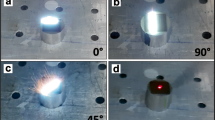
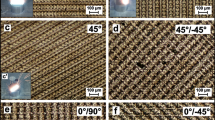
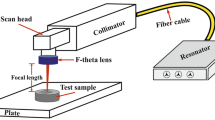
Abstract
This study investigated the surface properties of the laser-textured Ti-6Al-4V alloy. A nanosecond laser engraving device was used for laser engraving applications. An experimental setup was built using six basic process control parameters at different levels, namely hatching strategy, power, scan speed, frequency, line spacing, and pulse width. Textured surfaces were subjected to surface roughness and wettability testing. The results revealed that contact angle increases with a decrease in laser power and an increase in scan speed, frequency, and line spacing. The most influential parameter on the contact angle was found to be line spacing with a 27% impact rate; however, the contact angle was similarly affected by scan speed, power, and pulse width. Among 18 textured surfaces tested, three were found to display hydrophobic behavior, and their contact angles were 116°, 112°, and 109°, and the roughness values of surfaces giving those angles were 1.34, 2.44 and 2.25 µm, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tur K (2009) Biomaterials and tissue engineering for regenerative repair of articular cartilage defects. Turk J Rheumatol 24:206–217
Katti KS (2004) Biomaterials in total joint replacement. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 39(3):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2003.12.002
Ben-Nissan B, Pezzotti G (2004) Bioceramics: an introduction. Engineering materials for biomedical applications. World Scientific Publishing, New Jersey, pp 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812562227_0006
Machtei EE, Frankenthal S, Levi G, Elimelech R, Shoshani E, Rosenfeld O, Tagger-Green N, Shlomi B (2012) Treatment of peri-implantitis using multiple applications of chlorhexidine chips: a double-blind, randomized multi-centre clinical trial. Clin Periodontol 39(12):1198–1205. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12006
Abdal-hay A, Staples R, Alhazaa A, Fournier B, Al-Gawati M, Lee RSB, Ivanovski S (2022) Fabrication of micropores on titanium implants using femtosecond laser technology: perpendicular attachment of connective tissues as a pilot study. Opt Laser Technol 148:107624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107624
Niinomi M (2002) Recent metallic materials for biomedical applications. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 33(3):477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0109-2
Huiskes RI, Weinans H, Van Rietbergen B (1992) The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin Orthop Relat Res 274:124–134
Liu X, Chu PK, Ding C (2004) Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 47(3):49–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2004.11.001
Long M, Rack HJ (1998) Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—a materials science perspective. Biomaterials 19(18):1621–1639. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(97)00146-4
Wang K (1996) The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 213(1):134–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(96)10243-4
Tiainen L, Abreu P, Buciumeanu M, Silva F, Gasik M, Serna Guerrero R, Carvalho O (2019) Novel laser surface texturing for improved primary stability of titanium implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 98:26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.04.052
Minagar S, Wang J, Berndt CC, Ivanova EP, Wen C (2013) Cell response of anodized nanotubes on titanium and titanium alloys. J Biomed Mater Res A 101A(9):2726–2739. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.34575
Zhang W, Li Z, Huang Q, Xu L, Li J, Jin Y, Wang G, Liu X, Jiang X (2013) Effects of a hybrid micro/nanorod topography-modified titanium implant on adhesion and osteogenic differentiation in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Nanomed 8:257–265. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S39357
Pattanayak S, Sahoo AK, Routray R, Sahoo SK (2021) Micro engraving on Ti-6Al-4V using fiber laser for orthopedic implant-A study. Opt Fiber Technol 67:102745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2021.102745
Yu Z, Yin S, Zhang W, Jiang X, Hu J (2020) Picosecond laser texturing on titanium alloy for biomedical implants in cell proliferation and vascularization. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 108(4):1494–1504. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.34497
Wang Y, Zhang M, Li K, Hu J (2021) Study on the surface properties and biocompatibility of nanosecond laser patterned titanium alloy. Opt Laser Technol 139:106987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.106987
Raimbault O, Benayoun S, Anselme K, Mauclair C, Bourgade T, Kietzig A-M, Girard-Lauriault P-L, Valette S, Donnet C (2016) The effects of femtosecond laser-textured Ti-6Al-4V on wettability and cell response. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 69:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.072
Eghbali N, Naffakh-Moosavy H, Sadeghi Mohammadi S, Naderi-Manesh H (2021) The influence of laser frequency and groove distance on cell adhesion, cell viability, and antibacterial characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V dental implants treated by modern fiber engraving laser. Dent Mater 37(3):547–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2020.12.007
Huerta-Murillo D, García-Girón A, Romano JM, Cardoso JT, Cordovilla F, Walker M, Dimov SS, Ocaña JL (2019) Wettability modification of laser-fabricated hierarchical surface structures in Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Appl Surf Sci 463:838–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.09.012
Lawrence J, Hao L, Chew HR (2006) On the correlation between Nd:YAG laser-induced wettability characteristics modification and osteoblast cell bioactivity on a titanium alloy. Surf Coat Technol 200(18):5581–5589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.07.107
Zheng Q, Mao L, Shi Y, Fu W, Hu Y (2020) Biocompatibility of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy implants with laser microgrooved surfaces. Mater Technol 37(12):2039–2048. https://doi.org/10.1080/10667857.2020.1816011
