Abstract
Aim
This was to evaluate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of Portland cement (PC) added to radiopacifying agents in primary molar pulpotomies.
Methods
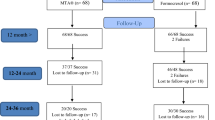
Thirty primary mandibular molars of children aged between 5 and 9 years were randomly assigned to the following groups: PC; PC with iodoform (PC + CHI3); PC with zirconium oxide (PC + ZrO2) and treated by pulpotomy technique. Clinical and radiographic follow-up assessments were performed at 6, 12 and 24 months. Statistical analysis was performed by Fisher’s exact test (P < 0.05).
Results
The clinical and radiographic evaluations showed 100 % success rates, and the results showed no statistically significant difference between groups.
Conclusions
According to this study, PC added to radiopacifying agents exhibited satisfactory clinical and radiographic results in primary molar pulpotomies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANSI/ADA Specification no 57—endodontic sealing material. American Dental Association. 2000.
Blanchard S, Boynton J. Current pulp therapy options for primary teeth. J Mich Dent Assoc. 2010;92:40–1.
Bortoluzzi EA, Guerreiro-Tanomaru JM, Tanomaru-Filho M, Duarte MA. Radiographic effect of different radiopacifiers on a potential retrograde filling material. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108:628–32.
Camilleri J, Cutajar A, Maallia B. Hydration characteristics of zirconium oxide replaced Portland cement for use as a root-end filling material. Dent Mater. 2011;27:845–54.
Camilleri J. Evaluation of the physical properties of an endodontic Portland cement incorporating alternative radiopacifiers used as root-end filling material. Int Endod J. 2010;43:231–40.
Coomaraswamy KS, Lumley PJ, Hofmann MP. Effect of bismuth oxide radiopacifier content on the material properties of an endodontic Portland cement-based (MTA-like) system. J Endod. 2007;33:295–8.
Coutinho-Filho T, De-Deus G, Klein L, et al. Radiopacity and histological assessment of Portland cement plus bismuth oxide. Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106:e69–77.
Cutajar A, Mallia B, Abela S, Camilleri J. Replacement of radiopacifier in mineral trioxide aggregate; characterization and determination of physical properties. Dent Mater. 2011;27:879–91.
Fernandes AP, Lourenço Neto N, Marques NCT, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of the use of low level laser therapy in vital pulp of primary teeth. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2014. doi:10.1111/ipd.12115.
Gomes Cornélio AL, Salles LP, Campos da Paz M, et al. Cytotoxicity of Portland cement with different radiopacifying agents: a cell death study. J Endod. 2011;37:203–10.
Hungaro Duarte MA, de Oliveira El, Kadre GD, et al. Radiopacity of Portland cement associated with different radiopacifying agents. J Endod. 2009;35:737–40.
Hungaro Duarte MA, Minotti PG, Rodrigues CT, et al. Effect of different radiopacifying agents on the physicochemical properties of white Portland cement and white mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod. 2012;38:394–7.
International Organization for Standardization ISO 6876. Dental root sealing materials. Geneva: Switzerland; 2001. pp. 1–10.
Kim EC, Lee BC, Chang HS, et al. Evaluation of the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of Portland cements containing bismuth oxide. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105:54–7.
Koçak S, Erten H, Baris E, Türk S, Alaçam T. Evaluation of the biocompatibility of experimentally manufactured Portland cement: an animal study. J Clin Exp Dent. 2014;6:17–21.
Lee SJ, Chung J, Na HS, et al. Characteristics of novel root-end filling material using epoxy resin and Portland cement. Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17:1009–15.
Lin PY, Chen HS, Wang YH, Tu YK. Primary molar pulpotomy: a systematic reviw and network meta-analysis. J Dent. 2014;42:1060–77.
Lourenço Neto N, Marques NCT, Fernandes AP, et al. Biocompatibility of Portland cement associated with different radiopacifying agents. J Oral Sci. 2014;56:29–34.
Marciano MA, Costa RM, Camilleri J, et al. Assessment of color stability of white mineral trioxide aggregate angelus and bismuth oxide in contact with tooth structure. J Endod. 2014;40:1235–40.
Morais CA, Bernardineli N, Garcia RB, Duarte MA, Guerisoli DM. Evaluation of tissue response to MTA and Portland cement with iodoform. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102:417–21.
Moretti AB, Sakai VT, Oliveira TM, et al. The effectiveness of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium hydroxide and formocresol for pulpotomies in primary teeth. Int Endod J. 2008;41:547–55.
Oliveira TM, Moretti ABS, Sakai VT, et al. Clinical, radiographic and histologic analysis of the effects of pulp capping materials used in pulpotomies of human primary teeth. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2013;14:65–71.
Parirokh M, Torabinejad M. Mineral trioxide aggregate: a comprehensive literature review—part III: clinical applications, drawbacks, and mechanism of action. J Endod. 2010;36:400–13.
Petrou MA, Alhamoi FA, Welk A, Altarabulsi M, Splieth CH. A randomized clinical trial on the use of medical Portland cement, MTA and calcium hydroxide in indirect pulp treatment. Clin Oral Investig. 2014;18:1383–9.
Ribeiro DA, Hungaro Duarte MA, Matsumoto MA, Marques ME, Salvador DM. Biocompatibility in vitro tests of mineral trioxide aggregate and regular and white Portland cements. J Endod. 2005;31:605–7.
Roberts HW, Toth JM, Berzins DW, Charlton DG. Mineral trioxide aggregate material use in endodontic treatment: a review of the literature. Dent Mater. 2008;24:149–64.
Sakai VT, Moretti AB, Oliveira TM, et al. Pulpotomy of human primary molars with MTA and Portland cement: a randomised controlled trial. Br Dent J. 2009;207:128–39.
Seale NS, Coll JA. Vital pulp therapy for the primary dentition. Gen Dent. 2010;58:194–200.
Weckwerth PH, Machado AC, Kuga MC, et al. Influence of radiopacifying agents on the solubility, pH and antimicrobial activity of Portland cement. Braz Dent J. 2012;23:515–20.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support—FAPESP (process #2009/11284-4) and all the patients and families who helped us carry out this study. The authors would like to thank Gentília Borges Carvalho Tavares, Lilian Rosana Candida and Maria Estela Alves de Lima Ferrari for excellent assistance. This study was funded by Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP Grant Number 2009/11284-4).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lourenço Neto, N., Marques, N.C.T., Fernandes, A.P. et al. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of Portland cement added to radiopacifying agents in primary molar pulpotomies. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 16, 377–382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-015-0177-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-015-0177-9