Abstract
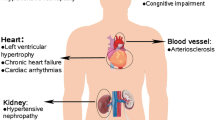
Olmesartan medoxomil is an antihypertensive drug of the class of angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonists (or blockers), characterized by tight and prolonged binding to AT1 receptor compared to other molecules within the same class. These characteristics produce effective and sustained blood pressure reductions in hypertensive patients at different cardiovascular risk profile with a good tolerability profile. After a brief description of the pharmacological characteristics of olmesartan, we will provide a thorough overview of the clinical studies that investigated its efficacy and safety in the clinical management of hypertensive patients both in monotherapy and in dual combination therapies with either thiazide diuretics or calcium channel blockers. These studies demonstrated that olmesartan-based antihypertensive strategy may indeed provide sustained BP control over the 24-h period in a wide proportion of hypertensive patients, thus contributing to a substantial progress in hypertension management. Finally, since growing evidence suggest that olmesartan may also exert potential favourable effects at vascular level, thereby antagonizing the vascular inflammatory process involved in the development and progression of atherosclerosis, the main clinical studies addressing this issue will be also discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redon J, Mourad JJ, Schmieder RE, Volpe M, Weiss TW. Why in 2016 are patients with hypertension not 100% controlled? A call to action. J Hypertens. 2016;34(8):1480–8.
Ettehad D, Emdin CA, Kiran A, Anderson SG, Callender T, Emberson J, et al. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016;387(10022):957–67.
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013;31(7):1281–357.
James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014;311(5):507–20.
Leung AA, Nerenberg K, Daskalopoulou SS, McBrien K, Zarnke KB, Dasgupta K, et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2016 Canadian Hypertension Education Program guidelines for blood pressure measurement, diagnosis, assessment of risk, prevention, and treatment of hypertension. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(5):569–88.
Volpe M, Rosei EA, Ambrosioni E, Cottone S, Cuspidi C, Borghi C, et al. 2012 consensus document of the Italian Society of Hypertension (SIIA): strategies to improve blood pressure control in Italy: from global cardiovascular risk stratification to combination therapy. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2013;20(1):45–52.
Redon J, Fabia MJ. Efficacy in angiotensin receptor blockade: a comparative review of data with olmesartan. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2009;10(3):147–56.
Mire DE, Silfani TN, Pugsley MK. A review of the structural and functional features of olmesartan medoxomil, an angiotensin receptor blocker. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005;46(5):585–93.
Oparil S, Williams D, Chrysant SG, Marbury TC, Neutel J. Comparative efficacy of olmesartan, losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan in the control of essential hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2001;3(5):283–91 (318).
Stumpe KO, Ludwig M. Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan compared with other antihypertensive drugs. J Hum Hypertens. 2002;16(Suppl 2):S24–8.
Brunner HR, Stumpe KO, Januszewicz A. Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan medoxomil and candesartan cilexetil assessed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Drug Investig. 2003;23(7):419–30.
Giles TD, Oparil S, Silfani TN, Wang A, Walker JF. Comparison of increasing doses of olmesartan medoxomil, losartan potassium, and valsartan in patients with essential hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007;9(3):187–95.
Elliott WJ. Circadian variation in the timing of stroke onset: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 1998;29(5):992–6.
Verdecchia P, Schillaci G, Guerrieri M, Gatteschi C, Benemio G, Boldrini F, et al. Circadian blood pressure changes and left ventricular hypertrophy in essential hypertension. Circulation. 1990;81(2):528–36.
Omboni S, Malacco E, Mallion JM, Volpe M, Zanchetti A, Study G. Twenty-four hour and early morning blood pressure control of olmesartan vs. ramipril in elderly hypertensive patients: pooled individual data analysis of two randomized, double-blind, parallel-group studies. J Hypertens. 2012;30(7):1468–77.
