Abstract
Aim
To compare the clinical, radiographic and histological responses of the pulp to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), calcium hydroxide (CH) and Portland cement (PC) when used as a pulpotomy agent in human primary teeth.
Study design
Forty-five mandibular primary molar teeth were randomly assigned to CH, MTA or PC groups and treated by pulpotomy technique.
Methods
The teeth were treated by conventional pulpotomy technique, differing only in the capping material for each group. Clinical and radiographic evaluations were recorded at 6-, 12- and 24-month follow-up. Teeth in the regular exfoliation period were further processed for histologic analysis.
Statistics
Data were tested using parametric tests at a significance level of 5 %. The histological results were expressed descriptively.
Results
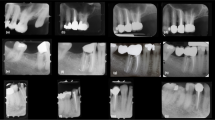
Clinically and radiographically, the MTA and PC groups showed 100 % success rates at 6, 12 and 24 months. In CH group, several teeth presented clinical and radiographic failures detected throughout the follow-up period, and internal resorption was a frequent radiographic finding. Histologic analysis revealed the presence of dentine-like mineralised material deposition obliterating the root canal in the PC and MTA groups. CH group presented, in most of the sections, necrotic areas in the root canals.
Conclusions
MTA and PC may serve as effective materials for pulpotomies of primary teeth as compared to CH. Although our results are very encouraging, further studies and longer follow-up assessments are needed in order to determine the safe clinical indication of Portland cement.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeinehchi M, Dadvand S, Fayazi S, Bayat-Movahed S. Randomized controlled trial of mineral trioxide aggregate and formocresol for pulpotomy in primary molar teeth. Int Endod J. 2007;40:261–7.
Ansari G, Ranjpour M. Mineral trioxide aggregate and formocresol pulpotomy of primary teeth: a 2-year follow-up. Int Endod J. 2010;43:413–8.
Cardoso-Silva C, Barbería E, Maroto M, García-Godoy F. Clinical study of mineral trioxide aggregate in primary molars. Comparison between grey and white MTA-a long term follow-up (84 months). J Dent. 2011;39:187–93.
Chacko V, Kukirose S. Human pulpal response to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA): a histologic study. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2006;30:203–10.
Conti TR, Sakai VT, Fornetti AP, et al. Pulpotomies with Portland cement in human primary molars. J Appl Oral Sci. 2009;17:66–9.
De-Deus G, Coutinho Filho T. The use of white Portland cement as an apical plug in a tooth with a necrotic pulp and wide-open apex: a case report. Int Endod J. 2007;40:653–60.
Erdem AP, Guven Y, Balli B, et al. Success rates of mineral trioxide aggregate, ferric sulfate, and formocresol pulpotomies: a 24-month study. Pediatr Dent. 2011;33:165–70.
Fuks AB. Pulpotomy in primary teeth. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2006;7:124.
Fuks AB, Papagiannoulis L. Pulpotomy in primary teeth: review of the literature according to standardized criteria. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2006;7:64–71.
Holan G, Eidelman E, Fuks AB. Long-term evaluation of pulpotomy in primary molars using mineral trioxide aggregate or formocresol. Pediatr Dent. 2005;27:129–36.
Holland R, de Souza V, Murata SS, et al. Healing process of dog dental pulp after pulpotomy and pulp covering with mineral trioxide aggregate or Portland cement. Braz Dent J. 2001;12:109–13.
Islam I, Chng HK, Yap AUJ. Comparison of the physical and mechanical properties of MTA and Portland cement. J Endod. 2006;32:193–7.
Maroto M, Barberia E, Planells P, Garcia Godoy F. Dentin bridge formation after mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) pulpotomies in primary teeth. Am J Dent. 2005;18:151–4.
Menezes R, Bramante CM, Letra A, Carvalho VGG, Garcia RB. Histologic evaluation of pulpotomies in dog using two types of mineral trioxide aggregate and white Portland cements as wound dressings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;98:376–9.
Min KS, Kim HI, Park HJ, et al. Human pulp cells response to Portland cement in vitro. J Endod. 2007;33:163–6.
Moretti AB, Sakai VT, Oliveira TM, et al. Effectiveness of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium hydroxide and formocresol for pulpotomies in primary teeth. Int Endod J. 2008;41:547–55.
Nair PN, Duncan HF, Pitt Ford TR, Luder HU. Histological, ultrastructural and quantitative investigations on the response of healthy human pulps to experimental capping with mineral trioxide aggregate: a randomized controlled trial. Int Endod J. 2008;41:128–50.
Ni Chaollai A, Monteiro J, Duggal MS. The teaching of management of the pulp in primary molars in Europe: a preliminary investigation in Ireland and the UK. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2009;10:98–103.
Ng FK, Messer LB. Mineral trioxide aggregate as a pulpotomy medicament: an evidence-based assessment. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2008;9:58–73.
Odabaş ME, Alaçam A, Sillelioğlu H, Deveci C. Clinical and radiographic success rates of mineral trioxide aggregate and ferric sulphate pulpotomies performed by dental students. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2012;13:118–22.
Qudeimat MA, Barrieshi-Nusair KM, Owais AI. Calcium hydroxide vs mineral trioxide aggregates for partial pulpotomy of permanent molars with deep caries. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2007;8:99–104.
Parirokh M, Torabinejad M. Mineral trioxide aggregate: a comprehensive literature review—Part III: clinical applications, drawbacks, and mechanism of action. J Endod. 2010;36:400–13.
Salako N, Joseph B, Ritwik P, et al. Comparison of bioactive glass, mineral trioxide aggregate, ferric sulfate and formocresol as pulpotomy agents in rat molar. Dent Traumatol. 2003;19:314–20.
Sakai VT, Moretti AB, Oliveira TM, et al. Pulpotomy of human primary molars with MTA and Portland cement: a randomised controlled trial. Br Dent J. 2009;8:128–9.
Seale NS, Coll JA. Vital pulp therapy for the primary dentition. Gen Dent. 2010;58:194–200.
Shahi S, Rahimi S, Yavari HR, et al. Effect of mineral trioxide aggregates and Portland cements on inflammatory cells. J Endod. 2010;36:899–903.
Simancas-Pallares MA, Díaz-Caballero AJ, Luna-Ricardo LM. Mineral trioxide aggregate in primary teeth pulpotomy. A systematic literature review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010;15:942–6.
Song JS, Mante FK, Romanow WJ, Kim S. Chemical analysis of powder and set forms of Portland cement, gray ProRoot MTA, white ProRoot MTA, and gray MTA-Angelus. Oral Sur Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102:809–15.
Steffen R, van Waes H. Understanding mineral trioxide aggregate/Portland-cement: a review of literature and background factors. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2009;10:93–7.
Waterhouse PJ, Nunn JH, Withworth JM, Soames JV. Primary molar pulp therapy—histological evaluation of failure. Int J Pediatr Dent. 2000;10:313–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, T.M., Moretti, A.B.S., Sakai, V.T. et al. Clinical, radiographic and histologic analysis of the effects of pulp capping materials used in pulpotomies of human primary teeth. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 14, 65–71 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-013-0015-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-013-0015-x