Abstract
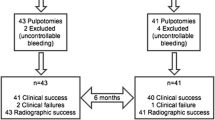
Aim: To prospectively compare the clinical success rate of partial pulpotomy treatment in permanent molars using calcium hydroxide (CH) and mineral trioxide aggregates (MTA) as pulp dressing agents. Methods: Restorable permanent first molars (64) with carious pulp exposures were randomly assigned to two groups; CH and MTA. A standardized operative procedure was followed in both groups. Following isolation and caries removal, the exposed superficial pulp tissue layers were removed with a sterile flame shape diamond bur to a depth of 2–4 mm. Bleeding was controlled and pulp dressed with either a paste of non-setting Ca(OH)2 followed by a setting layer of Ca(OH)2, or with grey MTA. The dressing materials in both groups were then covered with a layer of light cured glass ionomer cement. The teeth were either restored using amalgam, or where grossly carious with preformed metal crowns. Patients were scheduled for follow-up at 3, 6, 12 months and annually thereafter. Results: There were 34 patients (17 males and 17 females) with 51 teeth available for evaluation. The age of patients at the time of restoration ranged between 6.8 to 13.3 years (mean of 10.3 ±1.8 years). The follow-up period ranged from 25.4 to 45.6 months with an average of 34.8 ± 4.4 months. There was no statistically significant difference in the success rate of teeth treated with CH (91%) in comparison to teeth treated with MTA (93%). Radiographically, a hard tissue barrier under CH was noticed in 12 (55%) teeth compared with 18 (64%) teeth under MTA (p=0.4). Conclusions: MTA has clinical success rate comparable to CH as a pulp dressing material for partial pulpotomy in permanent molars with carious exposures
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeinehchi M, Eslami B, Ghanbariha M, Saffar AS. Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and calcium hydroxide as pulp-capping agents in human teeth: a preliminary report. Int Endod J 2003;36:225–31.
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Clinical Affairs Committee-Pulp Therapy Subcommittee; American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Council on Clinical Affairs. Guideline on pulp therapy for primary and young permanent teeth. Pediatr Dent 2005–2006;27 (Reference Manual):130-4.
Baratieri LN, Monteiro S Jr, Caldeira de Andrada MA. Pulp curettage-surgical technique. Quintessence Int 1989;20:285–93.
Barrieshi-Nusair KM, Qudeimat MA. A prospective clinical study of mineral trioxide aggregate for partial pulpotomy in cariously exposed permanent teeth. J Endod 2006;32:731–5.
Barthel CR, Rosenkranz B, Leuenberg A, Roulet JF. Pulp capping of carious exposures: treatment outcome after 5 and 10 years: a retrospective study. J Endod 2000;26:525–8.
Bergenholtz G, Spangberg L. Controversies in endodontics. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 2004;15:99–114.
Briso AL, Rahal V, Mestrener SR, Dezan Junior E. Biological response of pulps submitted to different capping materials. Braz Oral Res 2006;20:219–25.
Camilleri J, Pitt Ford TR. Mineral trioxide aggregate: a review of the constituents and biological properties of the material. Int Endod J 2006;39:747–54.
Camp JH, Barrett EJ, Pulver F. Pediatric Endodontics: Endodontic treatment for the primary and young permanent dentition; in Cohen S, Burns R.C. (eds): Pathway of the pulp. 8th ed. Mosby, Inc, St. Loius, Missouri; 2002. p.823–33.
Carrotte P. Endodontic treatment for children. Br Dent J 2005;198:9–15.
Chacko V, Kurikose S. Human pulpal response to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA): a histologic study. J Clint Pediatr Dent 2006;30:203–9.
Cox CF, Bergenholtz G, Heys DR, et al. Pulp capping of dental pulp mechanically exposed to oral microflora: a 1–2 year observation of wound healing in the monkey. J Oral Pathol 1985;14:156–68.
Cox CF. Microleakage related to restorative procedures. Proc Finn Dent Soc 1992;88:83–93.
de Lourdes Rodrigues Accorinte M, Reis A, et al. Influence of rubber dam isolation on human pulp responses after capping with calcium hydroxide and an adhesive system. Quintessence Int 2006;37:205–12.
Ettinger RL, Kambhu PP, Asmussen CM, Damiano PC. An in vitro evaluation of the integrity of stainless steel crown margins cemented with different luting agents. Spec Care Dentist 1998;18:78–83.
Faraco IM Jr, Holland R. Response of the pulp of dogs to capping with mineral trioxide aggregate or a calcium hydroxide cement. Dent Traumatol 2001;17:163–6.
Fong CD, Davis MJ. Partial pulpotomy for immature permanent teeth, its present and future. Pediatr Dent 2002;24:29–32.
