D, Treasure J (2009) Weak central coherence in eating disorders: a step towards looking for an endophenotype of eating disorders. J Clin ExpNeuropsychol 31(1):117–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803390802036092
Roberts ME, Tchanturia K, Stahl D, Southgate L, Treasure J (2007) A systematic review and meta-analysis of set-shifting ability in eating disorders. Psychol Med 37:1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291707009877
Kanakam N, Treasure J (2013) A review of cognitive neuropsychiatry in the taxonomy of eating disorders State, trait, or genetic? Cogn Neuropsychiatry 18:83–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/13546805.2012.682362
Brockmeyer T, Skunde M, Wu M, Bresslein E, Rudofsky G, Herzog W, Friederich HC (2014) Difficulties in emotion regulation across the spectrum of eating disorders. Compr Psychiatry 55:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2013.12.001
McClelland MM, Ponitz CC, Messersmith E, Tominey S (2010) Self-regulation: the integration of cognition and emotion. In: Lerner R (Series Ed) & Overton W (Vol Ed), Handbook of life-span development (Vol 1: Cognition, biology and methods, pp 509–553). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley
Demirci E (2018) Non suicidal self-injury, emotional eating and insomnia after child sexual abuse: Are those symptoms related to emotion regulation? J Forensic Leg Med 53:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jflm.2017.10.012
Rosenstein LK, Ellison WD, Walsh E, Chelminski I, Dalrymple K, Zimmerman M (2018) The role of emotion regulation difficulties in the connection between childhood emotional abuse and borderline personality features. Personal Disord 9(6):590–594. https://doi.org/10.1037/per0000294
Brockmeyer T, Pellegrino J, Maier C, Münch HM, Harmer CJ, Walther S, Herzog W, Friederich HC (2019) Blunted emotion-modulated startle reflex in anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord 52(3):270–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.23022
Foye U, Hazlett DE, Irving P (2019) Exploring the role of emotional intelligence on disorder eating psychopathology. Eat Weight Disord 24:299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0629-4
Laghi F, Bianchi D, Pompili S, Lonigro A, Baiocco R (2018) Metacognition, emotional functioning and binge eating in adolescence: the moderation role of need to control thoughts. Eat Weight Disord 23(6):861–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0603-1
Oldershaw A, Lavender T, Sallis H, Stahl D, Schmidt U (2015) Emotion generation and regulation in anorexia nervosa: a systematic review and meta-analysis of self-report data. Clin Psychol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2015.04.005
Segal A, Golan M (2016) Differences in emotion regulation along the eating disorder spectrum: cross sectional study in adolescents out patient care. J Psychol Clin Psychiatry 6(1):00314. https://doi.org/10.15406/jpcpy.2016.06.00314
Stice E (2002) Risk and maintenance factors for eating pathology: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull 128:825–848. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.128.5.825
Whiteside U, Chen E, Neighbors C, Hunter D, Lo T, Larimer M (2007) Difficulties regulating emotion: do binge eaters have fewer strategies to modulate and tolerate negative affect? Eat Behav 8:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2006.04.001
Aldao A, Nolen-Hoeksema S, Schweizer S (2010) Emotion-regulation strategies across psychopathology: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev 30:217–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2009.11.004
Goossens L, Van Malderen E, Van Durme K, Braet C (2016) Loss of control eating in adolescents: associations with adaptive and maladaptive emotion regulation strategies. Eat Behav 22:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2016.06.015
Adambegan M, Wagner G, Nader IW, Fernandez-Aranda F, Treasure J, Karwautz A (2012) Internalizing and externalizing behaviour problems in childhood contribute to the development of anorexia and bulimia nervosa—a study comparing sister pairs. Eur Eat Disord Rev 20:116–120. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.1152
Malagoli C, Usai MC (2018) WM in adolescence: What is the relationship with emotional regulation and behavioral outcomes? Front Psychol 9:844. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00844
Logan GD (1994) On the ability to inhibit thought and action: a user’s guide to the stop signal paradigm. In: Dagenbach D, Carr TH (eds) Inhibitory processes in attention, memory, and language. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 189–239
Verbruggen F, Logan GD (2008) Response inhibition in the stop-signal paradigm. Trends Cogn Sc 12:418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2008.07.005
Donders FC (1969) On the speed of mental processes. Acta Psycho 30:12–431
Hare TA, Tottenham N, Davidson MC, Glove GH, Casey BJ (2005) Contributions of amygdala and striatal activity in emotion regulation. Biol Psychiatry 57:624–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.12.038
Kane MJ, Hambrick DZ, Tuholski SW, Wilhelm O, Payne TW, Engle RW (2004) The generality of working memory capacity: a latent-variable approach to verbal and visuospatial memory span and reasoning. J Exp Psychol Gen 133:189–217. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.133.2.189
Daneman M, Carpenter PA (1980) Individual differences in working memory and reading. J Verbal Learning Verbal Behav 19:450–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5371(80)90312-6
Giromini L, Velotti P, de Campora G, Bonalume L, Zavattini GC (2012) Cultural adaptation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale: reliability and validity of an Italian version. J Clin Psychol 68:989–1007. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.21876
Achenbach T (2001) YSL ages 11-18, ASEBA, University of Vermont (USA). Italian version by A Frigerio (ed.)
