Abstract
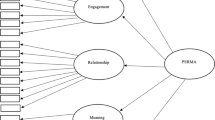
Improving people's well-being is a key way to meet people’s needs for a better life, and is of great importance in resolving the major contradictions in Chinese society. In this study, we evaluated peer relationships and self-actualization as potential mediators between physical exercise and subjective well-being in a sample of Chinese middle school students. A total of 1056 middle school students from six middle schools in Sichuan, China volunteered to complete questionnaires comprising the Physical Activity Rating Scale, Student Peer Relationship Scale, Short Index of Self-Actualization, Positive and Negative Affect Scale, and Satisfaction with Life Scale. Descriptive statistics, Pearson’s product-moment correlation, and structural equation modeling were conducted using SPSS statistics 19.0. and AMOS 21.0 statistical software. The results showed that peer relationships and self-actualization partially mediate between physical exercise and subjective well-being. The mediation analysis revealed two paths: first, the single mediating path via peer relationships [indirect effect = 0.091, 95% CI: (0.053, 0.132)] and second, the serial mediating path via peer relationships and self-actualization [indirect effect = 0.015, 95% CI: (0.008, 0.024)]. The study confirmed for the first time the serial mediating role of peer relationships and self-actualization between physical exercise and subjective well-being of middle school students. It was suggested that middle school students could improve their peer relationships during physical exercise, thereby increasing the level of self-actualization, which results in better subjective well-being.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are not openly available and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
An, H. Y., Chen, W., Wang, C. W., Yang, H. F., Huang, W. T., & Fan, S. Y. (2020). The relationships between physical activity and life satisfaction and happiness among young, middle-aged, and older adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(13), 4817. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134817
Asher, S. R., Hymel, S., & Renshaw, P. D. (1984). Loneliness in children. Child Development, 55(4), 1456–1464. https://doi.org/10.2307/1130015
Battalio, S. L., Huffman, S. E., & Jensen, M. P. (2020). Longitudinal associations between physical activity, anxiety, and depression in adults with long-term physical disabilities. Health Psychology, 39(6), 529.
Buecker, S., Simacek, T., Ingwersen, B., Terwiel, S., & Simonsmeier, B. A. (2021). Physical activity and subjective well-being in healthy individuals: A meta-analytic review. Health Psychology Review, 15(4), 574–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2020.1760728
Chen, Z. Y., & Yu, P. (2015). The influence of physical exercise on subjective well-being of college students: An intermediary effect of peer relationship. Journal of Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, 27(2), 165–171.
Courtwright, S. E., Le, P. A., & Jones, J. (2022). Emotional wellbeing in adolescents living with chronic conditions: A metasynthesis of the qualitative literature. Journal of Adolescent Health, 70(6), 864–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.12.020
Diener, E. (1984). Subjective well-being. Psychology. Bulletin, 95(3), 542–575. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.95.3.542
Diener, E. (2000). Subjective well-being: The science of happiness and a proposal for a national index. American Psychologist, 55(1), 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.55.1.34
Diener, E., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. Journal of Personality Assessment, 49(1), 71–75. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa4901_13
Ding, S. Y., Xiao, R., & Zhang, Z. (2016). The relationship between college students’ sports and life-meaning. Chinese Journal of School Health, 37, 445–448.
Ellingsen, M. M., Johannesen, S. L., Martinsen, E. W., Dahl, S. R., & Hallgren, M. (2020). Effects of acute exercise on drug craving, self-esteem, mood, and affect in adults with polysubstance use disorder: protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Jmir Research Protocols. https://doi.org/10.2196/18553
Endedijk, H. M., Breeman, L. D., Van, L. C. J., Hendrickx, M. M., Den, B. L., & Mainhard, T. (2022). The teacher’s invisible hand: A meta-analysis of the relevance of teacher-student relationship quality for peer relationships and the contribution of student behavior. Review of Educational Research, 92(3), 370–412. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543211051428
Field, A. (2009). Discovering statistics using SPSS. Sage Publications.
Gopinath, R. (2020). Prominence of self-actualization in organization. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 29(3), 11591–11602.
