Abstract
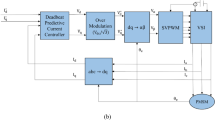
This paper describes the development of a state-of-the-art controller for induction motor drive to achieve smooth speed control under its different running conditions. The controller adopts indirect field-oriented control (IFOC) scheme for precise estimation of equivalent circuit parameters (ECPs) to generate PWM signals. The challenges for estimation of ECPs during the running condition due to change in motor temperature as well as the sudden change in its loading are dealt with a model reference adaptive system (MRAS) controller. The H–G diagram method-based reference model is utilized to estimate the reference ECPs without performing any physical tests of the motor. The backpropagation algorithm with an artificial neural network (BPANN) is utilized in its plant model while the weight and gain parameters of this model are tuned based on reference ECPs. The AdaDelta rule is utilized for fast convergence of the BPANN weights during starting conditions while stator temperature and other feedback enhance the overall performance with increased accuracy in ripple-free speed regulation. The results from MATLAB-based simulation and a hardware prototype controller using a DSPIC microcontroller with different running conditions show the efficacy of the proposed algorithm.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
In this work, no data have been taken from the internet. The machine specifications that have been utilized are present in the laboratory of our department.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
AdaDelta optimizer
- AI:
-
Artificial intelligence
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- ASD:
-
Adjustable speed drive
- BPANN:
-
Backpropagation artificial neural network
- CNN:
-
Convolution neural network
- DSP:
-
Digital signal processing
- ECPs :
-
Equivalent circuit parameters
- EKF:
-
Extended Kalman’s filter
- FLC:
-
Fuzzy logic controller
- FOC:
-
Field-oriented control
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
- GD:
-
Gradient descent method
- GNN:
-
Graphical neural networks
- GSA:
-
Gravitational search algorithm
- GUI:
-
Graphical user interface
- IFOC:
-
Indirect field-oriented control
- IM:
-
Induction motor
- LSTM:
-
The long short-term memory
- MMU:
-
Machine monitoring unit
- MRAS:
-
Model reference adaptive structure
- NN:
-
Neural network
- PSD:
-
Phase-sensitive detector
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- PT:
-
Physical test
- PWM:
-
Pulse width modulation
- RNN:
-
Recurrent neural network
- V s :
-
Rated stator voltage
- I s :
-
Rated stator current
- I nl :
-
No-load current
- ψ nl :
-
No-load flux
- V an, V bn, V cn :
-
Instantaneous phase voltages of IM
- N r :
-
Rated speed
- P out, P rcl, P scl, P nl :
-
Rated power, Rotor copper loss, Stator copper-loss, No-load power
- f, s :
-
Frequency, slip
- p f , p fnl :
-
Power factor rated, power factor at no load
- T :
-
Temperature at start
- T e :
-
Electromechanical torque
- v ds, v qs :
-
D–q axis stator voltage
- v dr, v qr :
-
D–q axis rotor voltage
- v α ,v β :
-
α–β Axis voltage
- P :
-
Active power referred to the α–β axis
- Q :
-
Reactive power referred to the α–β axis
- i ds, i qs :
-
D–q axis stator current
- i dr, i qr :
-
D–q axis rotor current
- ψ ds, ψ qs , ψ qr , ψ dr :
-
D–q axis flux
- I r :
-
Rotor current
- R s :
-
Stator resistance
- R r :
-
Rotor resistance
- X s :
-
Stator reactance
- X s :
-
Stator reactance
- X r :
-
Rotor reactance
- L s :
-
Stator inductance
- L r :
-
Rotor inductance
- X m :
-
Magnetizing reactance
- t 1, t 2, t 0 :
-
Switching instances of SPWM
- ω r :
-
Rotor angular speed
- L m :
-
Magnetizing inductance
- R s1 :
-
Stator resistance of MR
- R r1 :
-
Rotor resistance of MR
- L s1 :
-
Stator inductance of MR
- L s2 :
-
Rotor inductance of MR
- L m1 :
-
Mutual inductance of MR
- Z eqR :
-
Per phase impedance of MR
- Z eqP :
-
Per phase impedance of MP
- Z eq :
-
Per phase impedance
- v svm :
-
Voltage vector of SVM
- T pwm :
-
The time period of PWM
- M :
-
Modulation index
- G 1 :
-
Controller gain of the flux flow path
- G 2 :
-