Menci G, Demir AG, Waugh DG, Lawrence J, Previtali B (2019) Laser surface texturing of β-Ti alloy for orthopaedics: effect of different wavelengths and pulse durations. Appl Surf Sci 489:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.111
Wang X, Zheng H, Wan Y, Feng W, Lam YC (2018) Picosecond laser surface texturing of a stavax steel substrate for wettability control. Engineering 4(6):816–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.10.006
Peraire C, Arias JL, Bernal D, Pou J, León B, Arañó A, Roth W (2006) Biological stability and osteoconductivity in rabbit tibia of pulsed laser deposited hydroxylapatite coatings. J Biomed Mater Res A 77A(2):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.30556
Riveiro A, Maçon ALB, del Val J, Comesaña R, Pou J (2018) Laser surface texturing of polymers for biomedical applications. Front Phys 6:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2018.00016
Elias CN, Oshida Y, Lima JHC, Muller CA (2008) Relationship between surface properties (roughness, wettability and morphology) of titanium and dental implant removal torque. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 1(3):234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2007.12.002
Leone C, Genna S, Tagliaferri F (2020) Multiobjective optimisation of nanosecond fiber laser milling of 2024 T3 aluminium alloy. J Manuf Process 57:288–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.026
Banat D, Ganguly S, Meco S, Harrison P (2020) Application of high power pulsed nanosecond fibre lasers in processing ultra-thin aluminium foils. Opt Laser Eng 129:106075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106075
Jasim HA, Demir AG, Previtali B, Taha ZA (2017) Process development and monitoring in stripping of a highly transparent polymeric paint with ns-pulsed fiber laser. Opt Laser Technol 93:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.01.031
Wang Y, Zhao X, Ke C, Yu J, Wang R (2020) Nanosecond laser fabrication of superhydrophobic Ti6Al4V surfaces assisted with different liquids. Colloid Interface Sci Commun 35:100256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100256
Li C, Zhang J, Han J, Yao B (2021) A numerical solution to the effects of surface roughness on water–coal contact angle. Sci Rep 11(1):459. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80729-9
Ryan BJ, Poduska KM (2008) Roughness effects on contact angle measurements. Am J Phys 76(11):1074–1077. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.2952446
Wang J, Wu Y, Cao Y, Li G, Liao Y (2020) Influence of surface roughness on contact angle hysteresis and spreading work. Colloid Polym Sci 298(8):1107–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04680-x
Kulkarni M, Patil-Sen Y, Junkar I, Kulkarni CV, Lorenzetti M, Iglič A (2015) Wettability studies of topologically distinct titanium surfaces. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 129:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.03.024
Yang Z, Tian YL, Yang CJ, Wang FJ, Liu XP (2017) Modification of wetting property of Inconel 718 surface by nanosecond laser texturing. Appl Surf Sci 414:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.050
Li B-j, Li H, Huang L-j, Ren N-f, Kong X (2016) Femtosecond pulsed laser textured titanium surfaces with stable superhydrophilicity and superhydrophobicity. Appl Surf Sci 389:585–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.137
Pang M, Liu X, Liu K (2017) Effect of wettability on the friction of a laser-textured cemented carbide surface in dilute cutting fluid. Adv Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814017738154
Arcot Y, Samuel GL, Kong L (2022) Manufacturability and surface characterisation of polymeric microfluidic devices for biomedical applications. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121(5):3093–3110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09505-5
Riveiro A, Abalde T, Pou P, Soto R, del Val J, Comesaña R, Badaoui A, Boutinguiza M, Pou J (2020) Influence of laser texturing on the wettability of PTFE. Appl Surf Sci 515:145984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145984
Milne AJB, Amirfazli A (2012) The Cassie equation: how it is meant to be used. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 170(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.12.001
Palanivel R, Dinaharan I, Laubscher RF (2017) Microstructure evolution and mechanical characterization of Nd:YAG laser beam welded titanium tubes. Mater Charact 134:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2017.10.025
Manninen M, Hirvimäki M, Poutiainen I, Salminen A (2015) Effect of pulse length on engraving efficiency in nanosecond pulsed laser engraving of stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans B 46(5):2129–2136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0415-x
Prakash C, Kansal HK, Pabla BS, Puri S (2016) Multi-objective optimization of powder mixed electric discharge machining parameters for fabrication of biocompatible layer on β-Ti alloy using NSGA-II coupled with Taguchi based response surface methodology. J Mech Sci Technol 30(9):4195–4204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-016-0831-0
Dongre G, Rajurkar A, Raut R, Jangam S (2021) Preparation of super-hydrophobic textures by using nanosecond pulsed laser. Mater Today Proc 42:1145–1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.497
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by Dokuz Eylul University under project no. 2021.KB.FEN.043. The authors would like to acknowledge this financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Technical Editor: Izabel Fernanda Machado.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kasman, Ş., Uçar, İ.C. & Ozan, S. Investigation into the effects of laser texturing parameters on surface properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI biomedical alloy. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 45, 231 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-023-04165-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-023-04165-2