Riniolo TC (1999) Using a large control group for statistical comparison: evaluation of a between-groups median test. J Exp Educ 68(1):75–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220979909598495
Del Pozo A, Harbeck S, Zahn S, Kliem S, Kröger C (2018) Cognitive distortions in anorexia nervosa and borderline personality disorder. Psychiatry Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.11.043
Johnston J, Shu CY, Hoiles KJ, Patrick JF, Clarke PJF, Watson HJ, Dunlop PD, Egan SJ (2018) Perfectionism is associated with higher eating disorder symptoms and lower remission in children and adolescents diagnosed with eating disorders. Eat Behav 30:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2018.05.008
Katterman SN, Kleinman BM, Hood MM, Nackers LM, Corsica JA (2014) Mindfulness meditation as an intervention for binge eating, emotional eating, and weight loss: a systematic review. Eat Behav 15:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2014.01.005
Doba K, Berna G, Constant E, Nandrino JL (2018) Self-differentiation and eating disorders in early and middle adolescence: a cross-sectional path analysis. Eat Behav 29:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2018.03.003
Kaye WH, Frank GK, Bailer UF, Henry SE (2005) Neurobiology of anorexia nervosa: clinical implications of alterations of the function of serotonin and other neuronal systems. Int J Eat Disord 37:S15–S19. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20109
Di Bernardo M, Barciulli E, Ricca V, Mannucci E, Moretti S, Cabras PL, Rotella CM (1998) Binge eating scale in obese patients: validation of the Italian version. Minerva Psichiatr 39:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-011-0537-4
Cuzzolaro M, Vetrone G, Marano GF, Battacchi MW (1999) BUT: una nuova scala per la valutazione del disagio relativo all’immagine del corpo. Psichiatria dell’Infanzia e dell’adolescenza 66:417–428
Cuzzolaro M, Vetrone G, Marano G, Garfinkel P (2006) The Body Uneasiness Test (BUT): development and validation of a new body image assessment scale. Eat Weight Disord 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03327738
Calugi S, Sartirana M, Milanese C, El Ghoch M, Riolfi F, Dalle-Grave R (2018) The clinical impairment assessment questionnaire: validation in Italian patients with eating disorders. Eat Weight Disord 23:685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0477-
Garner DM, Olmsted MP, Polivy J (1983) Development and validation of a multidimensional EDI for anorexia nervosa and bulimia. Int J Eat Disord 2:15–34
Giannini M, Pannocchia L, Dalle Grave R, Muratori F (2008) Viglione V EDI-3 eating disorder inventory-3: manuale. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Bressi C, Taylor G, Parker J, Bressi S, Brambilla V, Aguglia E, Invernizzi G (1996) Cross validation of the factor structure of the 20-item toronto alexithymia scale: an Italian multicenter study. J Psychosom Res 41(6):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(96)00228-0
Sarno I, Preti E, Prunas A, Madeddu F (2011) SCL-90-R Symptom Checklist-90-R Adattamento italiano Firenze: Giunti, Organizzazioni Speciali
Funding
This work was supported by a doctoral grant and a research fellowship awarded to Chiara Malagoli by the University of Genoa and Accademia Ligure di Scienze e Lettere, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee (Ethical Code of Italian Psychology Order and the Ethical Guidelines of the Italian Association of Psychology) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. At the time we collected the data, no ethical committee was yet present to which we could refer to in our organization.
Informed consent
Informed written consent was obtained from the participants or their parents if they were minor before data collection.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malagoli, C., Cerro, P.F., Vecchiato, C. et al. Cognitive and emotional regulation in adolescents and young women with eating disorders. Eat Weight Disord 26, 375–383 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-020-00859-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-020-00859-x