Controller gain of the torque flow path
- G 3 :
-
Controller gain of the slip frequency
- ω s :
-
Synchronous speed
- ω r :
-
Rotor speed
- ω sl :
-
Slip speed
- τ R :
-
Rotor time constant
- M R , M P :
-
Reference and plant model
- h :
-
Hidden layer
- S :
-
Activation function
- η :
-
Learning rate
- g n :
-
Gradient
- r n :
-
Summation of the squared term of gradients
- w d :
-
Window size
- w (n + 1) :
-
Modified weight after nth iterations
- w n :
-
Current weight of nth iterations
- y :
-
The output of the forward path
- Y MR , Y MP :
-
Output ECP for reference and plant model
- b, e :
-
Loss function and error
References
Awadallah, M. A. (2008). Parameter estimation of induction machines from nameplate data using particle swarm optimisation and genetic algorithm techniques. Electric Power Components and Systems, 36(8), 801–814. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325000801911393
BENBOUZID (2003). The HG diagram model for induction motors analysis: Theoretical approach and applications. Electric Power Components and Systems, 31(3),211–239, https://doi.org/10.1080/15325000390112161
Bhowmick, D., Manna, M., & Chowdhury, S. K. (2018). Estimation of equivalent circuit parameters of transformer and induction motors from load data. IEEE Transaction on Industry Applications, 54(3), 2784–2791. https://doi.org/10.1109/tia.2018.2790378
Bose, B. K. (2002). Modern power electronics and AC drives. Prentice- Hall: Englewood Cliffs NJ, USA; ISBN 0–13–016743–6.
Cao, P., Zhang, X., & Yang, S. (2017). A unified-model-based analysis of MRAS for online rotor time constant estimation in an induction motor drive. IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, 64(6), 4361–4371. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2017.2668995
Çetin, O., Dalcalı, A., & Temurtaş, F. (2020). A comparative study on parameters estimation of squirrel cage induction motors using neural networks with unmemorized training. Emerging Science and Technology, an International Journal,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2020.03.011
Chacko, S., Bhende, C. N., Jain, S., & Nema, R. K. (2016). Rotor resistance estimation of vector controlled induction motor drive using GA/ PSO tuned fuzzy controller. International Journal on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 8(1), 218.
Chaturvedi, D. K., & Singh, M. P. (2019). Online equivalent circuit parameter estimation of three-phase induction motor using ANN. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (india) Series B, 100(4), 343–347.
Dubey, A. K., & Jain, V. (2019). Comparative study of convolution neural network’s relu and leaky-relu activation functions. In Applications of Computing, Automation and Wireless Systems in Electrical Engineering (pp. 873–880). Springer, Singapore. http://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6772-4_76.
Fortes, M. Z., Ferreira, V. H., & Coelho, A. P. F. (2013). The induction motor parameter estimation using genetic algorithm. IEEE Latin America Transactions. https://doi.org/10.1109/tla.2013.6684404
Haque, M. H. (2008). Determination of NEMA design induction motor parameters from manufacturer data. IEEE Transaction on Energy Conversion, 23(4), 997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1109/tec.2008.2001451
He, Y., Wang, Y., & Feng, Y. (2010). Parameter identification of an induction machine at standstill using vector construction method. IEEE Transaction on Power Electronics, 27(2), 905–915. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpel.2010.2089699
IEEE Std 112, (1991). Test procedure for polyphase induction motors and generators institute of electrical and electronics engineers: New York, NY, USA, https://doi.org/10.1109/ieeestd.1984.82451.
Jirdehi, M. A., & Rezaei, A. (2016). Parameter estimation of squirrel-cage induction motors using ANN and ANFIS. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 55(1), 357–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2016.01.026
Kan, J., Zhang, K., & Wang, Z. (2015). Indirect vector control with simplified rotor resistance adaption for induction machines. IET Power Electronics, 8(7), 1284–1294.