Havewala, M., Lorenzo, N. E., Seddio, K., Oddo, L. E., Novick, D. R., Fox, N. A., & Chronis-Tuscano, A. (2022). Understanding co-occurring ADHD and anxiety symptoms within a developmental framework: Risk and protective factors of early temperament and peer relations. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 50(7), 853–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-021-00891-0
Huang, H., & Zhao, Y. X. (2022). The connotation, characteristics and essence of people’s needs for a better life. Journal of Zhengzhou University of Light Industry (social Science Edition), 23(3), 1–6.
Li, D. Y. (2011). The self-realization theory of Maslow and the meaning of management. (Master Thesis. Central China Normal University). Available at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD2011&filename=1011136791.nh. Accessed March 22, 2023.
Li, Q. (2016). Study on the development of the young teachers in higher vocational colleges based on the Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. (Master Thesis. Southwest Jiaotong University). Available at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD201701&filename=1016170502.nh. Accessed March 22, 2023.
Li, J. T., Sun, J. H., Wang, L., Wang, N., & Zhu, P. L. (2019). A study on the relationship between exercise adherence behavior and subjective well-being among college students: The parallel mediating role of self-actualization and time management tendencies. Eleventh National Conference on Sports Science, Nanjing.
Li, Y., & Chen, Y. Y. (2020). The transformation of major social contradictions under the socialism with Chinese characteristics: The analysis extension theory. Journal of Technical Economics & Management, 286(5), 105–109.
Liang, D. Q. (1994). The relationship between stress level and exercise in college student. Chinese Mental Health Journal, (1), 5–6.
Liu, R., & Wang J. T. (2022). People’s needs for a better life in the new era: Basic implication, main performance and realization path. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 55(3), 11–17+127.
Liu, S. Q. (2000). Interacting with peers: The “magic” of self-actualization for children. Exposition of Family Education, 4, 45.
Liu, Z. H. (2020). Effects of physical exercise on negative emotion for university students: The mediating and moderating effects of self-efficacy and mental resilience. Journal of Physical Education, 27(5), 102–108.
Ma, B. B., Dai, W. J., & Li, C. N. (2019). Migrant adolescents’ interpersonal relationship and subjective well-being: The mediating effect of academic burnout and academic engagement. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 234(12), 63–71. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-3728.2019.12.010
Ma, C., Shi, Z. G., Wang, X. L., & Tian, Y. G. (2022). Influence of physical activity on college students’ subjective well-being: The mediating effect of peer relationship and self-cognition. China Journal of Health Psychology, 30(6), 893–899.
Mcmahon, G., Creaven, A. M., & Gallagher, S. (2020). Stressful life events and adolescent well-being: The role of parent and peer relationships. Stress and Health, 36(3), 299–310.
Melo, M., Martinssilva, P., Andrade, A., Moura, R., & Bispo, M. (2021). Barriers, adaptability, employability, and satisfaction: Career perceptions of business students. Revista de Administração Contemporânea, 25(6), e190124. https://doi.org/10.1590/1982-7849rac2021190124.en
Moake, T. R., & Patel, A. S. (2021). A cross-stressor adaptation perspective on challenge stressors, dietary behavior, and exercise of college students. The Social Science Journal, 2, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/03623319.2020.1867948
Mokhtarian, P. L. (2019). Subjective well-being and travel: Retrospect and prospect. Transportation, 46, 493–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-018-9935-y
Moreira, A. L., Yunes, M. Â. M., Nascimento, C. R. R., & Bedin, L. M. (2021). Children’s subjective well-being, peer relationships and resilience: An integrative literature review. Child Indicators Research, 14(5), 1723–1742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-021-09843-y
Mumcu, H. E., Yazici, Ö. F., & Yilmaz, O. (2021). Effect of 12-week recreational activity program on digital game addiction and peer relationships qualities in children. Acta Medica Mediterranea, 37, 2919.
Noltemeyer, A., James, A. G., Bush, K., Bergen, D., Barrios, V., & Patton, J. (2021). The relationship between deficiency needs and growth needs: The continuing investigation of Maslow’s theory. Child & Youth Services, 42(1), 24–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/0145935X.2020.1818558
Oberle, E., Guhn, M., Gadermann, A. M., Thomson, K., & Schonert-Reichl, K. A. (2018). Positive mental health and supportive school environments: A population-level longitudinal study of dispositional optimism and school relationships in early adolescence. Social Science & Medicine, 214, 154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2018.06.041
Okafor, A., & Abraham, N. M. (2021). Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory: Relationship between the higher needs and teachers’ service delivery in public secondary schools in Rivers State, Nigeria. International Journal of Innovative Education Research, 9(2), 172–179.