Ford TR, Torabinejad M, McKendry DJ, Hong CU, Kariyawasam SP. Use of mineral trioxide aggregate for repair of furcal perforations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1995;79:756–63.
Ford TR, Torabinejad M, Abedi HR, Bakland LK, Kariyawasam SP. Using mineral trioxide aggregate as a pulp-capping material. J Am Dent Assoc 1996;127:1491–4.
Fridland M, Rosado R. MTA solubility: a long term study. J Endod 2005;31:376–9.
Holland R, de Souza V, Nery MJ, et al. Reaction of rat connective tissue to implanted dentin tubes filled with mineral trioxide aggregate or calcium hydroxide. J Endod 1999;25:161–6.
Holland R, de Souza V, Murata SS, et al. Healing process of dog dental pulp after pulpotomy and pulp covering with mineral trioxide aggregate or Portland cement. Braz Dent J 2001;12:109–13.
Islam I, Chng HK, Yap AU. X-ray diffraction analysis of mineral trioxide aggregate and Portland cement. Int Endod J 2006;39:220–5.
Iwamoto CE, Adachi E, Pameijer CH, et al. Clinical and histological evaluation of white ProRoot MTA in direct pulp capping. Am J Dent 2006;19:85–90.
Langeland K. Tissue response to dental caries. Endod Dent Traumatol 1987;3:149–71.
Lee ES. A new mineral trioxide aggregate root-end filling technique. J Endod 2000;26:764–5.
Martin FE. Carious pulpitis: microbiological and histopathological considerations. Aust Endod J 2003;29:134–7.
Mass E, Zilberman U. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of partial pulpotomy in carious exposure of permanent molars. Pediatr Dent 1993;15:257–9.
Massler M. Therapy conductive to healing of the human pulp. Oral Surg 1972;34:122–30.
Mejare I, Cvek M. Partial pulpotomy in young permanent teeth with deep carious lesions. Endod Dent Traumatol 1993;9:238–42.
Myers K, Kaminski E, Lautenschlager E, Miller D. The effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on the dog pulp. J Endod 1996;22:198.
Nosrat IV, Nosrat CA. Reparative hard tissue formation following calcium hydroxide application after partial pulpotomy in cariously exposed pulps of permanent teeth. Int Endod J 1998;31:221–6
Olsson H, Petersson K, Rohlin M. Formation of a hard tissue barrier after pulp cappings in humans. A systematic review. Int Endod J 2006;39:429–42.
Schuurs AH, Gruythuysen RJ, Wesselink PR. Pulp capping with adhesive resin-based composite vs. calcium hydroxide: a review. Endod Dent Traumatol. 2000;16:240–50.
Silva AF, Tarquinio SB, Demarco FF, et al. The influence of haemostatic agents on healing of healthy human dental pulp tissue capped with calcium hydroxide. Int Endod J 2006;39:309–16.
Stanley H. Calcium hydroxide and vital pulp therapy; in: Harygreaves K and Goodis H.E. (eds):Seltzer and Bender’s Dental Pulp. Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc Carol Stream, IL; 2002. p.309–24.
Subay RK, Suzuki S, Suzuki S, et al. Human pulp response after partial pulpotomy with two calcium hydroxide products. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1995;80:330–7.
Takita T, Hayashi M, Takeichi O, et al. Effect of mineral trioxide aggregate on proliferation of cultured human dental pulp cells. Int Endod J 2006;39:415–22.
Torabinejad M, Watson TF, Pitt Ford TR. Sealing ability of a mineral trioxide aggregate when used as a root end filling material. J Endod 1993;19:591–5.
Torabinejad M, Hong CU, McDonald F, Pitt Ford TR. Physical and chemical properties of a new root-end filling material. J Endodont 1995;21:349–53.
Torabinejad M, Pitt Ford TR, McKendry DJ, et al. Histologic assessment of mineral trioxide aggregate as a root-end filling in monkeys. J Endod 1997;23:225–8.
Tziafas D, Smith AJ, Lesot H. Designing new treatment strategies in vital pulp therapy. J Dent 2000;28:77–92.
Tziafas D, Pantelidou O, Alvanou A, et al. The dentinogenic effect of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) in short-term capping experiments. Int Endod J 2002;35:245–54.
Wu MK, Kontakiotis EG, Wesselink PR. Long-term seal provided by some root-end filling materials. J Endod. 1998;24:557–60.
Zander HA. Reaction of the pulp to calcium hydroxide. J Dent Res 1939;18:373–79.
Zilberman U, Mass E, Sarnat H. Partial pulpotomy in carious permanent molars. Am J Dent 1989;2:147–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qudeimat, M.A., Barrieshi-Nusair, K.M. & Owais, A.I. Calcium Hydroxide vs. Mineral Trioxide Aggregates for Partial Pulpotomy of Permanent Molars with Deep Caries. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 8, 99–104 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262577
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262577