Karanayil, B., Rahman, M. F., & Grantham, C. (2007). Online stator and rotor resistance estimation using artificial neural networks for vector controlled speed snsorless induction motor drive. IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, 54(1), 167–176. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2006.888778
Laowanitwattana, J. & Uatrongjit, S., (2015, October). Induction motor states and parameter estimation using Extended Kalman filter with reduced number of measurements. 18th International conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS) (pp. 1631–1635). Thailand: IEEE. http://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/icems.2015.7385302.
Lee, K., Frank, S., Sen, P.K., Polese, L.G., Alahmad, M. & Waters, C., (2012, September). Estimation of induction motor equivalent circuit parameters from nameplate data. In 2012 North American Power Symposium (NAPS) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Lin, W. M., Su, T. J., & Wu, R. C. (2012). Parameter identification of induction machine with a starting n- load low-voltage test. IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, 59(1), 352–360. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2011.2148674
Maiti, S., Chakraborty, C., Hori, Y., & Ta, M. C. (2008). Model reference adaptive controller-based rotor resistance and speed estimation techniques for vector controlled induction motor drive using reactive power. IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, 55(2), 594–601. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2007.911952
Nordin, K. B., Novotny, D. W., & Zinger, D. S. (1985). The influence of motor parameter deviations in feedforward field orientation drive systems. IEEE Transaction on Industry Applications, 4, 1009–1015. https://doi.org/10.1109/tia.1985.349571
Odhano, S., Pescetto, P., Ali, A. H., Hinkkanen, M., Pellegrino, G., & Bojoi, R. (2019). Parameter identification and self commissioning in AC motor drives: A technology status review. IEEE Transaction on Power Electronics. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpel.2018.2856589
Reed, D. M., Hofmann, H. F., & Sun, J. (2016). Offline identification of induction machine parameters with core loss estimation using stator current locus. IEEE Transaction on Energy Conversion, 31(4), 1549–1558. https://doi.org/10.1109/tec.2016.2601781
Ruan, J., & Wang, S. (2015). A prediction error method-based self commissioning scheme for parameter identification if induction motors in sensorless drives. IEEE Transaction on Energy Conversion, 30(1), 384–393. https://doi.org/10.1109/tec.2014.2346198
Sdid, M. S. N., & Benbouzid, M. E. H. (2000). HG diagram based rotor parameter identification for induction motors thermal monitoring. IEEE Transaction on Energy Conversions, 15(1), 14–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/60.849110
Wlas, M., Krzeminski, Z., & Toliyat, H. A. (2008). Neural-network -based parameter estimations of induction motors. IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, 55(4), 1783–1794. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2008.918615
Wu, R. C., Tseng, Y. W., & Chen, C. Y. (2018). Estimating parameters of the induction machine by the polynomial regression. Applied Science, 8(7), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071073
Yang, S., Ding, D., Li, X., Xie, Z., Zhang, X., & Chang, L. (2017). A novel online parameter estimation method for indirect field oriented control induction motor drives. IEEE Transaction on Energy Conversion, 32(4), 1562–1573. https://doi.org/10.1109/tec.2017.2699681
Zeiler, M. D. (2012). Adadelta: an adaptive learning rate method. arXiv preprint asXiv:1212.5701.
Zhang, H., Gong, S.J. & Dong, Z.Z., (2013, October). On-line parameter identification of induction motor based on RLS algorithm. International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS) (pp. 2132–2137).Busan Korea (South). IEEE. http://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/icems.2013.6713208.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Mr. Rakesh Das research scholar of the Applied Physics department of CU for helping us to develop the MMU.
Funding
This section is not applicable in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work has been prepared entirely by TB under the supervision of JNB.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, T., Bera, J.N. An Improved Torque Ripple Reduction Controller for Smooth Operation of Induction Motor Drive. J Control Autom Electr Syst 34, 247–264 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-022-00945-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-022-00945-8