Omodan, B. I., & Abejide, S. O. (2022). Reconstructing Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs towards inclusive infrastructure development needs assessment. Journal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development, 6(2), 1483.
Özkan, A., Yaşartürk, F., & Elçi, G. (2021). The relationship between leisure satisfaction, physical activity level and healthy life-style behaviors of sport science students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Physical Education of Students, 25(5), 257–264.
Qiao, Y. C., & Fan, Y. Z. (2020). Interrogation and response: Eight basic problems in the study of the relationship between physical activity and happiness. Journal of Shanghai University of Sport, 44(7), 1–15.
Rubio, R. M., Granero-Gallegos, A., & Gomez-Lopez, M. (2020). The satisfaction of basic psychological needs in Physical Education classes and their relationship with satisfaction with life in adolescents. Revista Complutense De Educacion, 31(1), 45–54.
Seligman, M. E. P. (2011). Flourish: A visionary new understanding of happiness and well-being. New York, NY: Free Press.
Wang, L., Zhang, C. S., Zhong, B. S., & Su, M. (2019). Main social contradictions and sports development in China in the new era. Journal of Beijing Sport University, 42(2), 8–15+54. https://doi.org/10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2019.02.002
Wang, C., & Fan, X. (2020). Research progress and prospect of sports behavior affecting social anxiety. China Journal of Health Psychology, 28(11), 1750–1754.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063
Wen, Z. L., & Ye, B. J. (2014). Analyses of mediating effects: The development of methods and models. Advances in Psychological Science, 22(5), 731–745. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Wu, M., Hu, S. Y., Zhou, X. R., & Bian, Y. F. (2021). Interaction between family support, parent-child conflict and subjective well-being of junior high school students: A cross-lag analysis. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 29(4), 808–813.
Xu, L. L., & Dong, B. L. (2020). Relationship between peer relationship, subjective exercise experience, and adolescents’ leisure physical exercise habits: A cross-lagged analysis. Journal of Tianjin University of Sport, 35(6), 697–702.
Yang, R. H., & Chen, Z. Y. (2010). The relationship between actual-ideal discrepancy and self-efficacy, self-actualization, self-identity and mental symptoms. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 18(4), 507–508+468+4. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2010.04.004
Yin, C. J., & Fu, X. L. (2004). Analysis and perspective on mental health effects of physical exercise. China Sport Science, 24(6), 37–39+44. https://doi.org/10.16469/j.css.2004.06.011
Yu, G. L. (2022). A new interpretation of mental health: The well-being perspective. Journal of Beijing Normal University (social Sciences), 289(1), 72–81. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-0209.2022.01.011
Zhang, Y. L. (2008). The test of correlation between self-concept and school adjustment (Master Thesis. Northwest University). Available at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD2008&filename=2008076540.nh. Accessed March 22, 2023.
Zhang, Y., & Li, L. (2021). Influence of sports participation on subjective well-being: Based on sociological empirical research. Journal of Shenyang Sport University, 40(2), 92–102+117. https://doi.org/10.12163/j.ssu.20201805
Zhang, J. H., Chu, Y. X., & Lin, C. D. (2008). Construct of test on creative teaching behavior in teachers. Psychological Development and Education, 94(3), 107–112.
Zhang, L., & Zuo, B. (2007). Eudaimonic well-being: A review on psychological well-being. Advances in Psychological Science, 95(1), 134–139. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-3710.2007.01.021
Zhang, X. (2003). Analysis of the characteristics and functions of adolescent peer relationships. Contemporary Education Sciences, 1, 37–39.
Zhong, Z. (2022). An empirical analysis of the influence of physical exercise on adolescents’ mental health and its intermediary mechanism. Journal of Jilin Sport University, 38(1), 77–84. https://doi.org/10.13720/j.cnki.22-1286.2022.01.014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS: conceptualization and resources. YS and S-P C: methodology and software. YS and H-DX: analysis, data curation, and writing — original draft preparation. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee at the Xi’an Jiaotong University following the Declaration of Helsinki. The participants provided written informed consent to participate in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Y., Chen, SP. & Xie, HD. The Effect of Physical Exercise on Subjective Well-Being in Chinese Middle School Students: The Mediation Roles of Peer Relationships and Self-Actualization. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 33, 615–623 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-023-00757-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-023-00757-7