Smith DH, Dubiel R, Jones M. Use of 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring to assess antihypertensive efficacy: a comparison of olmesartan medoxomil, losartan potassium, valsartan, and irbesartan. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005;5(1):41–50.
Malacco E, Omboni S, Volpe M, Auteri A, Zanchetti A. Antihypertensive efficacy and safety of olmesartan medoxomil and ramipril in elderly patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension: the ESPORT study. J Hypertens. 2010;28(11):2342–50.
Mason RP. Optimal therapeutic strategy for treating patients with hypertension and atherosclerosis: focus on olmesartan medoxomil. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011;7:405–16.
Fliser D, Buchholz K, Haller H. Olmesartan EUTo, pravastatin in I, atherosclerosis I. Antiinflammatory effects of angiotensin II subtype 1 receptor blockade in hypertensive patients with microinflammation. Circulation. 2004;110(9):1103–7.
Smith RD, Yokoyama H, Averill DB, Schiffrin EL, Ferrario CM. Reversal of vascular hypertrophy in hypertensive patients through blockade of angiotensin II receptors. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2008;2(3):165–72.
Stumpe KO, Agabiti-Rosei E, Zielinski T, Schremmer D, Scholze J, Laeis P, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness and plaque volume changes following 2-year angiotensin II-receptor blockade. The Multicentre Olmesartan atherosclerosis Regression Evaluation (MORE) study. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2007;1(2):97–106.
Hirohata A, Yamamoto K, Miyoshi T, Hatanaka K, Hirohata S, Yamawaki H, et al. Impact of olmesartan on progression of coronary atherosclerosis a serial volumetric intravascular ultrasound analysis from the OLIVUS (impact of OLmesarten on progression of coronary atherosclerosis: evaluation by intravascular ultrasound) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(10):976–82.
Hirohata A, Yamamoto K, Miyoshi T, Hatanaka K, Hirohata S, Yamawaki H, et al. Four-year clinical outcomes of the OLIVUS-Ex (impact of olmesartan on progression of coronary atherosclerosis: evaluation by intravascular ultrasound) extension trial. Atherosclerosis. 2012;220(1):134–8.
Burbure N, Lebwohl B, Arguelles-Grande C, Green PH, Bhagat G, Lagana S. Olmesartan-associated sprue-like enteropathy: a systematic review with emphasis on histopathology. Hum Pathol. 2016;50:127–34.
Ianiro G, Bibbo S, Montalto M, Ricci R, Gasbarrini A, Cammarota G. Systematic review: sprue-like enteropathy associated with olmesartan. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40(1):16–23.
Redon J, Pichler G, Missed Dose Study G. Comparative study of the efficacy of olmesartan/amlodipine vs. perindopril/amlodipine in peripheral and central blood pressure parameters after missed dose in type 2 diabetes. Am J Hypertens. 2016;29(9):1055–62.
Ruilope LM. Clinical efficacy and safety of olmesartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in patients with essential hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4(6):1237–48.
Rump LC, Sellin L. Combination therapy for hypertension: focus on high-dose olmesartan medoxomil (40 mg) plus hydrochlorothiazide. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010;11(13):2231–42.
Rump LC, Girerd X, Sellin L, Stegbauer J. Effects of high dose olmesartan medoxomil plus hydrochlorothiazide on blood pressure control in patients with grade 2 and grade 3 hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2011;25(9):565–74.
Sellin L, Stegbauer J, Laeis P, Rump LC. Adding hydrochlorothiazide to olmesartan dose dependently improves 24-h blood pressure and response rates in mild-to-moderate hypertension. J Hypertens. 2005;23(11):2083–92.
Chrysant SG, Weber MA, Wang AC, Hinman DJ. Evaluation of antihypertensive therapy with the combination of olmesartan medoxomil and hydrochlorothiazide. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17(3):252–9.
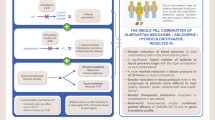
Kereiakes DJ, Maa JF, Shojaee A, Dubiel R. Effect of an olmesartan medoxomil-based treatment algorithm on systolic blood pressure in patients with stage 1 or 2 hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10(4):239–46.
Izzo JL Jr, Neutel JM, Silfani T, Dubiel R, Walker F. Efficacy and safety of treating stage 2 systolic hypertension with olmesartan and olmesartan/HCTZ: results of an open-label titration study. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007;9(1):36–44.
Kereiakes DJ, Neutel J, Stoakes KA, Waverczak WF, Xu J, Shojaee A, et al. The effects of an olmesartan medoxomil-based treatment algorithm on 24-hour blood pressure levels in elderly patients aged 65 and older. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2009;11(8):411–21.
Neutel JM, Kereiakes DJ, Waverczak WF, Stoakes KA, Xu J, Shojaee A. Effects of an olmesartan medoxomil based treatment algorithm on 24-hour blood pressure control in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26(3):721–8.
Punzi H, Neutel JM, Kereiakes DJ, Shojaee A, Waverczak WF, Dubiel R, et al. Efficacy of amlodipine and olmesartan medoxomil in patients with hypertension: the AZOR Trial Evaluating Blood Pressure Reductions and Control (AZTEC) study. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;4(4):209–21.
Parati G, Ochoa JE, Ramos C, Hoshide S, Lonati L, Bilo G. Efficacy and tolerability of olmesartan/amlodipine combination therapy in patients with mild-to-severe hypertension: focus on 24-h blood pressure control. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;4(5):301–13.
Punzi H, Shojaee A, Waverczak WF, Maa JF. Efficacy of amlodipine and olmesartan medoxomil in hypertensive patients with diabetes and obesity. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011;13(6):422–30.
Chrysant SG, Melino M, Karki S, Lee J, Heyrman R. The combination of olmesartan medoxomil and amlodipine besylate in controlling high blood pressure: COACH, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 8-week factorial efficacy and safety study. Clin Ther. 2008;30(4):587–604.
Volpe M, Brommer P, Haag U, Miele C. Efficacy and tolerability of olmesartan medoxomil combined with amlodipine in patients with moderate to severe hypertension after amlodipine monotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre study. Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(1):11–25.
Barrios V, Boccanelli A, Ewald S, Girerd X, Heagerty A, Krzesinski JM, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of olmesartan medoxomil in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension: the OLMEBEST Study. Clin Drug Investig. 2007;27(8):545–58.
Sharman JE, Laurent S. Central blood pressure in the management of hypertension: soon reaching the goal? J Hum Hypertens. 2013;27(7):405–11.
Ruilope LM, Schaefer A. Efficacy of Sevikar(R) compared to the combination of perindopril plus amlodipine on central arterial blood pressure in patients with moderate-to-severe hypertension: Rationale and design of the SEVITENSION study. Contemp Clin Trials. 2011;32(5):710–6.
Liau CS, Lee CM, Sheu SH, Ueng KC, Chien KL, Su TC, et al. Efficacy and safety of olmesartan in the treatment of mild-to-moderate essential hypertension in Chinese patients. Clin Drug Investig. 2005;25(7):473–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Expert review of the manuscript has been founded by Menarini International Operations Luxembourg S.A. (MIOL).
Conflict of interest
MV has served in international advisory boards of Daiichi Sankyo, Menarini International, Amgen and Novartis, and has lectured in symposia supported by Guidotti and Malesci; GT has lectured in symposia supported by Menarini, Malesci, Guidotti; CS, VM, RC and AB have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain data derived by any current studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. The clinical studies mentioned were provided with specific ethical approval.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volpe, M., Santolamazza, C., Mastromarino, V. et al. Monotherapy and Dual Combination Therapies Based on Olmesartan: A Comprehensive Strategy to Improve Blood Pressure Control. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 24, 243–253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-017-0216-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-017-0216-1